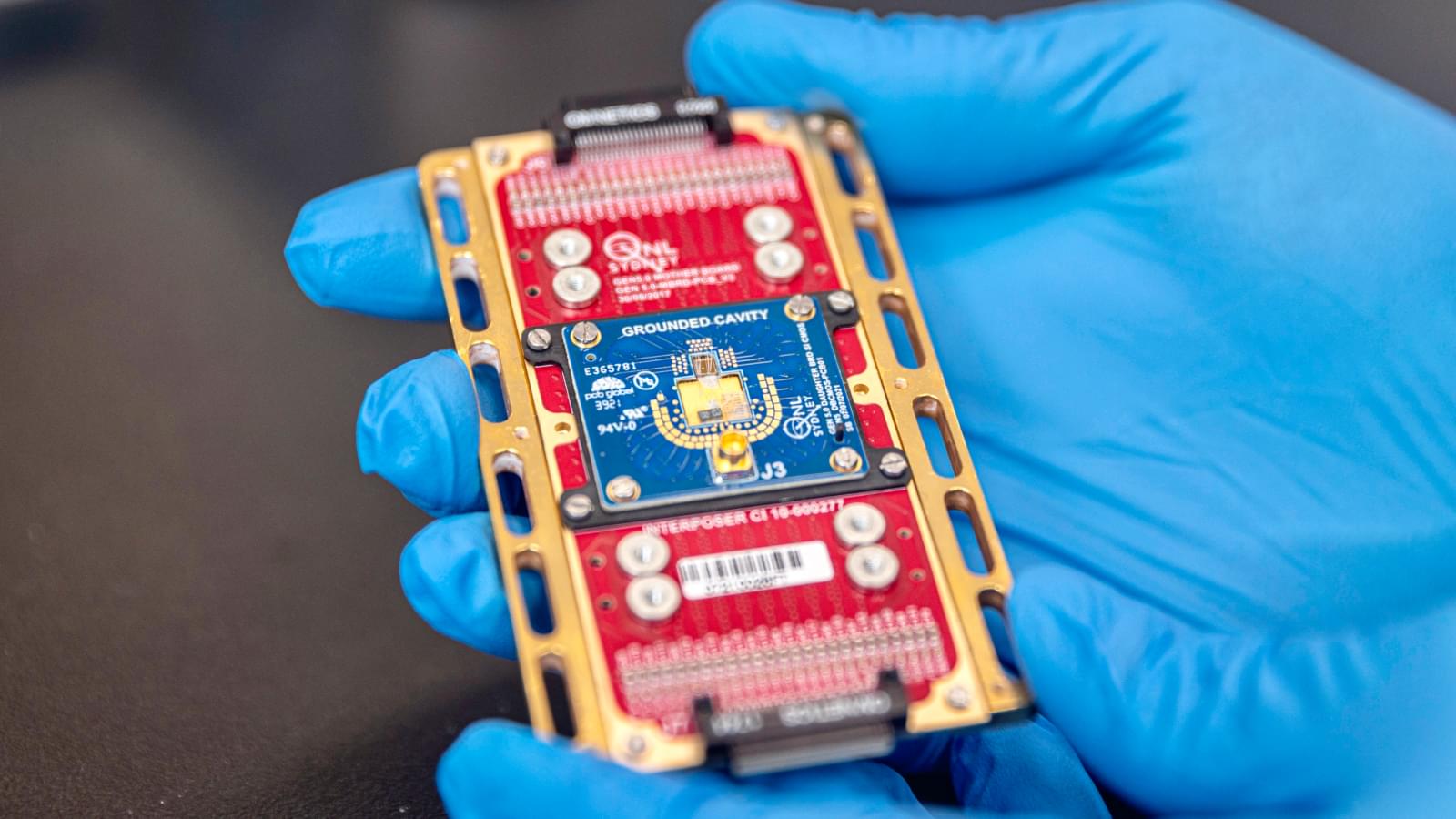
Could we replace the brain with computer chips? Reality is much more complex and the brain seems to be much more than just a biological computer.


The advance warning period is key for this sort of voluntary program, especially one counting on participation from hyperscale data centers with sensitive IT equipment worth billions, Kavulla said.
“This should not be the kind of demand response where you’re calling it with no notice and curtailing the customer straight off,” he said.

The use of electronics in various forms is on the rise, from wearable devices like smartwatches to implantable devices like body-implanted sensors, skin-worn smart patches, and disposable monitoring devices. These devices, which are inevitably discarded after use, contribute to the growing problem of electronic waste (e-waste), a significant environmental concern.
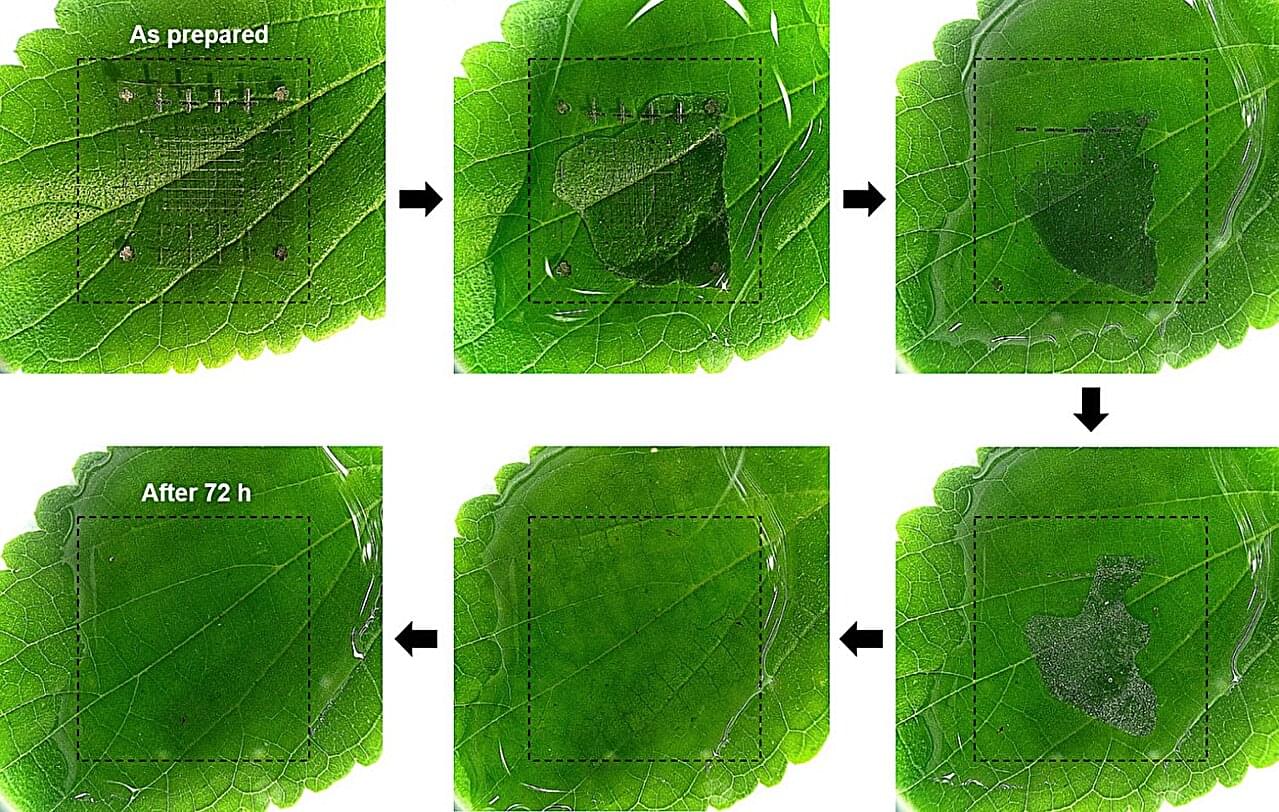
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has announced that a joint research team, led by Dr. Sangho Cho of the Center for Extreme Materials Research and Dr. Yongho Joo of the Center for Functional Composite Materials Research, has developed a polymeric material that offers high-performance data storage while completely degrading within days when immersed in water. The research is published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
The material is biocompatible and stable enough for implantation in the human body, and the onset of degradation can be controlled by adjusting the thickness and the composition of the protective layer. Once this protective layer dissolves, the material degrades naturally in water within approximately three days, without leaving any residue.
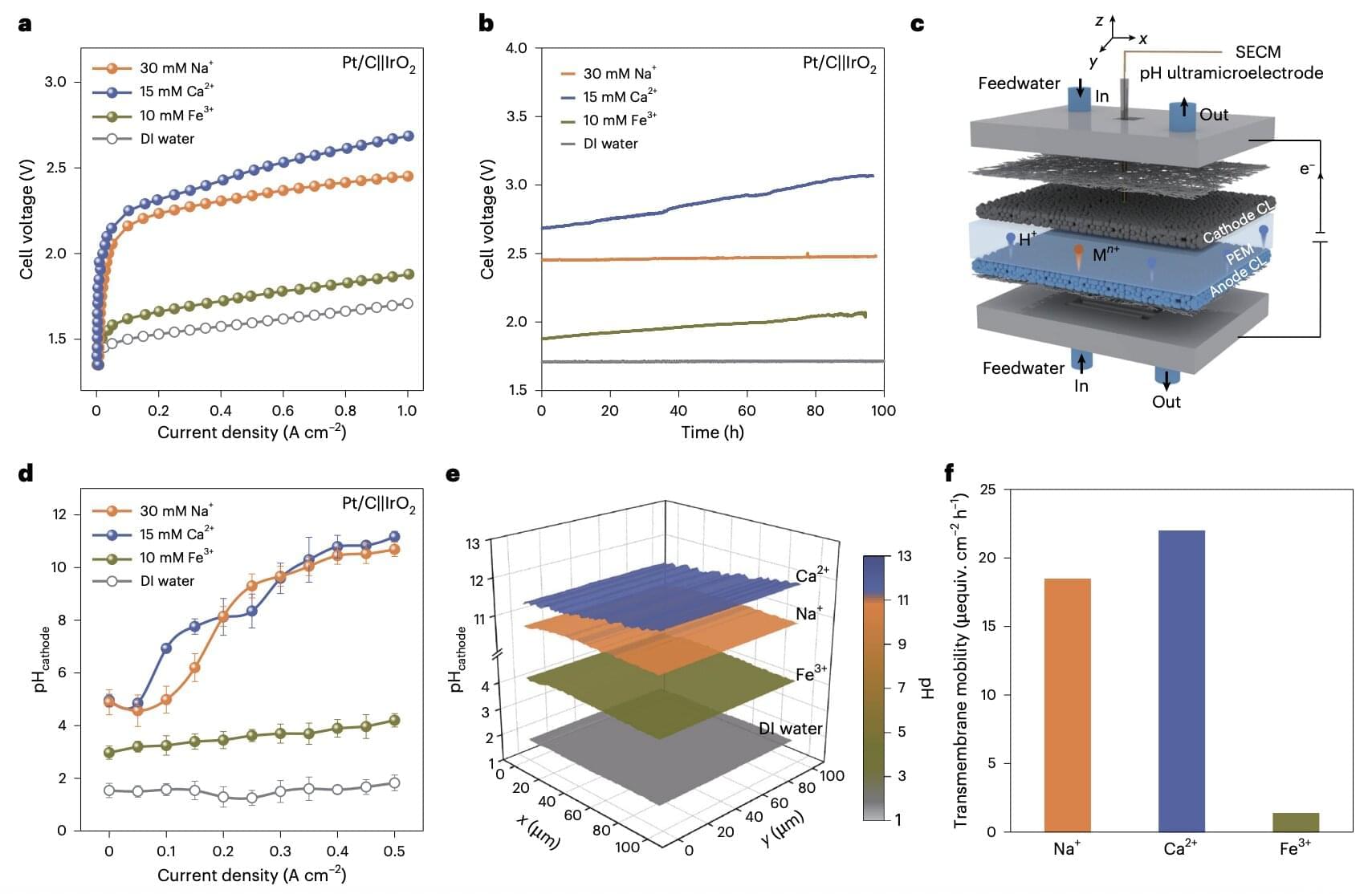
In recent years, energy engineers have been working on a wide range of technologies that could help to generate and store electrical power more sustainably. These include electrolyzers, devices that could use electricity sourced via photovoltaics, wind turbines or other energy technologies to split water (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2), via a process known as electrolysis.
The hydrogen produced by electrolyzers could in turn be used in fuel cells, devices that convert the chemical energy in hydrogen into electricity without combustion and could be used to power trucks, buses, forklifts and various other heavy vehicles, or could provide back-up power for hospitals, data centers and other facilities.
Many recently designed electrolyzers prompt the splitting of water into hydrogen using a proton exchange membrane (PEM), a membrane that selectively allows protons (H+) to pass through, while blocking gases.
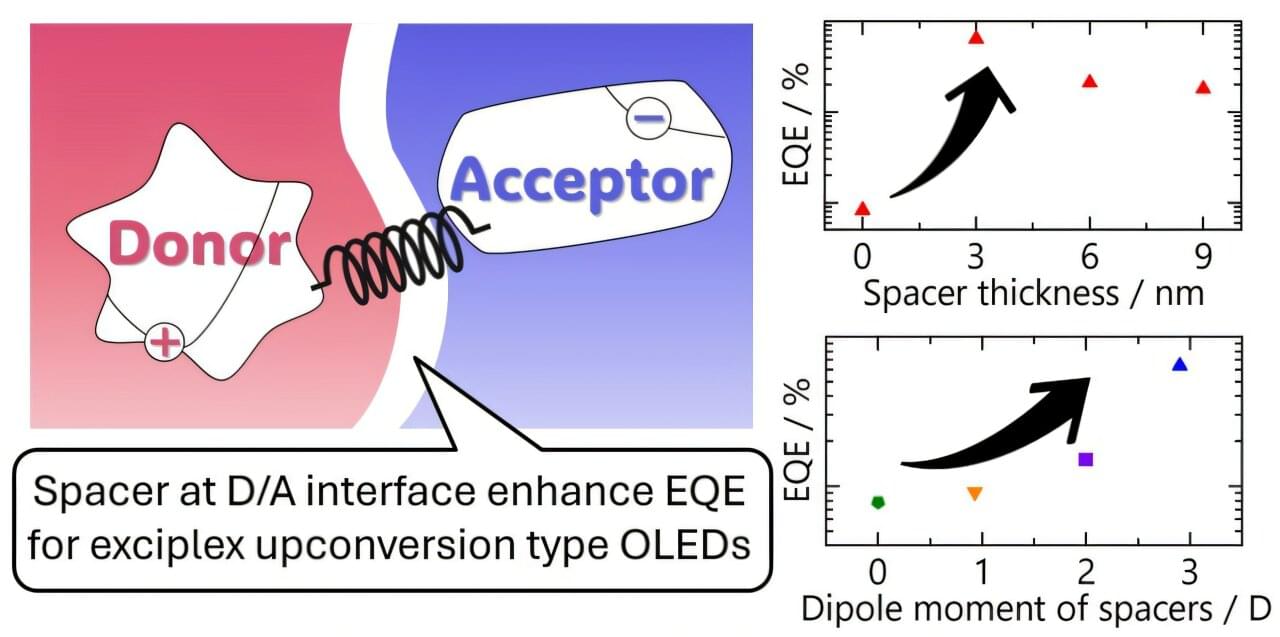
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have transformed display and lighting technology with their vivid colors, deep contrast, and energy efficiency. As demand grows for lighter, thinner, and more energy-saving devices—especially in wearables, foldables, and portable electronics—there’s increasing interest in OLEDs that can operate at lower voltages without compromising performance.
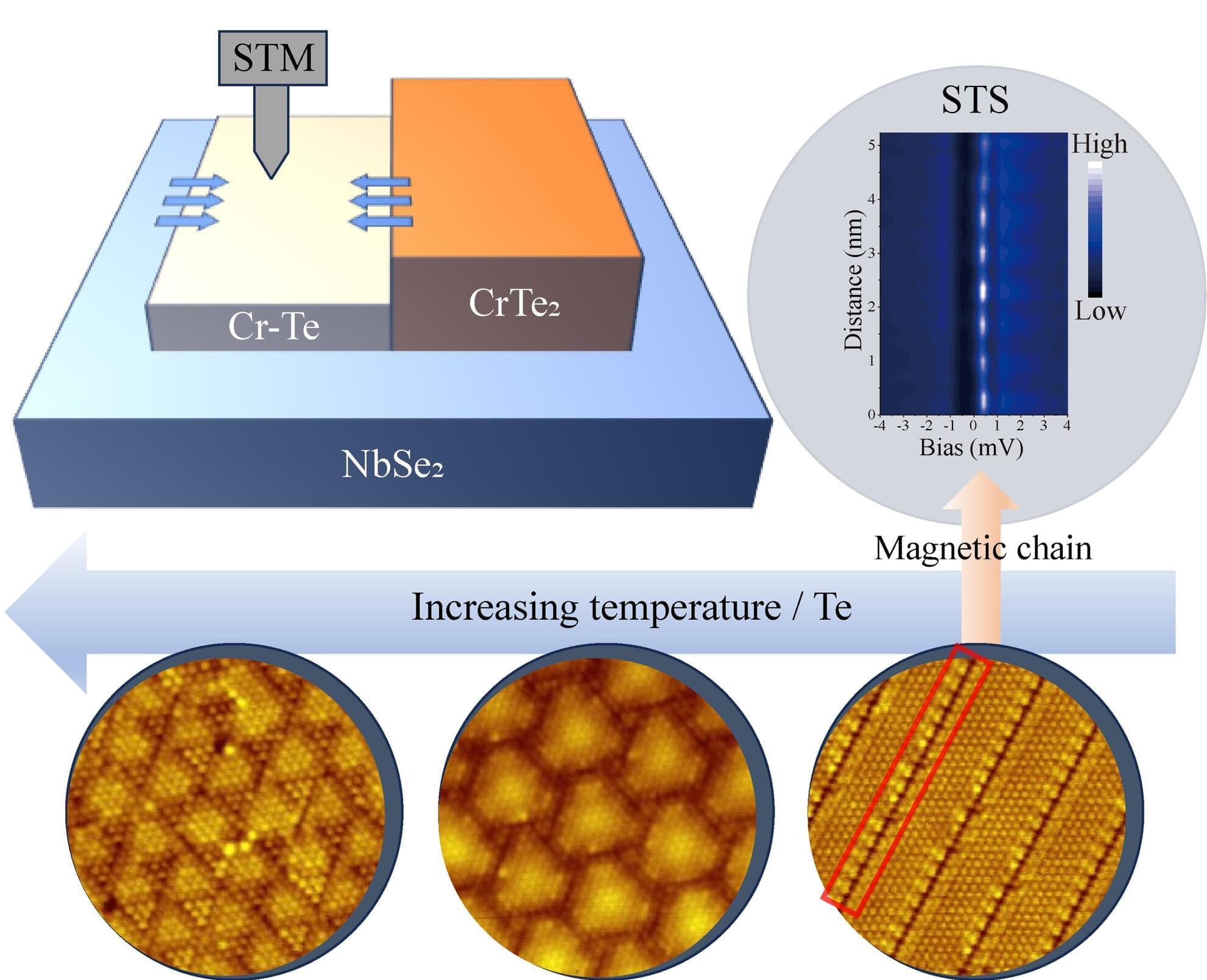
Magnetic-superconducting hybrid systems are key to unlocking topological superconductivity, a state that could host Majorana modes with potential applications in fault-tolerant quantum computing. However, creating stable, controllable interfaces between magnetic and superconducting materials remains a challenge.
Traditional systems often struggle with lattice mismatches, complex interfacial interactions, and disorder, which can obscure the signatures of topological states or mimic them with trivial phenomena. Achieving precise control over magnetic structures at the atomic scale has been a long-standing challenge in this field.
Published in Materials Futures, the researchers developed a novel sub-monolayer CrTe2/NbSe2 heterostructure. By carefully depositing Cr and Te on NbSe2 substrate, they observed a two-stage growth process: an initial compressed Cr-Te layer forms with a lattice constant of 0.35 nm, followed by the formation of an atomically flat CrTe2 monolayer with a lattice constant of 0.39 nm. Annealing the Cr-Te layer can trigger stress-relief reconstruction, which creates stripe-like patterns with edges that host localized magnetic moments, effectively forming one-dimensional magnetic chains.
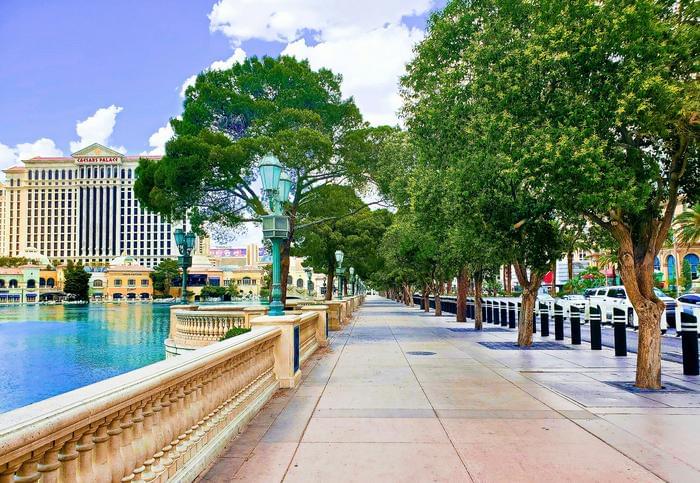

How can trees provide relief from extreme heat in urban climates? This is what a recent study published in Environmental Research Climate hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated using urban street trees to provide shade relief from extreme temperatures, which continue to increase due to climate change. This study has the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, legislators, city planners, and the public better understand the benefits of trees for cooling urban spaces in the face of the increasing threat of climate change.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models between July and August 2022 to simulate how street tree planting in Las Vegas could provide relief from extreme heat and heat exposure. The goal of the study was to ascertain the overall effectiveness of planting non-native trees in an urban setting while estimating the amount of water they would need to survive and provide shade relief from extreme heat. In the end, the researchers found that desert environments are too hot for trees to adequately provide shade relief, primarily due to the trees’ water conservation efforts.
“Urban trees are not a silver bullet for cooling our cities, particularly for desert cities like Las Vegas,” said Dr. Juan Henao, who is a postdoctoral researcher at the Desert Research Institute and lead author of the study. “But they provide significant shade and of course other benefits. I know that I prefer to see trees, and they can help store carbon. We just need to remember that in order to cool the air, they need to release water vapor, and we need to give them enough water to do that. Any hot, dry city will need to consider these tradeoffs and really do their research to identify the right species for planting efforts.”