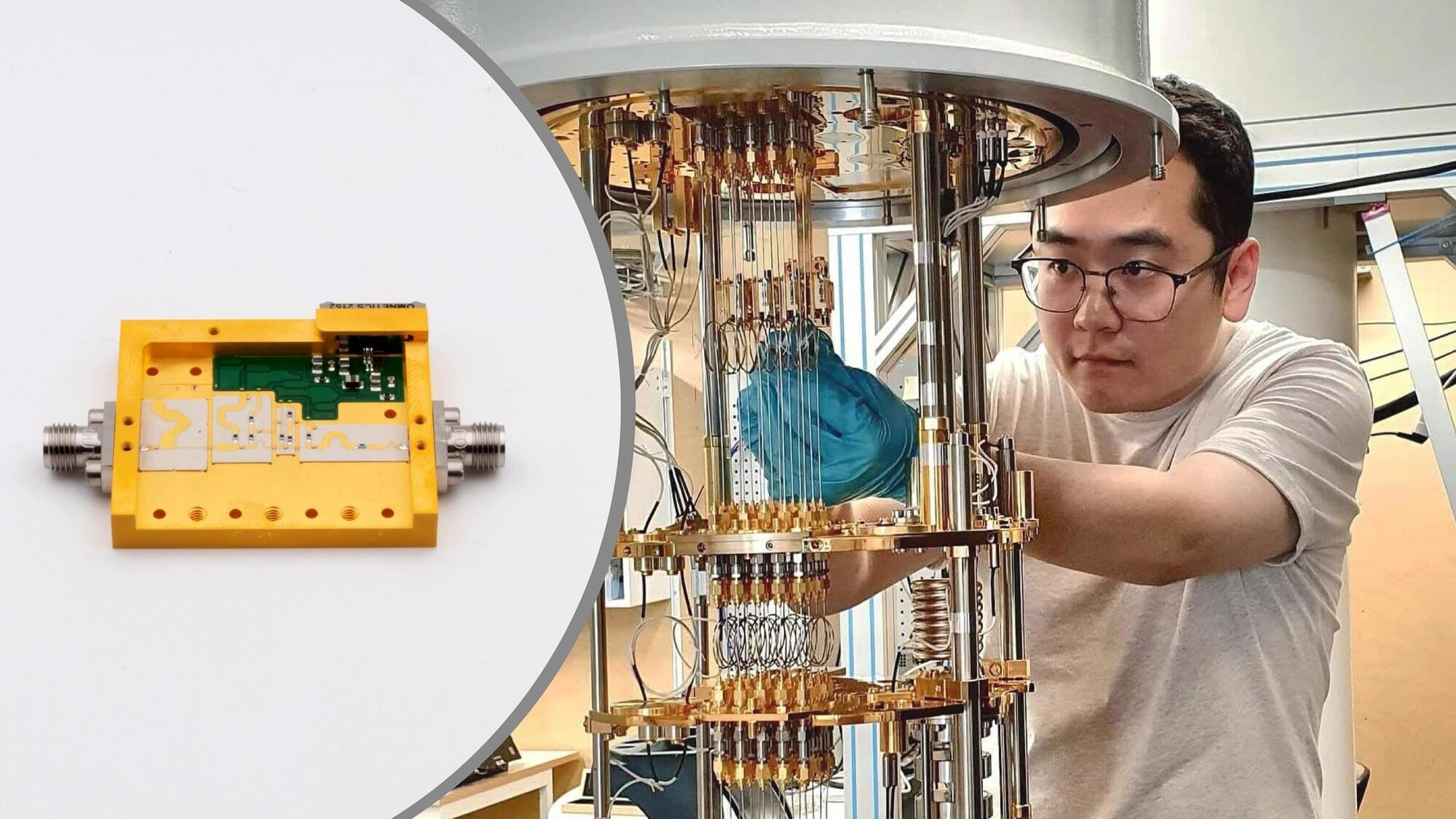
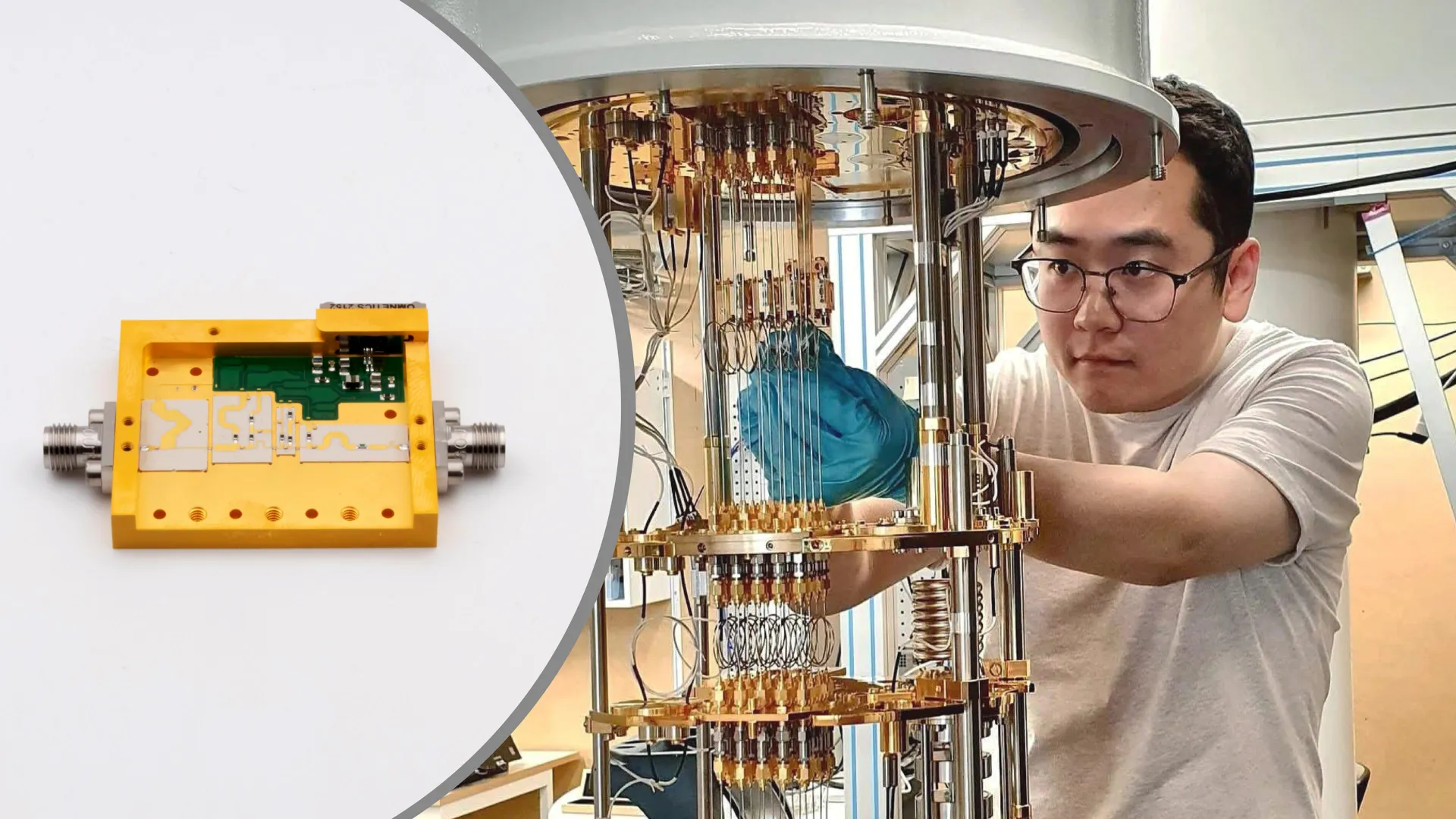
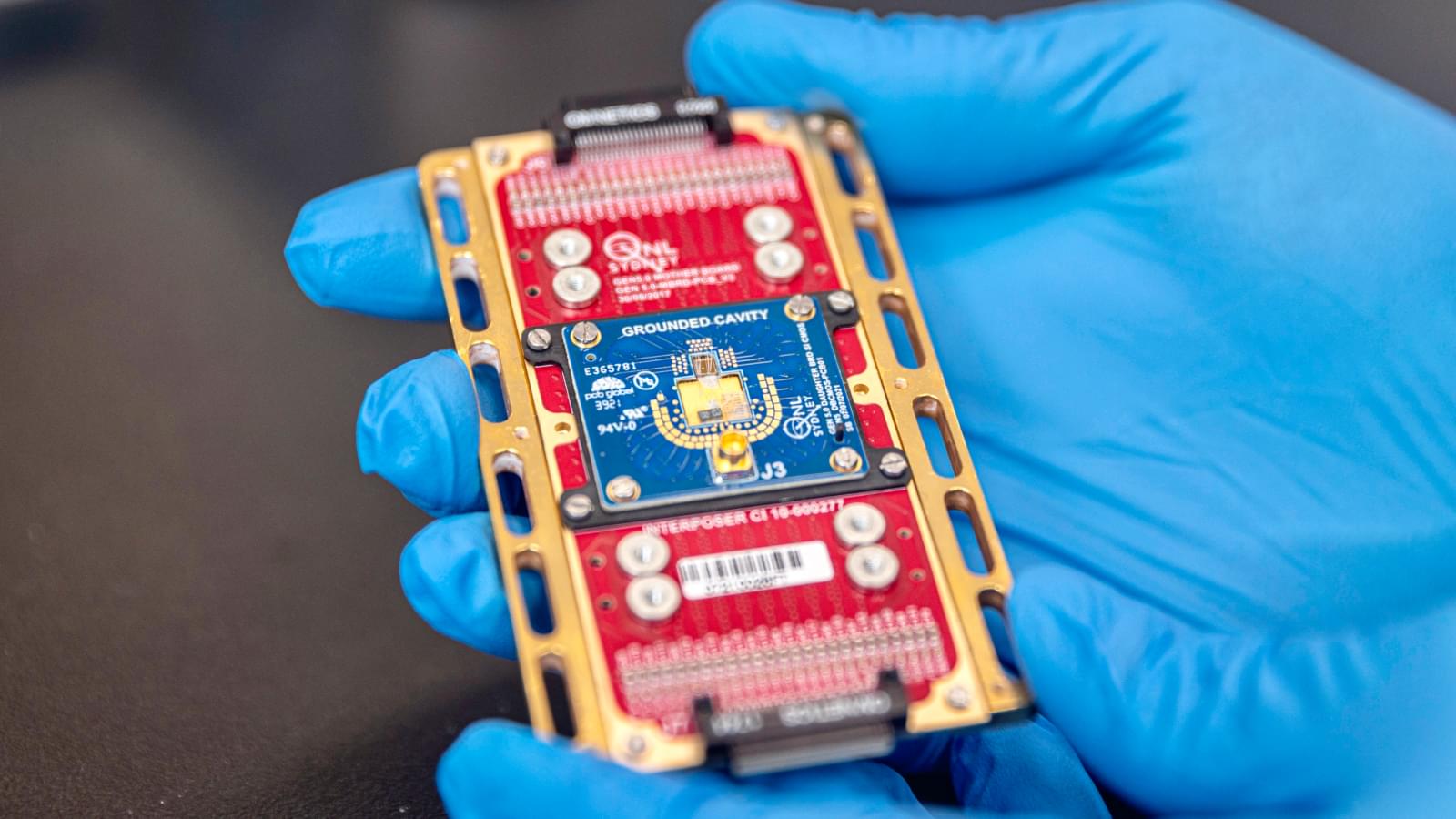
Quantum computers just got cooler—literally—thanks to a smart amplifier that slashes heat without sacrificing speed.
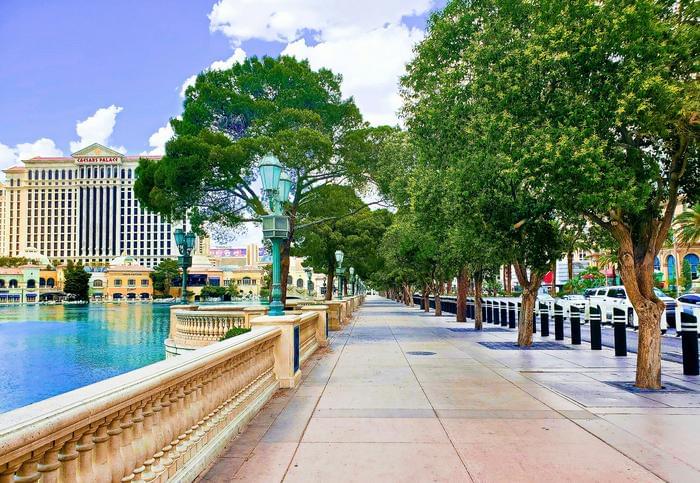


How can trees provide relief from extreme heat in urban climates? This is what a recent study published in Environmental Research Climate hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated using urban street trees to provide shade relief from extreme temperatures, which continue to increase due to climate change. This study has the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, legislators, city planners, and the public better understand the benefits of trees for cooling urban spaces in the face of the increasing threat of climate change.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models between July and August 2022 to simulate how street tree planting in Las Vegas could provide relief from extreme heat and heat exposure. The goal of the study was to ascertain the overall effectiveness of planting non-native trees in an urban setting while estimating the amount of water they would need to survive and provide shade relief from extreme heat. In the end, the researchers found that desert environments are too hot for trees to adequately provide shade relief, primarily due to the trees’ water conservation efforts.
“Urban trees are not a silver bullet for cooling our cities, particularly for desert cities like Las Vegas,” said Dr. Juan Henao, who is a postdoctoral researcher at the Desert Research Institute and lead author of the study. “But they provide significant shade and of course other benefits. I know that I prefer to see trees, and they can help store carbon. We just need to remember that in order to cool the air, they need to release water vapor, and we need to give them enough water to do that. Any hot, dry city will need to consider these tradeoffs and really do their research to identify the right species for planting efforts.”
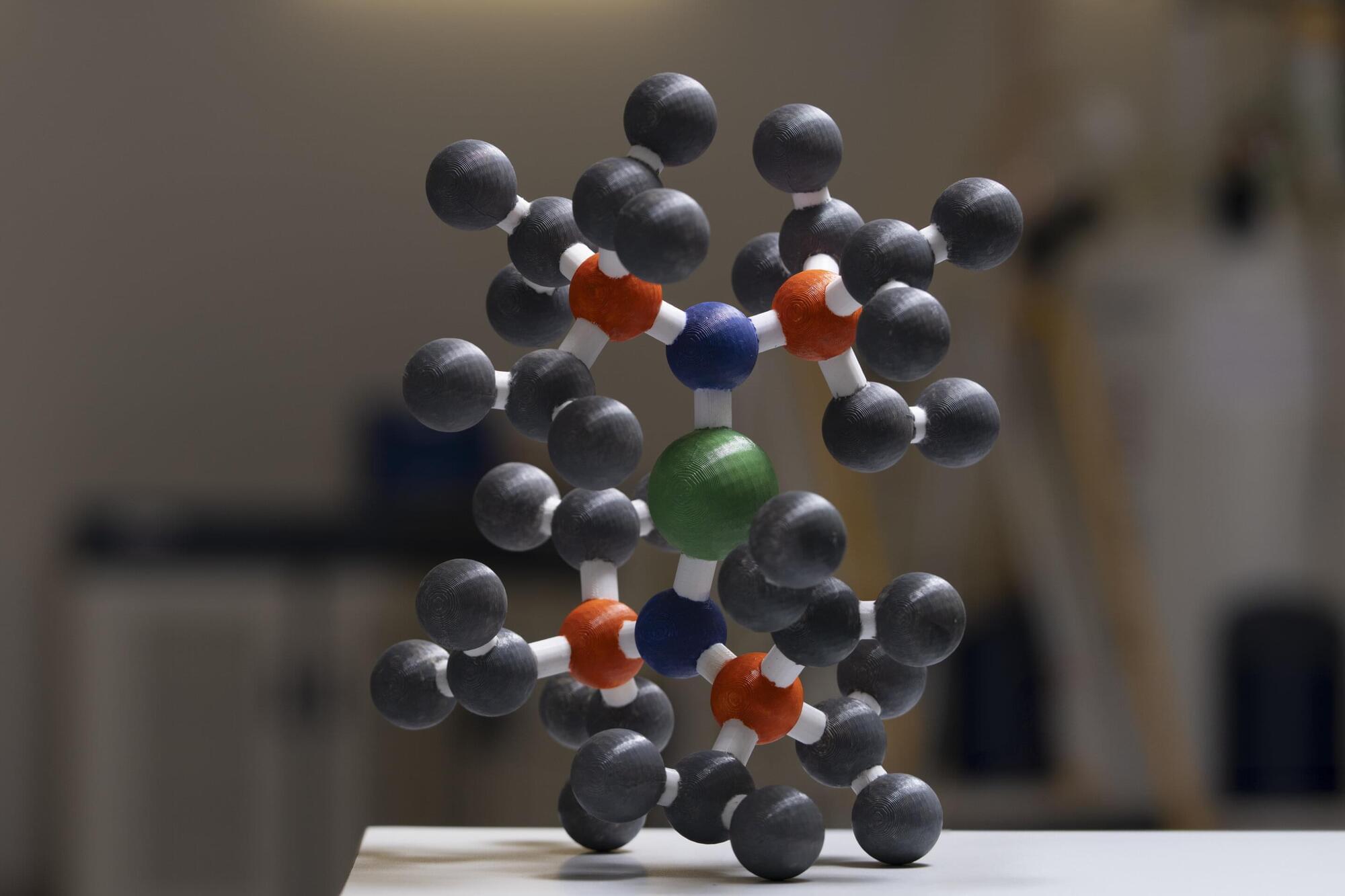


Researchers at the University of Sydney have successfully performed a quantum simulation of chemical dynamics with real molecules for the first time, marking a significant milestone in the application of quantum computing to chemistry and medicine.
Understanding in real time how atoms interact to form new compounds or interact with light has long been expected as a potential application of quantum technology. Now, quantum chemist Professor Ivan Kassal and Physics Horizon Fellow Dr Tingrei Tan, have shown it is possible using a quantum machine at the University of Sydney.
The innovative work leverages a novel, highly resource-efficient encoding scheme implemented on a trapped-ion quantum computer in the University of Sydney Nanoscience Hub, with implications that could help transform medicine, energy and materials science.
University of Sydney scientists have made a big step towards future design of treatments for skin cancer or improved sunscreen by modelling photoactive chemical dynamics with a quantum computer.
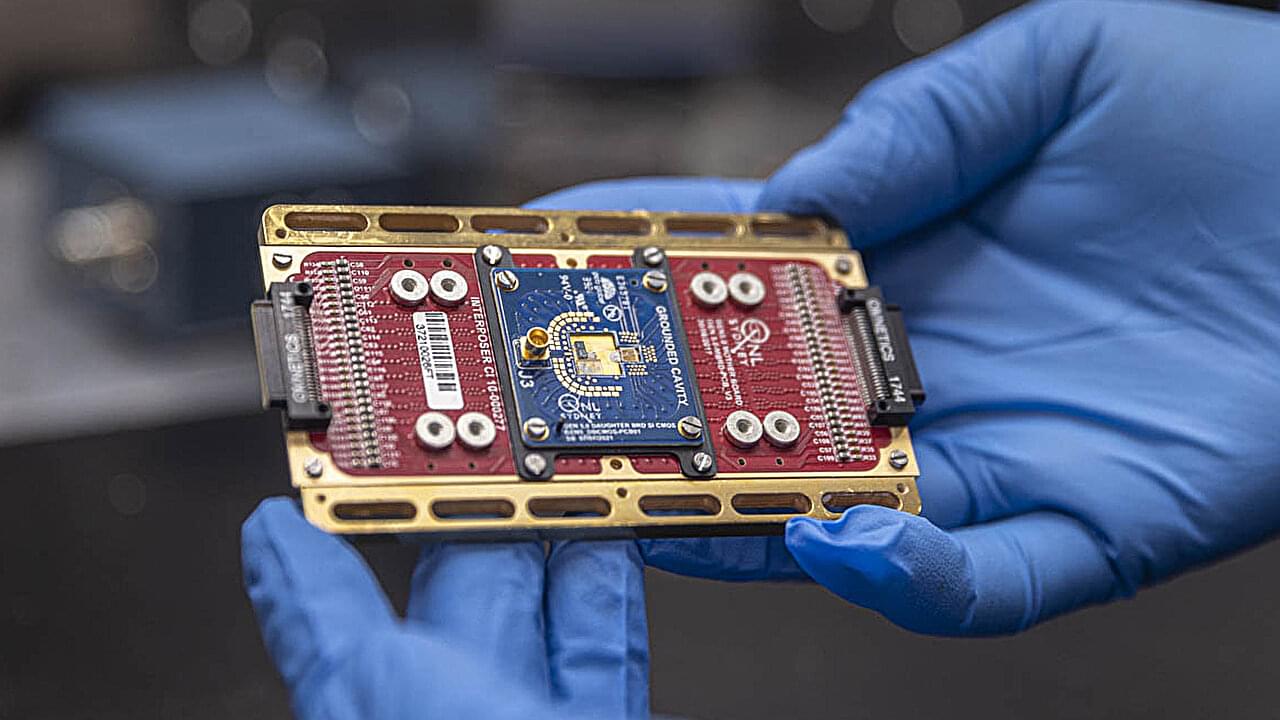
Developing technology that allows quantum information to be both stable and accessible is a critical challenge in the development of useful quantum computers that operate at scale. Research published in the journal Nature provides a pathway for scaling the number of quantum transistors (known as qubits) on a chip from current numbers under 100 to the millions needed to make quantum computation a practical reality. The result is enabled by new cryogenic control electronics that operate at close to absolute zero, developed at the University of Sydney.
Lead researcher Professor David Reilly from the University of Sydney Nano Institute and School of Physics said, “This will take us from the realm of quantum computers being fascinating laboratory machines to the stage where we can start discovering the real-world problems that these devices can solve for humanity.”
The paper is the result of industry cooperation between the University of Sydney and the University of New South Wales through the respective quantum tech spin-out companies Emergence Quantum and Diraq. Professor Reilly’s company, Emergence Quantum, was established this year to commercialize quantum control technologies and other advanced electronics like the chip presented in this Nature paper.
It can be found inside gas giants such as Jupiter and is briefly created during meteorite impacts or in laser fusion experiments: warm dense matter. This exotic state of matter combines features of solid, liquid and gaseous phases. Until now, simulating warm dense matter accurately has been considered a major challenge.
An international team led by researchers from the Center for Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS) at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) in Germany and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has succeeded in describing this state of matter much more accurately than before using a new computational method. The approach could advance laser fusion and help in the synthesis of new high-tech materials.
The team presents its results in the journal Nature Communications.
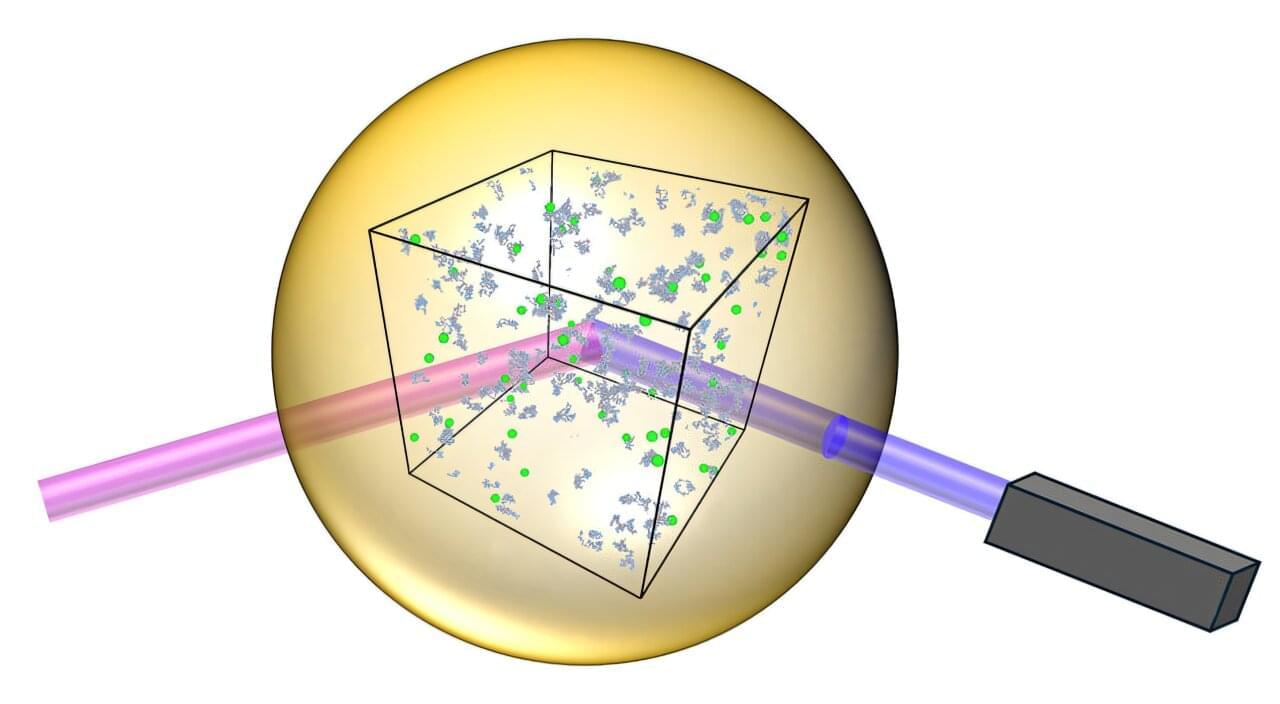
Landauer’s principle is a thermodynamics concept also relevant in information theory, which states that erasing one bit of information from an information system results in the dissipation of at least a specific amount (i.e., kBTln2) of energy. This principle has so far been primarily considered in the context of classical computers and information processing systems.
Yet researchers at TU Vienna, the Freie Universität Berlin, the University of British Columbia, the University of Crete and the Università di Pavia recently extended Landauer’s principle to quantum many-body systems, systems made up of many interacting quantum particles.
Their paper, published in Nature Physics, introduces a viable approach to experimentally probe this crucial principle in a quantum regime and test theoretical predictions rooted in quantum thermodynamics.
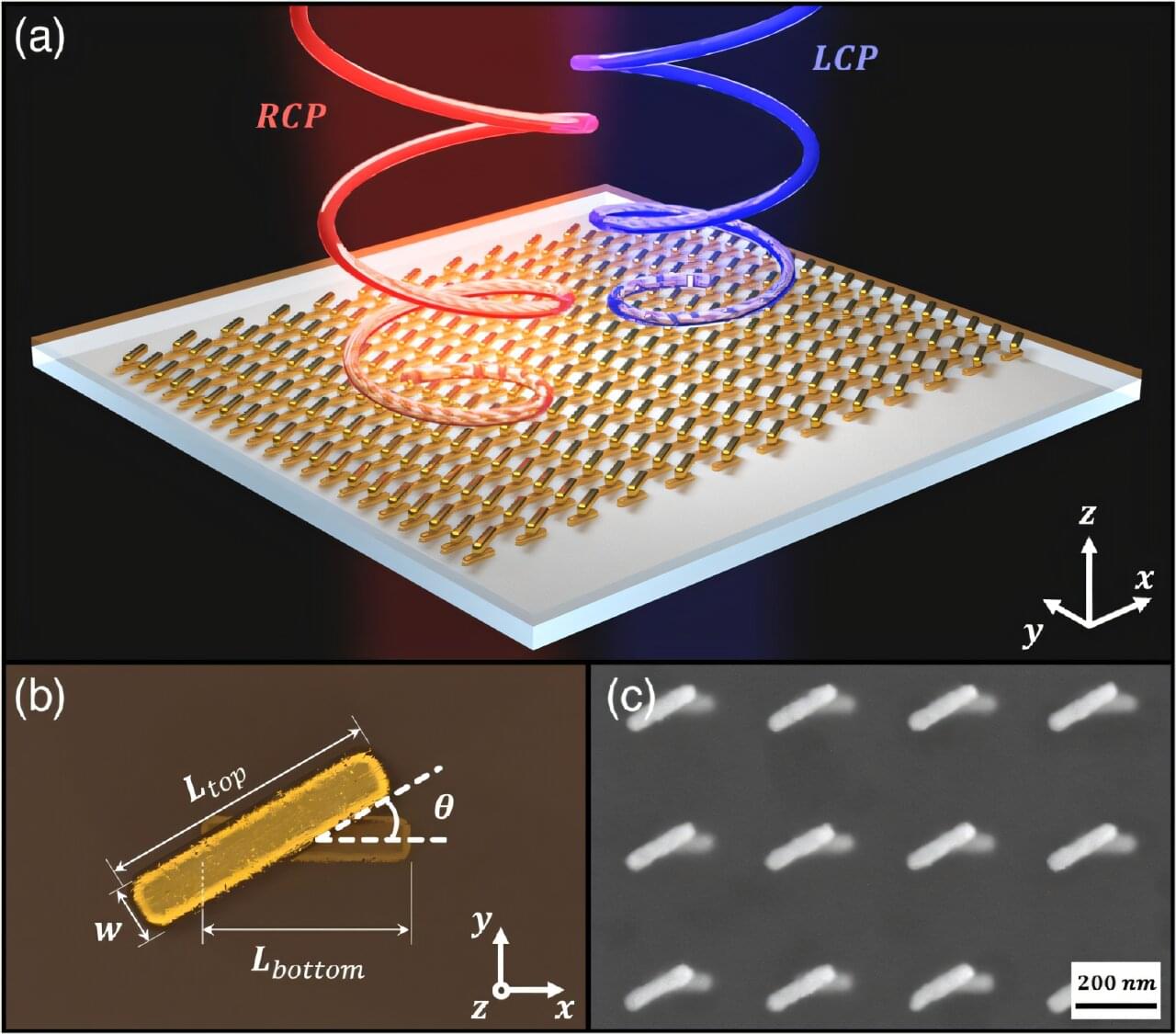
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have achieved a long-sought milestone in photonics: creating tiny optical devices that are both highly sensitive and durable—two qualities that have long been considered fundamentally incompatible.
This rare coexistence of sensitivity and durability could lead to a new generation of photonic devices that are not only precise and powerful but also much easier and cheaper to produce at scale. This could open the door to advanced sensors and technologies ranging from highly sensitive medical diagnostics and environmental sensors to more secure communication systems, all built into tiny, chip-scale devices.
Achieving both properties has been a challenge because devices that are sensitive enough to detect tiny changes in their environment are often fragile and prone to breaking down if even the smallest imperfections arise during manufacturing. This makes them expensive and difficult to produce at scale. Meanwhile, making such devices more rugged often means compromising their precision.