Neuralink, led by Elon Musk, has accomplished a major feat by implanting a brain chip in a human for the first time. Discover the groundbreaking advancements in brain-computer interfaces.


To try everything Brilliant has to offer—free—for a full 30 days, visit https://brilliant.org/Inkbox. The first 200 of you will get 20% off Brilliant’s annual premium subscription.
I designed my own 16-Bit Computer in Microsoft Excel without using Visual Basic scripts, plugins, or anything other than plain Excel. This system on a spreadsheet is based off of a custom Instruction Set Architecture that has a total of 23 instruction mnemonics and 26 opcodes.
The main design of the CPU is broken into a fetch unit, control unit, arithmetic logic unit, register file, PC unit, several multiplexers, a memory control unit, a 128KB RAM table, and a 128×128 16-color display.
Try it out down below:
https://github.com/InkboxSoftware/excelCPU
This video was sponsored by Brilliant.
computer chip by MITHUN T M from Noun Project.
Memory by Alvida from Noun project.
Calculator by Uswa KDT from Noun Project.
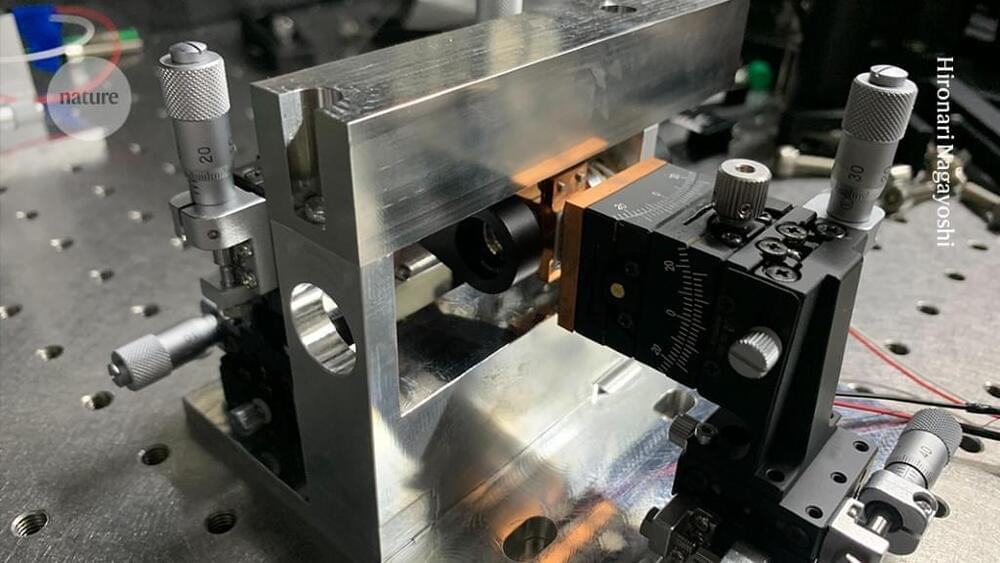
With a quick pulse of light, researchers can now find and erase errors in real time.
Researchers have developed a method that can reveal the location of errors in quantum computers, making them up to ten times easier to correct. This will significantly accelerate progress towards large-scale quantum computers capable of tackling the world’s most challenging computational problems, the researchers said.
Led by Princeton University ’s Jeff Thompson, the team demonstrated a way to identify when errors occur in quantum computers more easily than ever before. This is a new direction for research into quantum computing hardware, which more often seeks to simply lower the probability of an error occurring in the first place.

Jan 29 (Reuters) — The first human patient has received an implant from brain-chip startup Neuralink on Sunday and is recovering well, the company’s billionaire founder Elon Musk said.
“Initial results show promising neuron spike detection,” Musk said in a post on the social media platform X on Monday.
Spikes are activity by neurons, which the National Institute of Health describes as cells that use electrical and chemical signals to send information around the brain and to the body.
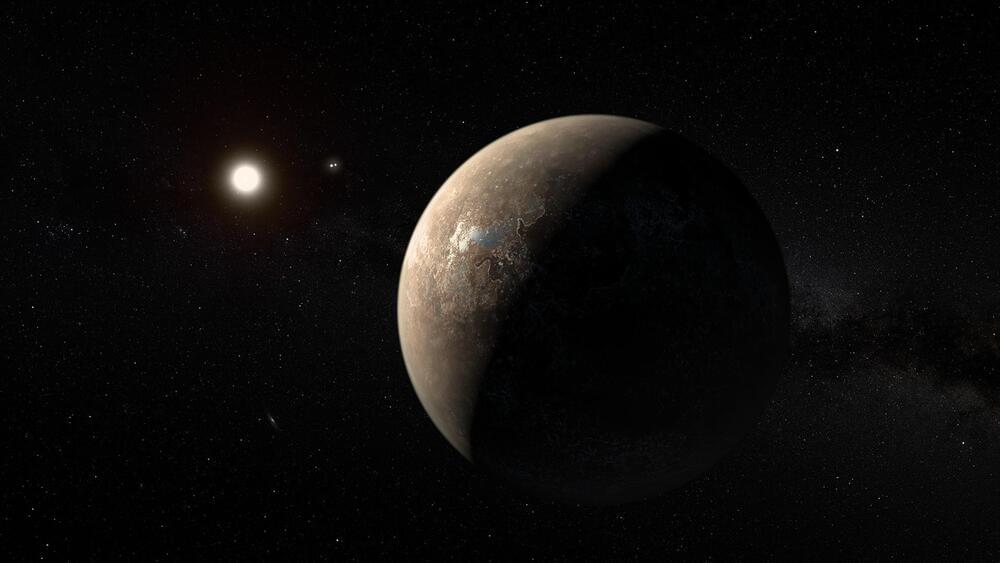


“Not every planet is suitable for direct imaging, but that’s why simulations give us a rough idea of what the ELTs [Extremely Large Telescopes] would have delivered and the promises they’re meant to hold when they are built,” said Huihao Zhang.
What aspects of an exoplanet should astronomers focus on to find signs of extraterrestrial life? Should they focus on the parent star, the exoplanet’s surface, or something else? This is what a recent study published in The Astronomical Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers from The Ohio State University (OSU) discuss how astronomers could use the next generation of telescopes, specifically the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and other Extremely Large Telescopes (ELTs), to conduct more in-depth analyses of an exoplanet’s atmosphere, specifically searching for signs of oxygen and methane, as these are present in the Earth’s atmosphere. This study holds the potential to not only establish criteria for searching for signs of extraterrestrial life, but how astronomers can search for this criterion, as well.
For the study, the researchers used computers models to simulate how an exoplanet’s atmosphere on 10 nearby rocky exoplanets could be analyzed for oxygen, water, methane, and carbon dioxide using what’s known as the direct imaging method with ELTs. The direct imaging method is where astronomers blot out the intense glare from the parent star, making exoplanets orbiting it “appear”, making them easier to identify and study. In the end, the researchers found that GJ 887 b (11 light-years away) was the most promising candidate for detecting biosignatures in its atmosphere while Proxima Centauri b (4.4 light-years away) was found to only be detectable for carbon dioxide.
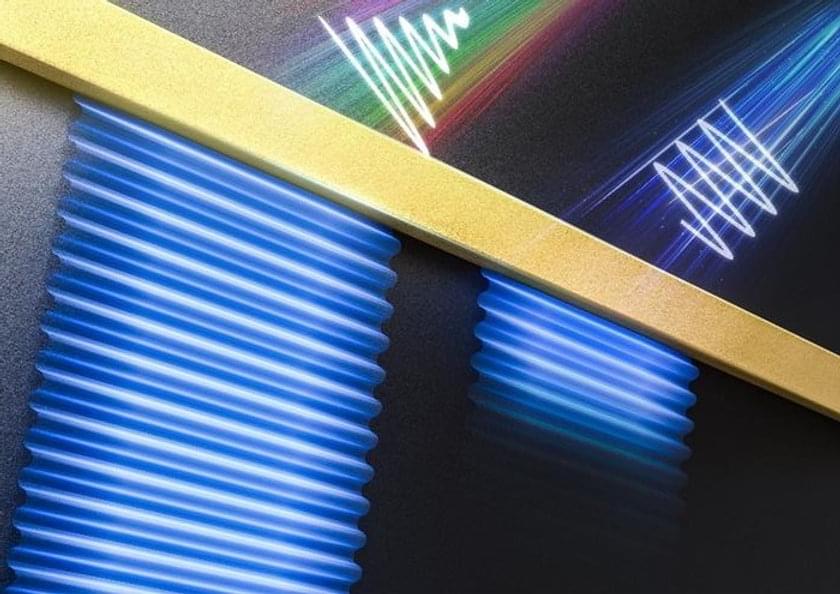
A collaborative research team co-led by Professor Shuang ZHANG, the Interim Head of the Department of Physics, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), along with Professor Qing DAI from National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, China, has introduced a solution to a prevalent issue in the realm of nanophotonics – the study of light at an extremely small scale. Their findings, recently published in the prestigious academic journal Nature Materials, propose a synthetic complex frequency wave (CFW) approach to address optical loss in polariton propagation. These findings offer practical solutions such as more efficient light-based devices for faster and more compact data storage and processing in devices such as computer chips and data storage devices, and improved accuracy in sensors, imaging techniques, and security systems.
Surface plasmon polaritons and phonon polaritons offer advantages such as efficient energy storage, local field enhancement, and high sensitivities, benefitting from their ability to confine light at small scales. However, their practical applications are hindered by the issue of ohmic loss, which causes energy dissipation when interacting with natural materials.
Over the past three decades, this limitation has impeded progress in nanophotonics for sensing, superimaging, and nanophotonic circuits. Overcoming ohmic loss would significantly enhance device performance, enabling advancement in sensing technology, high-resolution imaging, and advanced nanophotonic circuits.
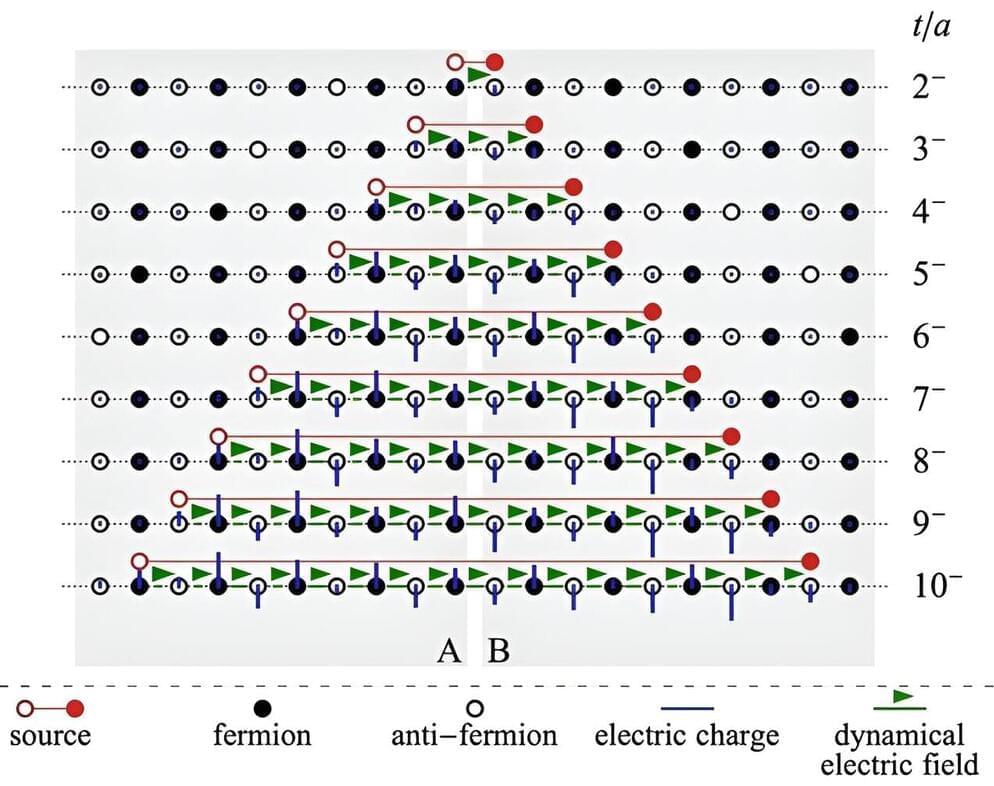
Collisions of high energy particles produce “jets” of quarks, anti-quarks, or gluons. Due to the phenomenon called confinement, scientists cannot directly detect quarks. Instead, the quarks from these collisions fragment into many secondary particles that can be detected.
Scientists recently addressed jet production using quantum simulations. They found that the propagating jets strongly modify the quantum vacuum—the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. In addition, the produced quarks retain quantum entanglement, the linkage between particles across distances. This finding, published in Physical Review Letters, means that scientists can now study this entanglement in experiments.
This research performed quantum simulations that have detected the modification of the vacuum by the propagating jets. The simulations have also revealed quantum entanglement among the jets. This entanglement can be detected in nuclear experiments. The work is also a step forward in quantum-inspired classical computing. It may result in the creation of new application-specific integrated circuits.