Scientists see the potential in using ice for long term data storage.


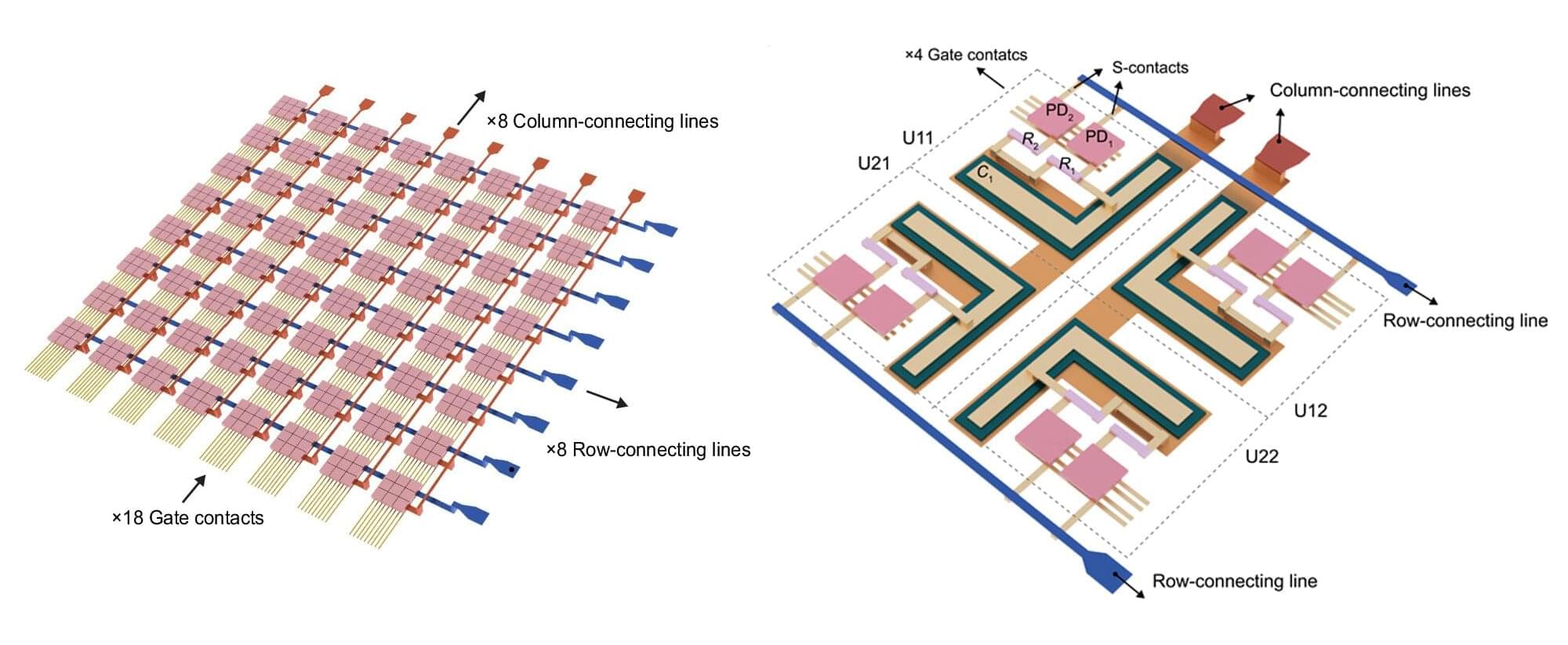
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have pushed forward the development of computer vision with new, silicon-based hardware that can both capture and process visual data in the analog domain. Their work, described in the journal Nature Communications, could ultimately add to large-scale, data-intensive and latency-sensitive computer vision tasks.
“This is very powerful retinomorphic hardware,” says Guangyu Xu, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering and adjunct associate professor of biomedical engineering at UMass Amherst. “The idea of fusing the sensing unit and the processing unit at the device level, instead of physically separating them apart, is very similar to the way that human eyes process the visual world.”
Existing computer vision systems often involve exchanging redundant data between physically separated sensing and computing units.


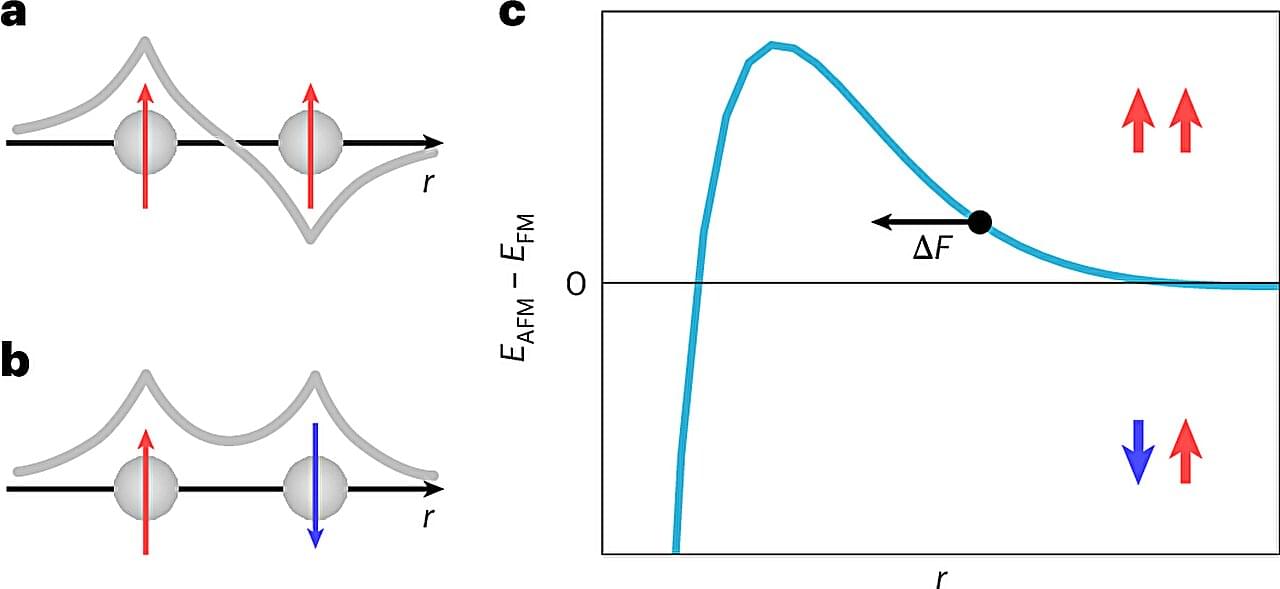
Research from the University of St Andrews has set a new benchmark for the precision with which researchers can explore fundamental physics in quantum materials. The work has implications extending from materials science to advanced computing, as well as confirming a nearly 100-year-old prediction.
The researchers explored magnetoelastic coupling, which is the change in the size or shape of a material when exposed to a magnetic field. It is usually a small effect, but one that has technological consequences.
A team from the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of St Andrews has now discovered that this effect is remarkably large in a case where one wouldn’t have expected it—in a transition metal oxide. Oxides are a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. High-temperature superconductors are one of the most prominent examples of a transition metal oxide.



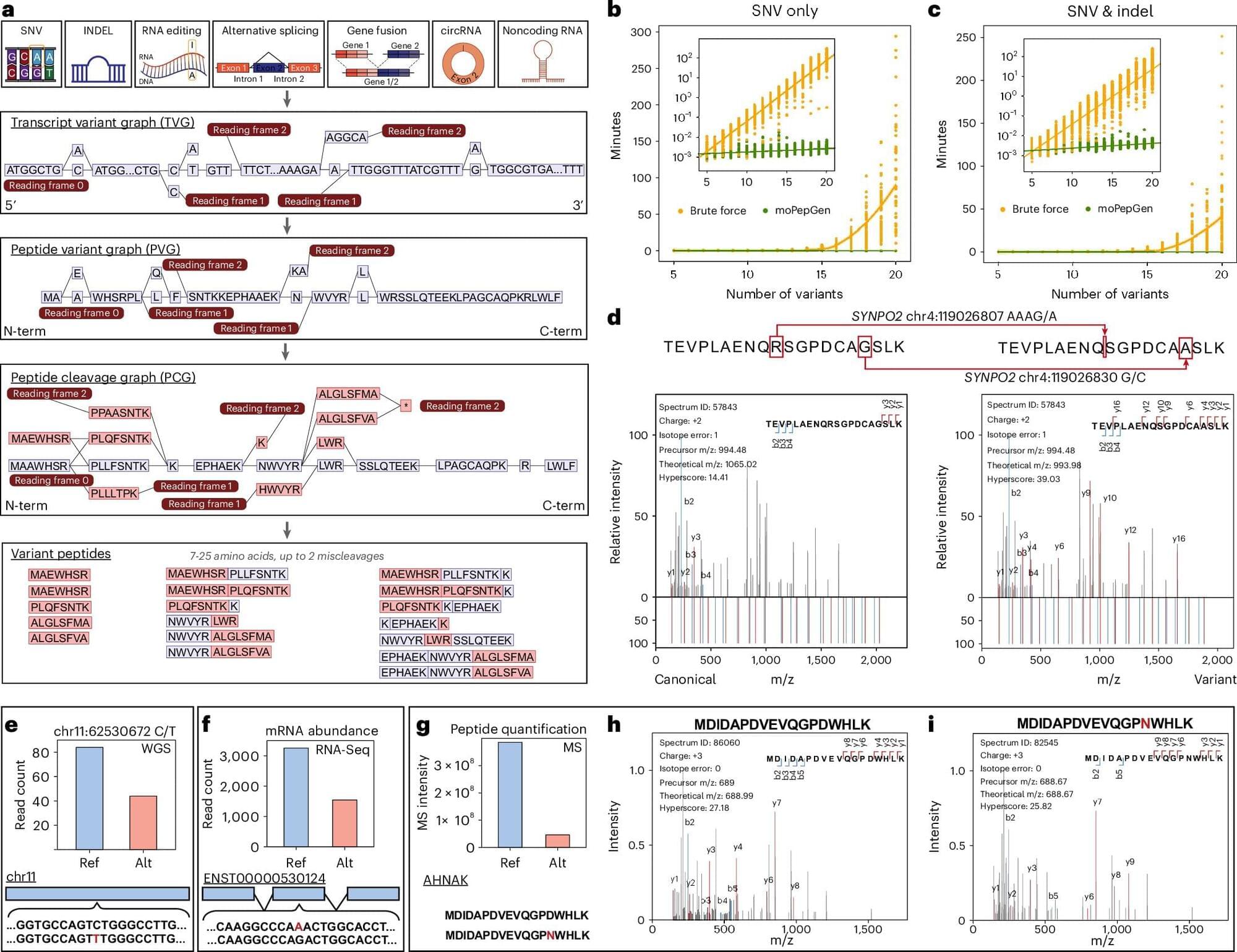
Scientists at UCLA and the University of Toronto have developed an advanced computational tool, called moPepGen, that helps identify previously invisible genetic mutations in proteins, unlocking new possibilities in cancer research and beyond.
The tool, described in Nature Biotechnology, will help understand how changes in our DNA affect proteins and ultimately contribute to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other conditions. It provides a new way to create diagnostic tests and to find treatment targets previously invisible to researchers.
Proteogenomics combines the study of genomics and proteomics to provide a comprehensive molecular profile of diseases. However, a major challenge has been the inability to accurately detect variant peptides, limiting the ability to identify genetic mutations at the protein level. Existing proteomic tools often fail to capture the full diversity of protein variations.