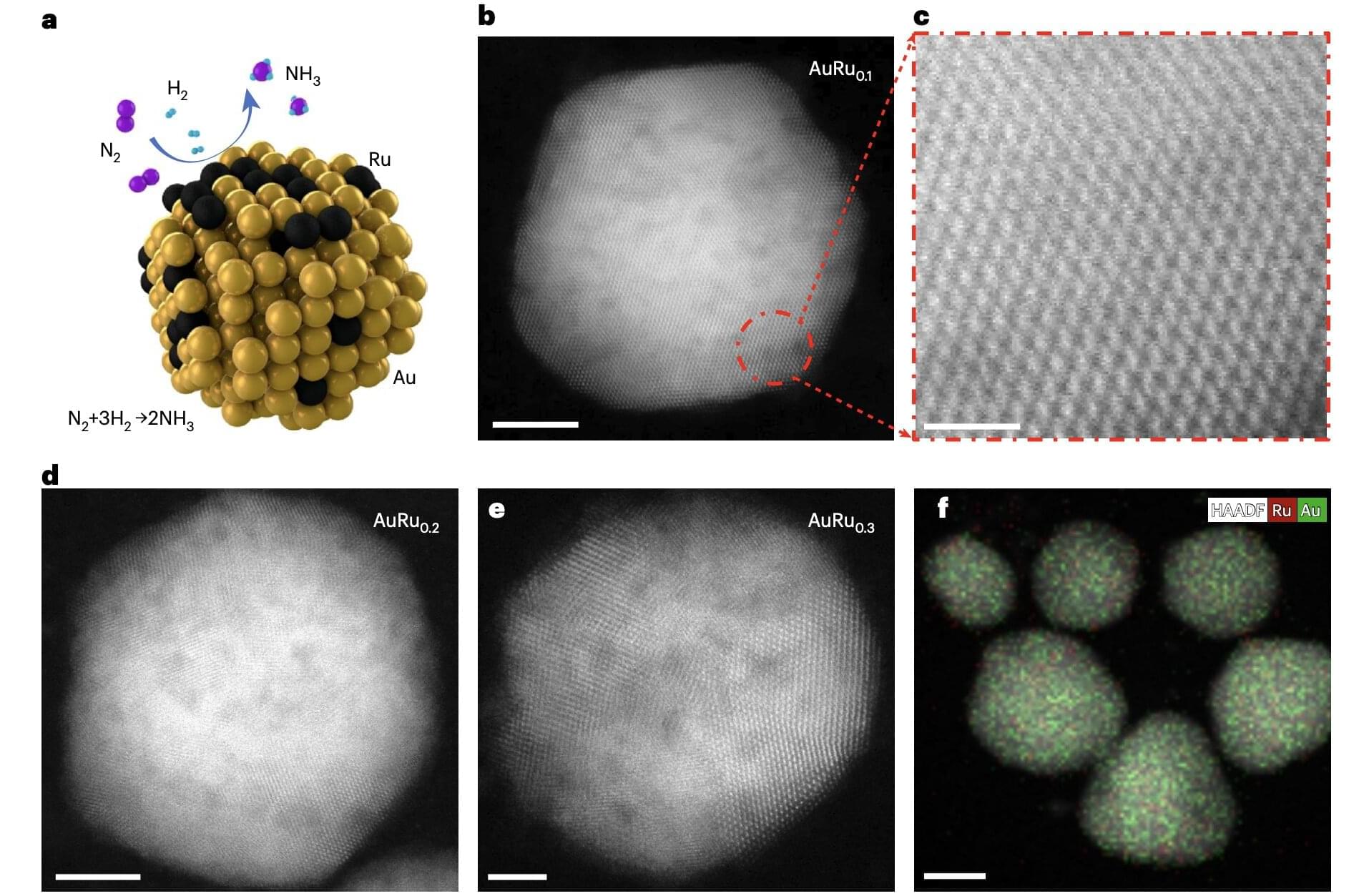
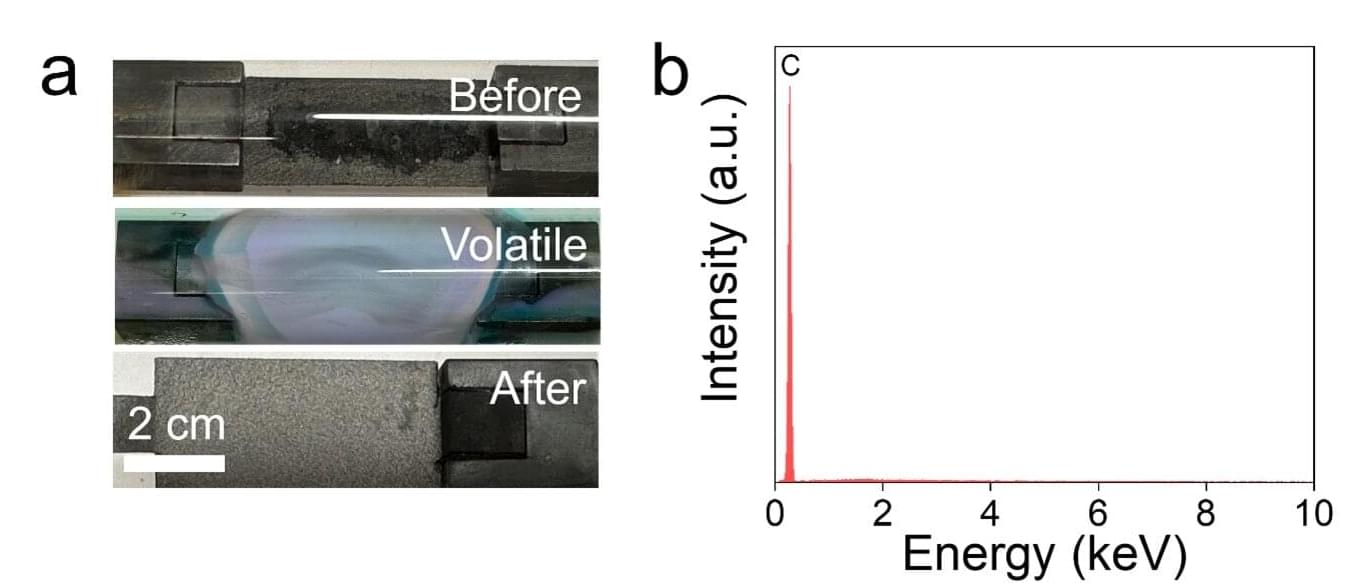
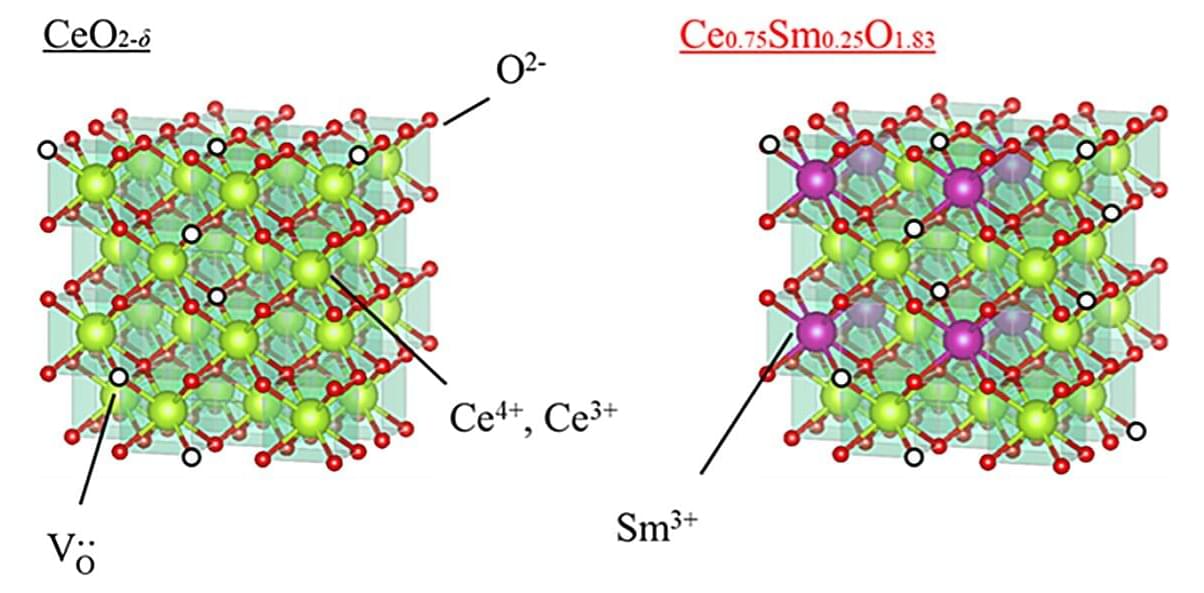
The road to a more sustainable planet may be partially paved with manganese. According to a new study by researchers at Yale and the University of Missouri, chemical catalysts containing manganese—an abundant, inexpensive metallic element—proved highly effective in converting carbon dioxide into formate, a compound viewed as a potential key contributor of hydrogen for the next generation of fuel cells.
The new study appears in the journal Chem. The lead authors are Yale postdoctoral researcher Justin Wedal and Missouri graduate research assistant Kyler Virtue; the senior authors are professors Nilay Hazari of Yale and Wesley Bernskoetter of Missouri.