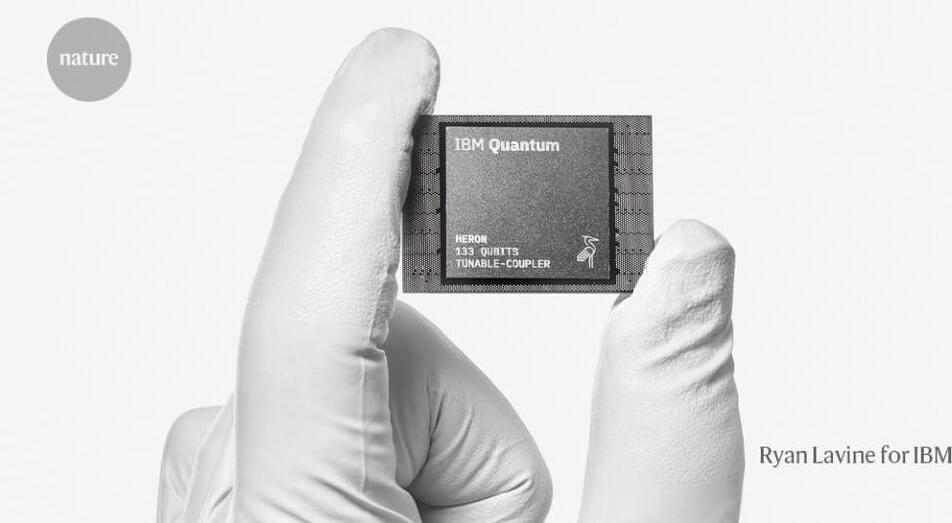
The company announces its latest huge chip — but will now focus on developing smaller chips with a fresh approach to ‘error correction’


The field of research focusing on self-propelled particles, known as active particles, is rapidly expanding. In most theoretical models, these particles are assumed to maintain a constant swimming speed. However, this assumption does not hold true for many experimentally produced particles, like those propelled by ultrasound for medical applications. Their propulsion speed varies with orientation.
A team of physicists, led by Prof. Raphael Wittkowski from the University of Münster and including Prof. Michael Cates from the University of Cambridge, conducted a collaborative study to explore how this orientation-dependent speed influences the behavior of particle systems, particularly in cluster formation.
They combined computer simulations with theoretical analysis to uncover new effects in systems of active particles with orientation-dependent speeds. Their findings were recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
It is now contributing carbon-free energy to the grid that serves Google’s Nevada data centers.

A newly discovered trade-off in the way time-keeping devices operate on a fundamental level could set a hard limit on the performance of large-scale quantum computers, according to researchers from the Vienna University of Technology.
While the issue isn’t exactly pressing, our ability to grow systems based on quantum operations from backroom prototypes into practical number-crunching behemoths will depend on how well we can reliably dissect the days into ever finer portions. This is a feat the researchers say will become increasingly more challenging.
Whether you’re counting the seconds with whispers of Mississippi or dividing them up with the pendulum-swing of an electron in atomic confinement, the measure of time is bound by the limits of physics itself.
Computers, cars, mobile phones, toasters: countless everyday objects contain microchips. They’re tiny, unremarkable and cheap, but since the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, they’ve been at the center of a political and industrial tug of war.
Against the backdrop of the trade war between China and the US, “The Microchip War” spotlights all the aspects of this conflict. In the film, the world’s most influential actors in this industrial sector weigh in.
No one is in any doubt that microprocessors are as strategically important as oil. The battle over microchips could potentially redefine the geopolitical world order. In the United States and Europe, fears over a microprocessor shortage have led to a flood of investment pledges. After ceding microchip production to Asia in the 1990s, market leaders in the West are now trying to bring production back home and thereby regain control of the production chain.
This resulted in the adoption of new legislation in 2022: the European Chips Act initiated by the EU Commission under Ursula von der Leyen and — in response to this — the American “Chip and Science Act” initiated by Joe Biden. China, the US, Europe: major global powers fighting over tiny microchips. Pandemic and resource scarcity have fueled the desire for industrial reconquest and economic superiority.
But is this reindustrialization actually possible? Can the West challenge the foundations of globalization in this way?
#documentary #dwdocumentary #usa #europe #asia.

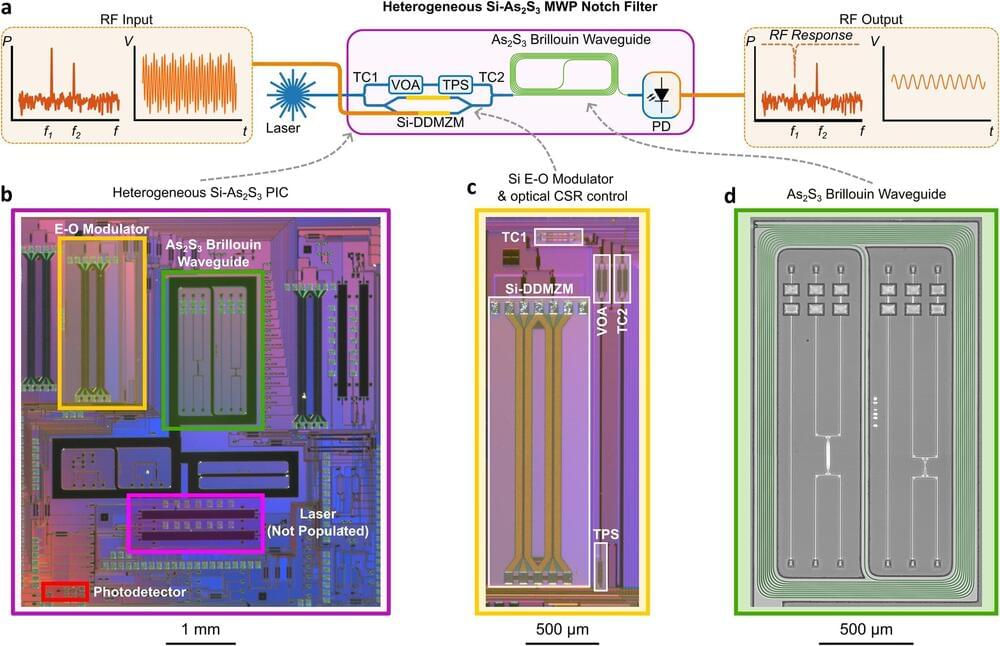
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have invented a compact silicon semiconductor chip that integrates electronics with photonic, or light, components. The new technology significantly expands radio-frequency (RF) bandwidth and the ability to accurately control information flowing through the unit.
Expanded bandwidth means more information can flow through the chip and the inclusion of photonics allows for advanced filter controls, creating a versatile new semiconductor device.
Researchers expect the chip will have applications in advanced radar, satellite systems, wireless networks and the roll-out of 6G and 7G telecommunications and also open the door to advanced sovereign manufacturing. It could also assist in the creation of high-tech value-add factories at places like Western Sydney’s Aerotropolis precinct.

About 15% or $2.7 billion of Nvidia’s revenue for the quarter ended October came from Singapore, a U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission filing showed. Revenue coming from Singapore in the third quarter jumped 404.1% from the $562 million in revenue recorded in the same period a year ago. This outpaced Nvidia’s overall revenue growth of 205.5% from a year ago.
Singapore only trailed behind the U.S. (34.77%,) Taiwan (23.91%) and China including Hong Kong (22.24%) in Nvidia’s third-quarter sales rankings.
“I would highly think it’s due to data centers as Singapore has quite a lot of data centers and cloud service providers,” Maybank Securities analyst Jarick Seet told CNBC.
The Asian superpower has introduced its first homegrown Lower Power Double Data Rate 5 (LPDDR5) chip for smartphones.
Avalon_Studio/iStock.
ChangXin Memory Technologies (CXMT) announced the LPDDR5 chip, a next-generation memory technology initially introduced by Samsung Electronics in 2018, in a press release.
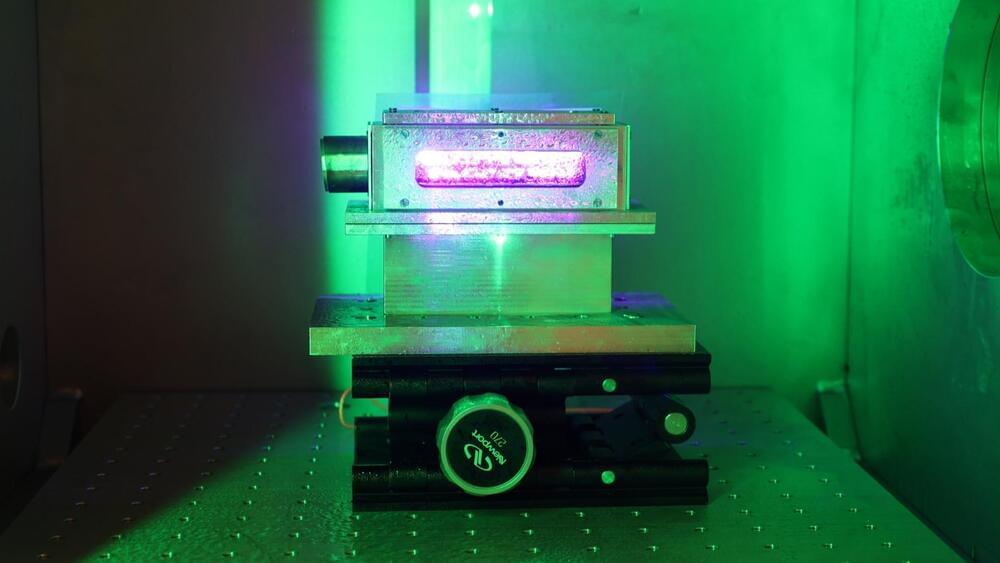

The accelerator, an advanced wakefield laser accelerator, is under 20 feet long, generating a 10 billion electron-volt (10 GeV) electron beam.
Bjorn “Manuel” Hegelich, associate professor of physics at UT and CEO of TAU Systems, alluding to the size of the chamber where the beam was produced stated: “We can now reach those energies in 10 centimeters.”
Scientists are aiming to use this technology for assessing the resilience of space-bound electronics against radiation, capturing the 3D internal configurations of emerging semiconductor chip designs, and potentially pioneering new cancer treatments and advanced medical imaging methodologies.
Furthermore, the statement noted that this accelerator could also be used to drive another device called an X-ray free electron laser, which could take slow-motion movies of processes on the atomic or molecular scale.