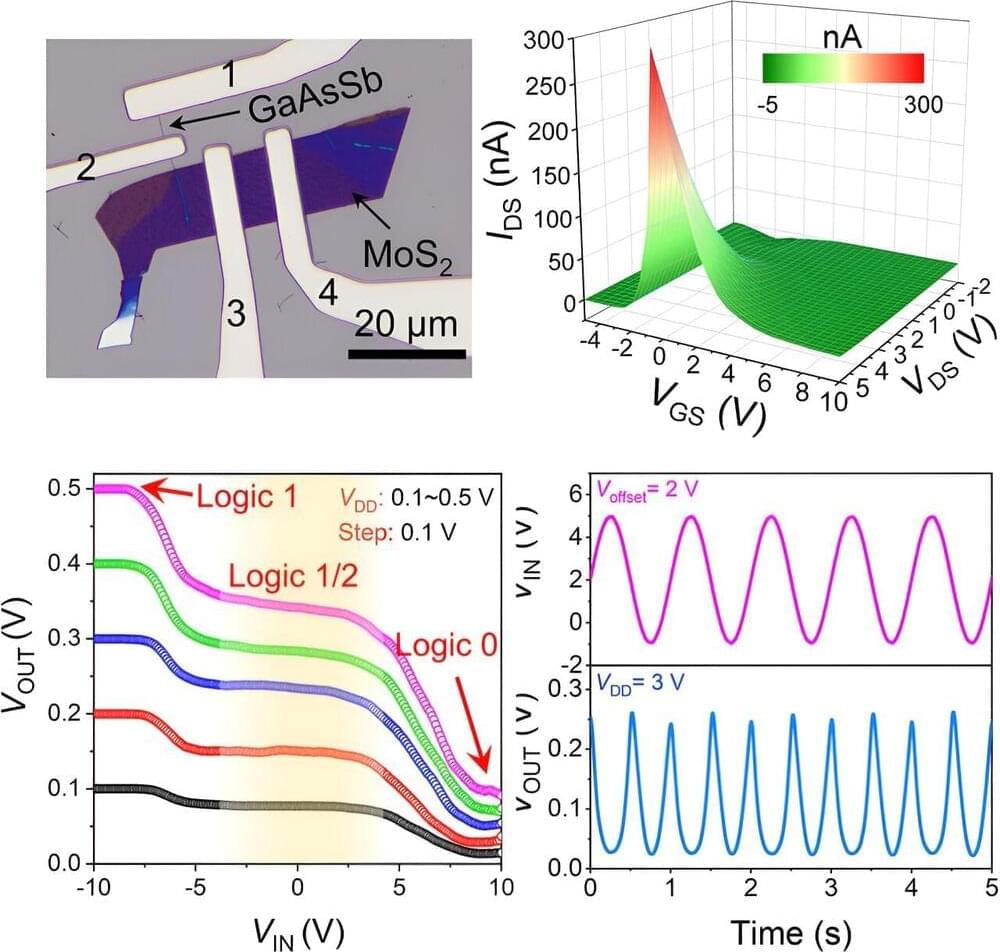
The downscaling of electronic devices, such as transistors, has reached a plateau, posing challenges for semiconductor fabrication. However, a research team led by materials scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently discovered a new strategy for developing highly versatile electronics with outstanding performance using transistors made of mixed-dimensional nanowires and nanoflakes.
This innovation paves the way for simplified chip circuit design, offering versatility and low power dissipation in future electronics. The findings, titled “Multifunctional anti-ambipolar electronics enabled by mixed-dimensional 1D GaAsSb/2D MoS2 heterotransistors,” were published in the journal Device.
In recent decades, as the continuous scaling of transistors and integrated circuits has started to reach physical and economic limits, fabricating semiconductor devices in a controllable and cost-effective manner has become challenging. Further scaling of transistor size increases current leakage and thus power dissipation. Complex wiring networks also have an adverse impact on power consumption.