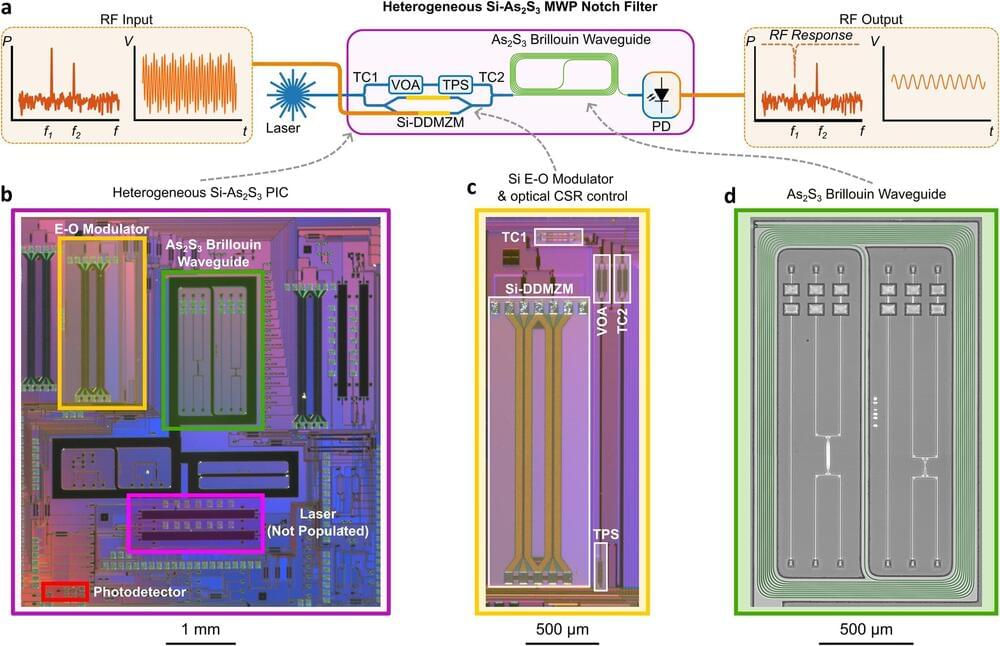
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have invented a compact silicon semiconductor chip that integrates electronics with photonic, or light, components. The new technology significantly expands radio-frequency (RF) bandwidth and the ability to accurately control information flowing through the unit.
Expanded bandwidth means more information can flow through the chip and the inclusion of photonics allows for advanced filter controls, creating a versatile new semiconductor device.
Researchers expect the chip will have applications in advanced radar, satellite systems, wireless networks and the roll-out of 6G and 7G telecommunications and also open the door to advanced sovereign manufacturing. It could also assist in the creation of high-tech value-add factories at places like Western Sydney’s Aerotropolis precinct.