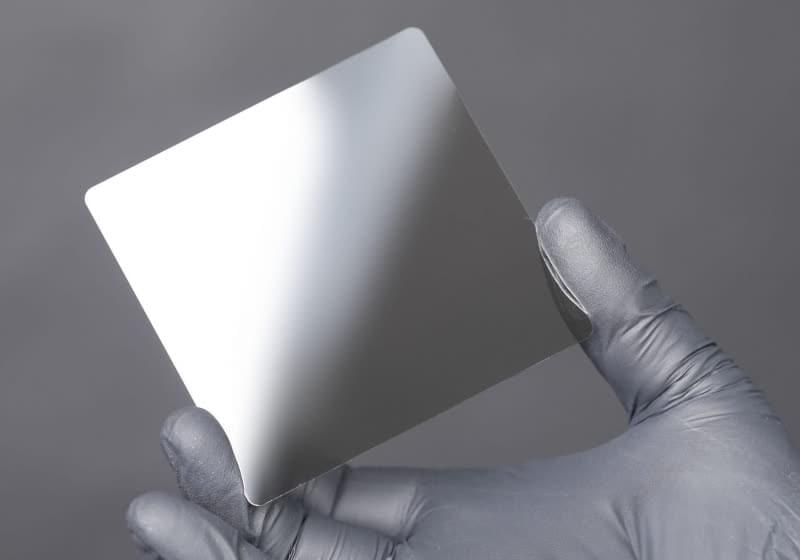
As more data is archived digitally, the inherent fragility of bits remains a pressing issue. The answer may lie in ceramics. Western Digital has invested in Cerabyte, a company developing a groundbreaking storage technology designed to preserve data reliably for millennia.
Cerabyte’s technology stores digital data on ceramic nanolayers, using lasers to etch QR code-like matrices representing bits. Ceramics, known for their resistance to corrosion and extreme heat, have endured for millennia. The German startup claims its storage method could preserve digital data for over 5,000 years.
Cerabyte recently demonstrated its technology’s durability by heating a prototype storage medium to 250°C in an oven. Both the medium and the archived data emerged unscathed. The company stated its ceramic-based solution could meet the rising demand for long-term data storage platforms.