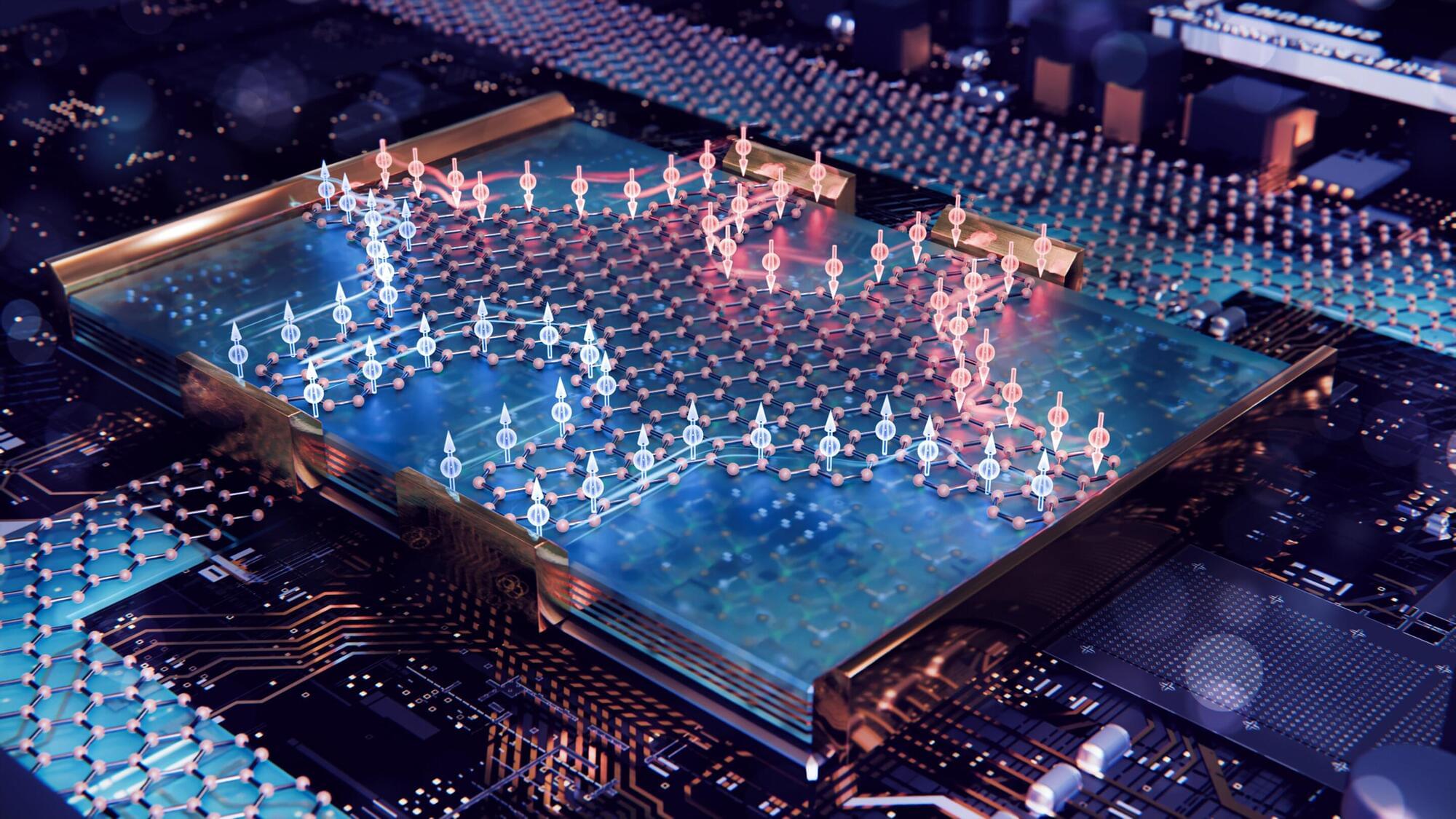
Scientists from TU Delft (The Netherlands) have observed quantum spin currents in graphene for the first time without using magnetic fields. These currents are vital for spintronics, a faster and more energy-efficient alternative to electronics. This breakthrough, published in Nature Communications, marks an important step towards technologies like quantum computing and advanced memory devices.
Quantum physicist Talieh Ghiasi has demonstrated the quantum spin Hall (QSH) effect in graphene for the first time without any external magnetic fields. The QSH effect causes electrons to move along the edges of the graphene without any disruption, with all their spins pointing in the same direction.
“Spin is a quantum mechanical property of electrons, which is like a tiny magnet carried by the electrons, pointing up or down,” Ghiasi explains. “We can leverage the spin of electrons to transfer and process information in so-called spintronics devices. Such circuits hold promise for next-generation technologies, including faster and more energy-efficient electronics, quantum computing, and advanced memory devices.”