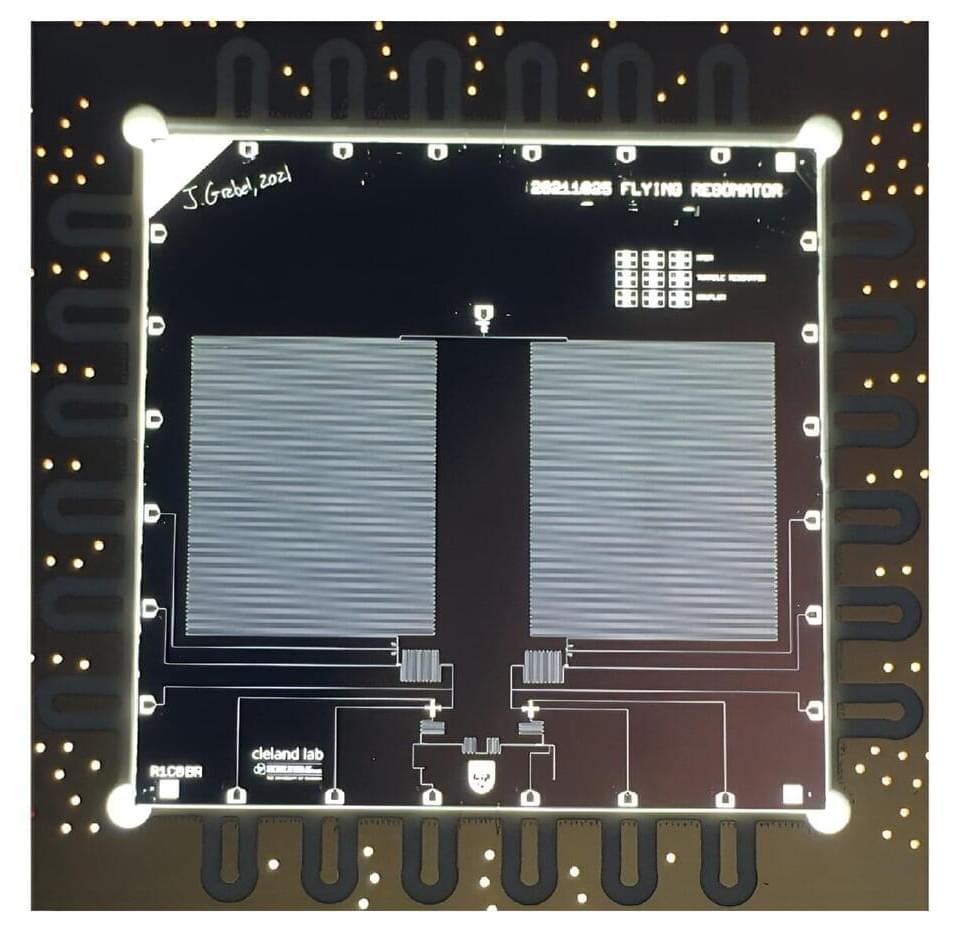
Devices that exhibit electrical resonance, have a nominally infinite number of quantum levels.
Over the past few decades, quantum physicists and engineers have been trying to develop new, reliable quantum communication systems. These systems could ultimately serve as a testbed to evaluate and advance communication protocols.
Researchers at the University of Chicago recently introduced a new quantum communication testbed with remote superconducting nodes and demonstrated bidirectional multiphoton communication on this testbed. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, could open a new route towards realizing the efficient communication of complex quantum states in superconducting circuits.
“We are developing superconducting qubits for modular quantum computing and as a quantum communication testbed,” Andrew Cleland, co-author of the paper, told Phys.org. “Both rely on being able to communicate quantum states coherently between qubit ‘nodes’ that are connected to one another with a sparse communication network, typically a single physical transmission line.”