The quantum computer, called Starling, will use 200 logical qubits — and IBM plans to follow this up with a 2,000-logical-qubit machine in 2033


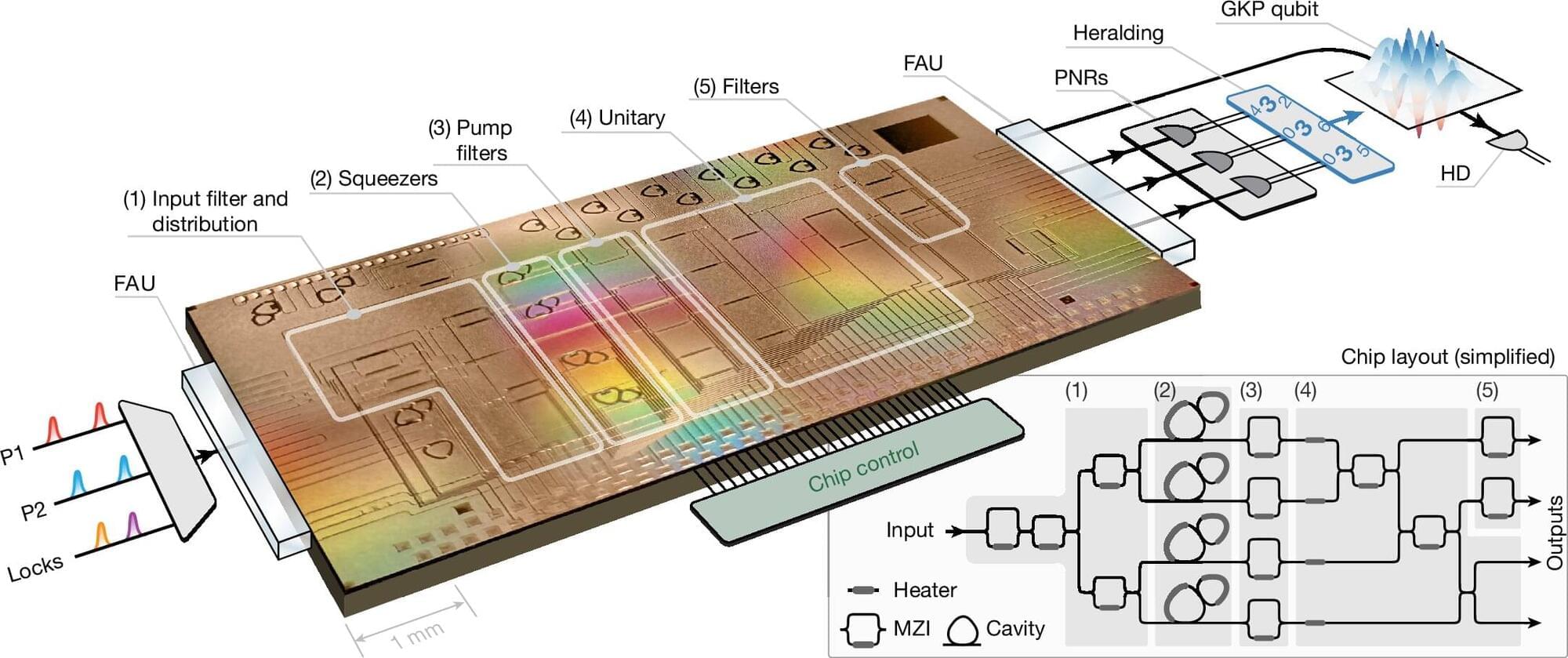
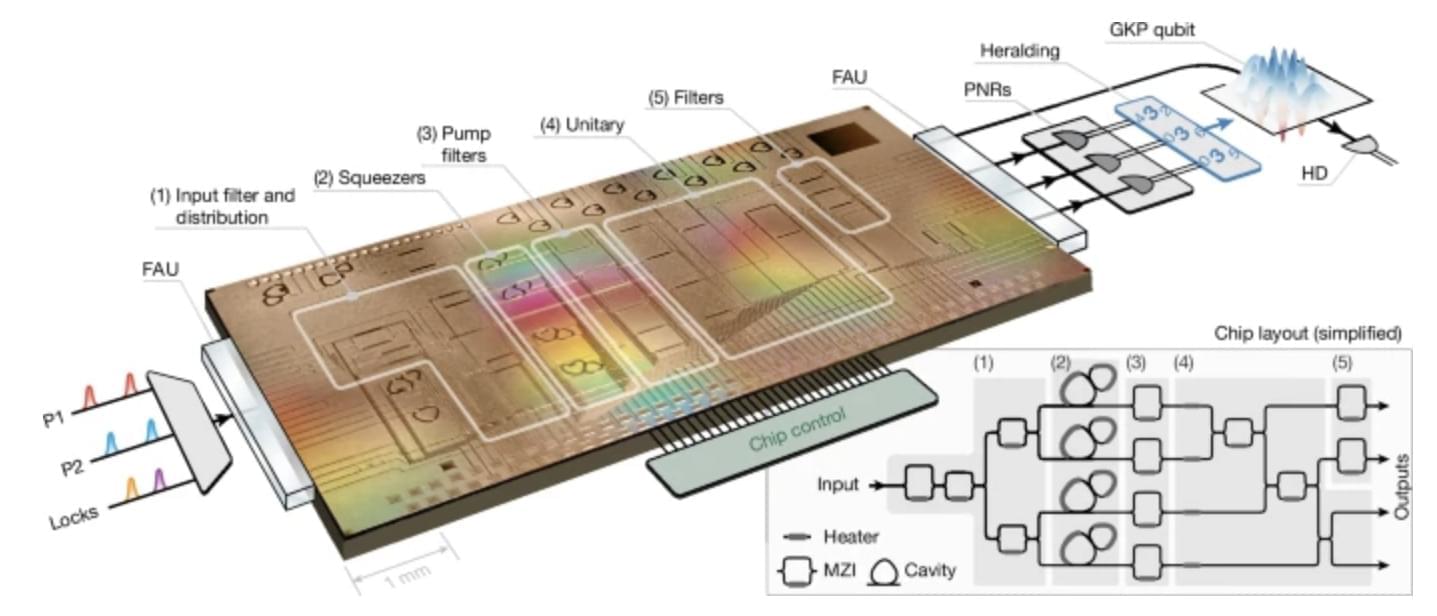
Xanadu has achieved a significant milestone in the development of scalable quantum hardware by generating error-resistant photonic qubits on an integrated chip platform. A foundational result in Xanadu’s roadmap, this first-ever demonstration of such qubits on a chip is published in Nature.
This advance builds on Xanadu’s recent announcement of the Aurora system, which demonstrated—for the first time—all key components required to build a modular, networked, and scalable photonic quantum computer. With this latest demonstration of robust qubit generation using silicon-based photonic chips, Xanadu further strengthens the scalability pillar of its architecture.
The quantum states produced in this experiment, known as Gottesman–Kitaev–Preskill (GKP) states, consist of superpositions of many photons to encode information in an error-resistant manner—an essential requirement for future fault-tolerant quantum computers. These states allow logic operations to be performed using deterministic, room-temperature-compatible techniques, and they are uniquely well-suited for networking across chips using standard fiber connections.
IBM has just unveiled its boldest quantum computing roadmap yet: Starling, the first large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computer—coming in 2029. Capable of running 20,000X more operations than today’s quantum machines, Starling could unlock breakthroughs in chemistry, materials science, and optimization.
According to IBM, this is not just a pie-in-the-sky roadmap: they actually have the ability to make Starling happen.
In this exclusive conversation, I speak with Jerry Chow, IBM Fellow and Director of Quantum Systems, about the engineering breakthroughs that are making this possible… especially a radically more efficient error correction code and new multi-layered qubit architectures.
We cover:
- The shift from millions of physical qubits to manageable logical qubits.
- Why IBM is using quantum low-density parity check (qLDPC) codes.
- How modular quantum systems (like Kookaburra and Cockatoo) will scale the technology.
- Real-world quantum-classical hybrid applications already happening today.
- Why now is the time for developers to start building quantum-native algorithms.
00:00 Introduction to the Future of Computing.
01:04 IBM’s Jerry Chow.
01:49 Quantum Supremacy.
02:47 IBM’s Quantum Roadmap.
04:03 Technological Innovations in Quantum Computing.
05:59 Challenges and Solutions in Quantum Computing.
09:40 Quantum Processor Development.
14:04 Quantum Computing Applications and Future Prospects.
20:41 Personal Journey in Quantum Computing.
24:03 Conclusion and Final Thoughts.
You may not have heard of tantalum, but chances are you’re holding some right now. It’s an essential component in our cell phones and laptops, and currently, there’s no effective substitute. Even if you plan to recycle your devices after they die, the tantalum inside is likely to end up in a landfill or shipped overseas, being lost forever.
As a researcher focused on critical materials recovery, I’ve spent years digging through electronic waste, not seeing it as garbage, but as an urban mine filled with valuable materials like tantalum.
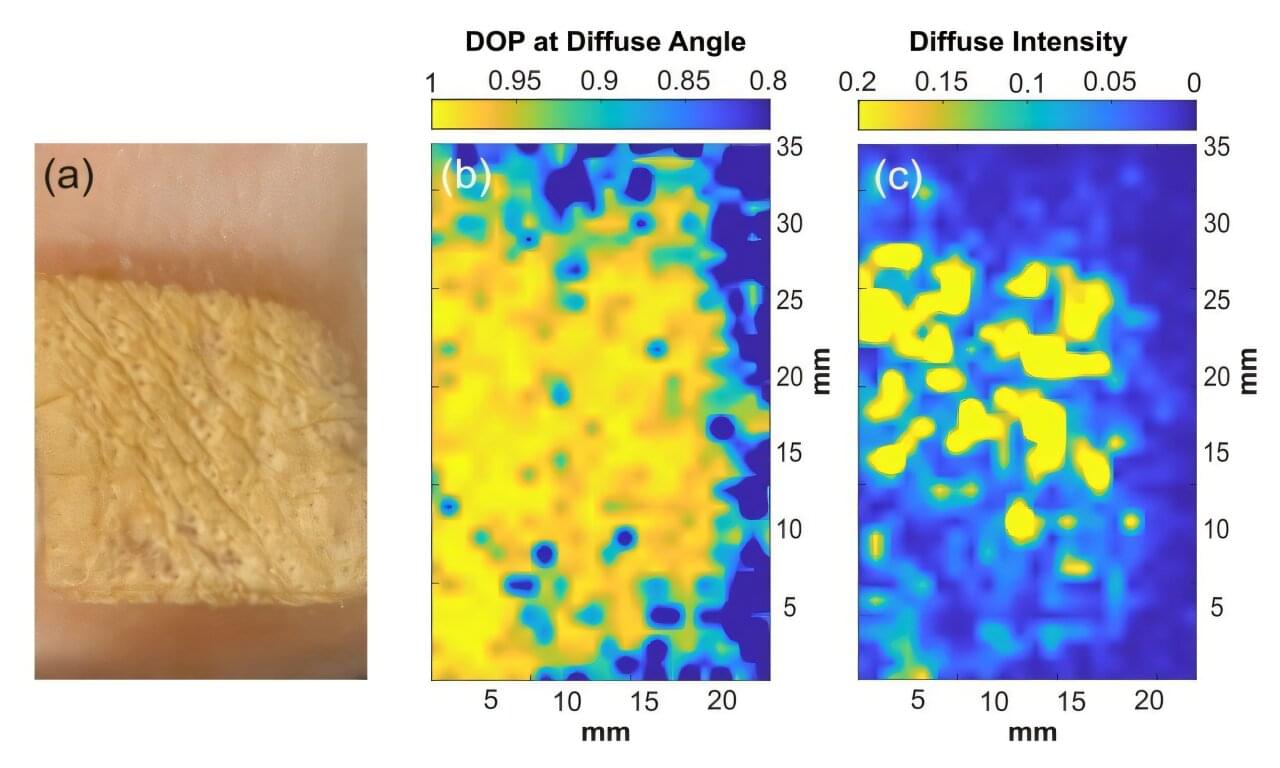
Recent advances in electronics and optics have opened new possibilities for terahertz (THz) waves—an invisible type of light that falls between infrared light and microwaves on the spectrum. The use of THz scattering for medical diagnosis is a promising frontier in this field, as THz waves can probe tissue structures in ways that traditional imaging methods cannot. Emerging THz measurement methods have the potential to detect subtle changes in tissue architecture that occur in diseases like cancer and burn injuries, serving as a powerful diagnostic tool.
However, existing THz imaging techniques face significant limitations for medical applications. Most existing approaches rely primarily on water content differences between healthy and diseased tissue as their main source of diagnostic contrast—an approach that proves overly simplistic for complex disease conditions.
Moreover, while polarization measurements of reflected THz waves seem to be valuable for tissue diagnosis, the underlying mechanisms that create different polarization responses in tissues remain poorly understood. This gap in understanding underscores a need for computational models capable of explaining and predicting the phenomena that researchers have observed experimentally.

In a monumental breakthrough, scientists have measured the speed of quantum entanglement for the first time—an achievement that is set to radically transform the way we understand the quantum world. For years, quantum entanglement was thought to be an instantaneous process, but this new research, published in Physical Review Letters, has pushed the boundaries of our knowledge, providing new insights into the quantum realm and setting the stage for revolutionary advances in data security and computational technologies.
Physicists at the University of Oxford have set a new global benchmark for the accuracy of controlling a single quantum bit, achieving the lowest-ever error rate for a quantum logic operation—just 0.000015%, or one error in 6.7 million operations. This record-breaking result represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement over the previous benchmark, set by the same research group a decade ago.
To put the result in perspective: a person is more likely to be struck by lightning in a given year (1 in 1.2 million) than for one of Oxford’s quantum logic gates to make a mistake.
The findings, to be published in Physical Review Letters, are a major advance towards having robust and useful quantum computers.
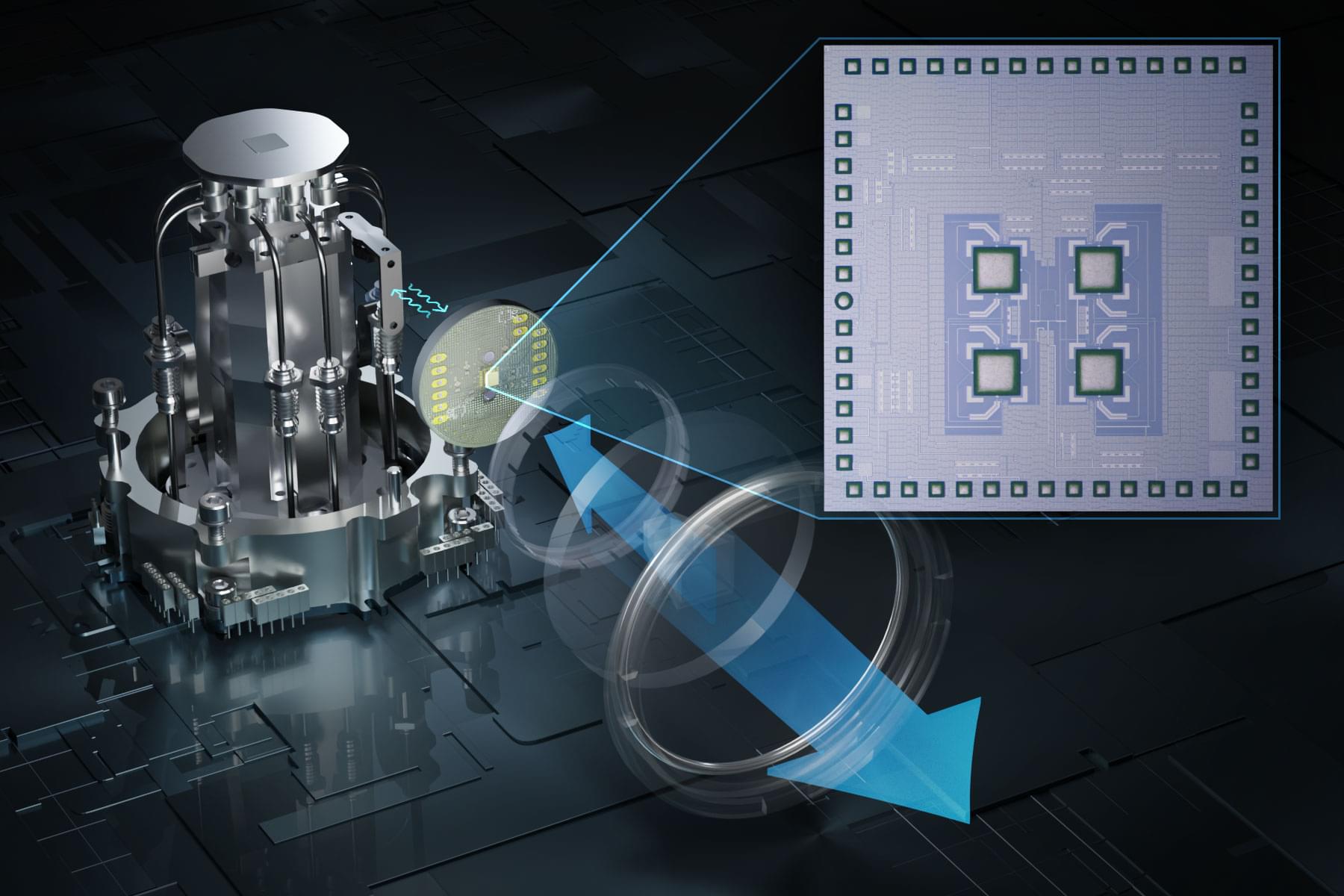
Heat causes errors in the qubits that are the building blocks of a quantum computer, so quantum systems are typically kept inside refrigerators that keep the temperature just above absolute zero (−459 degrees Fahrenheit).
But quantum computers need to communicate with electronics outside the refrigerator, in a room-temperature environment. The metal cables that connect these electronics bring heat into the refrigerator, which has to work even harder and draw extra power to keep the system cold. Plus, more qubits require more cables, so the size of a quantum system is limited by how much heat the fridge can remove.
To overcome this challenge, an interdisciplinary team of MIT researchers has developed a wireless communication system that enables a quantum computer to send and receive data to and from electronics outside the refrigerator using high-speed terahertz waves.
(From 2023)
A new wireless terahertz communication system enables a super-cold quantum computer to send and receive data without generating too much error-causing heat.

The universe is full of spectacular and violent events, but few are more dramatic than a black hole tearing apart a star. Now, thanks to advanced computer simulations, scientists have gotten their closest look yet at what this cosmic catastrophe might actually look — and even sound — like.
A team of astronomers, led by theoretical astrophysicist Elias Most of the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), modeled the dramatic final milliseconds before a neutron star, the incredibly dense core left behind by a massive stellar explosion, is devoured by a black hole.