Angstrom age is right around the corner – for state-of-the-art chips, anyway.



Dr. Janice Brahney: “Only recently have we started to see troubling outbreaks of toxic algal blooms in mountain environments. So, these changes are happening fast and are really concerning. It’s important we get to the bottom of this.”
What impact does atmospheric dust have on algae? This is what a recent study published in Global Change Biology hopes to address as a team of researchers from Utah State University (USU) investigated how increased dust concentrations in the Earth’s atmosphere could lead to larger algae blooms, impacting life on both land and in the oceans. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the acceptable amounts of dust and algae on the Earth and their impact on aquatic life, specifically in mountain ranges across the globe. The reason mountain headwater regions were the focus of the study was because they provide approximately 50% of the world’s population with fresh water.
“Only recently have we started to see troubling outbreaks of toxic algal blooms in mountain environments,” said Dr. Janice Brahney, who is an associate professor in the Watershed Sciences Department at USU and a co-author on the study. “So, these changes are happening fast and are really concerning. It’s important we get to the bottom of this. Toxic blooms in mountain lakes like the ones we’ve seen recently in remote mountain lakes are unprecedented.”
For the study, the researchers compared algae blooms and supplemented this with computer models to ascertain how atmospheric dust raining down onto the planet could impact aquatic communities, specifically with mountainous regions across the globe. In the end, the researchers found that increased atmospheric dust deposits not only increase algae populations, but also increase their tolerances for increased temperatures and pH, which are considered significant climate change factors.


Researchers at the University of California, Irvine and Los Alamos National Laboratory, publishing in the latest issue of Nature Communications, describe the discovery of a new method that transforms everyday materials like glass into materials scientists can use to make quantum computers.
“The materials we made are substances that exhibit unique electrical or quantum properties because of their specific atomic shapes or structures,” said Luis A. Jauregui, professor of physics & astronomy at UCI and lead author of the new paper. “Imagine if we could transform glass, typically considered an insulating material, and convert it into efficient conductors akin to copper. That’s what we’ve done.”
Conventional computers use silicon as a conductor, but silicon has limits. Quantum computers stand to help bypass these limits, and methods like those described in the new study will help quantum computers become an everyday reality.
Apple’s latest gadget, the Apple Vision Pro, is a mixed-reality headset that promises to immerse users in a new dimension of spatial computing. But what makes this device so special, and how does it work?
To find out, the folks at iFixit did what they do best: they took it apart. In their usual fashion, they documented the process in a video and an article, giving us a glimpse of the inner workings of Apple’s most advanced hardware ever.
The teardown was challenging, as the Apple Vision Pro is complex and delicate. It took a lot of heat, tools, and patience to pry open the front glass, which revealed a maze of wires, sensors, and displays.
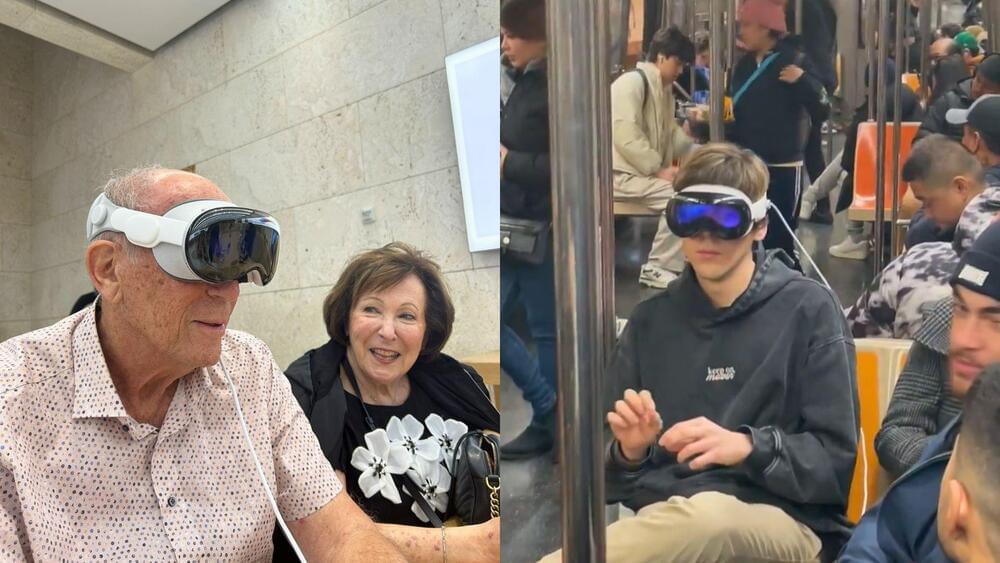

Apple has always been known for its innovative products, but its latest creation might be its most ambitious. The Apple Vision Pro is a headset that promises to revolutionize how we interact with technology by seamlessly blending the digital and physical worlds.
The device, which costs a whopping $3,500, has already hit the stores and attracted much attention. Some people are eager to try out the new possibilities of spatial computing, while others are mocking the sight of people wearing the bulky and futuristic-looking gadget.
One of the first to test the Apple Vision Pro in the real world was Casey Neistat, a popular social media personality and filmmaker. In a video posted on Saturday, he showed how he used the device in its passthrough mode, allowing him to see his surroundings through cameras and screens while accessing various virtual features.

Scientists outline new processes for leveraging hafnia’s ferroelectric features with the aim of enhancing high-performance computing.
Scientists and engineers have been pushing for the past decade to leverage an elusive ferroelectric material called hafnium oxide, or hafnia, to usher in the next generation of computing memory. A team of researchers including the University of Rochester’s Sobhit Singh published a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study outlining progress toward making bulk ferroelectric and antiferroelectric hafnia available for use in a variety of applications.
In a specific crystal phase, hafnia exhibits ferroelectric properties—that is, electric polarization that can be changed in one direction or another by applying an external electric field. This feature can be harnessed in data storage technology. When used in computing, ferroelectric memory has the benefit of non-volatility, meaning it retains its values even when powered off, one of several advantages over most types of memory used today.
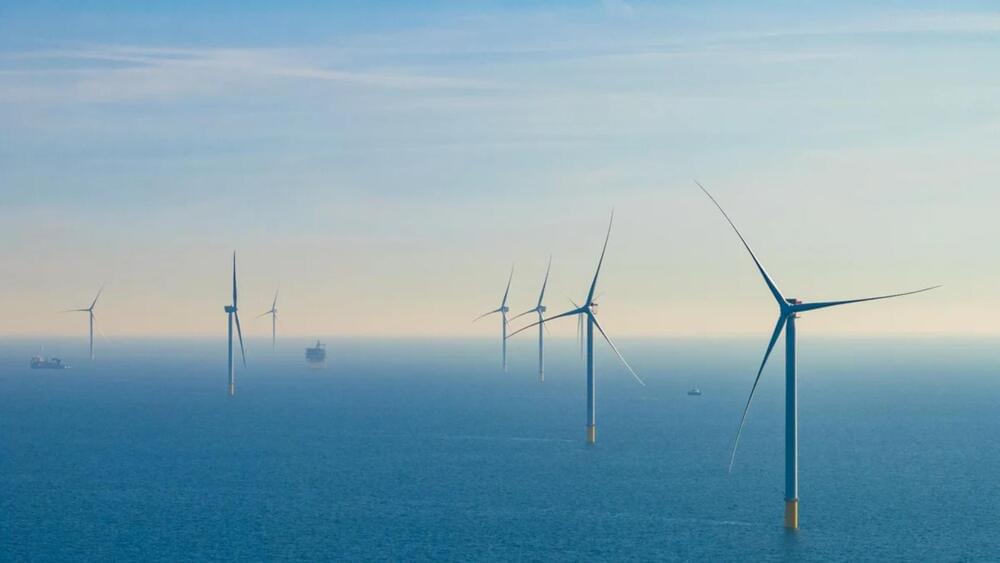

The mega tech company’s ambition is to operate on carbon-free energy by 2030.
In its most substantial offshore wind project deal to date, Google has signed power purchase agreements (PPAs) for over 700 megawatts of clean energy to power its European data centers.
The company’s announcement is in line with its ambitious goal to achieve net-zero emissions across all of its operations and value chain by 2030, as per Google’s Environmental Report published last year.
Deals across Italy, Poland, Belgium and Netherlands
In the Netherlands, the search engine behemoth will get electricity from two projects — Hollandse Kust North V and West VI — off the coast, which is expected to provide about six percent of the country’s electricity consumption.