A large, decades-long population study suggests that the relationship between diet and dementia may hinge on subtle chemical differences in everyday foods and water.

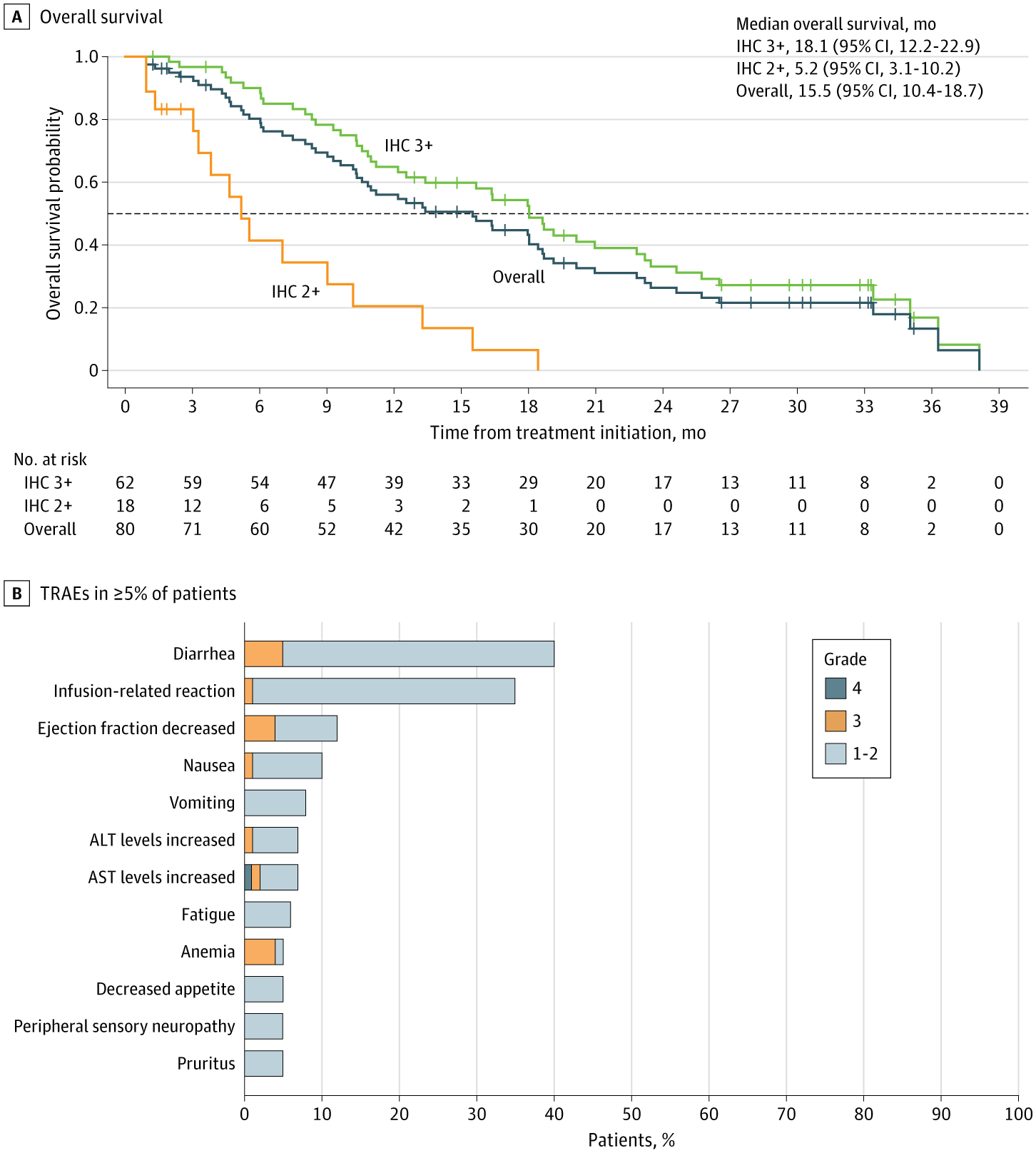
Among adults with treatment-refractory, HER2-positive BiliaryTractCancer, zanidatamab produced sustained, meaningful clinical responses and extended survival compared to prior standards.
In patients with immunohistochemistry (IHC) 3+ tumors, response rates and overall survival were notably higher than those with IHC 2+ tumors, substantiating the use of reflex IHC testing to identify candidates for HER2-targeted therapy.
Safety remained consistent over 33 months of follow-up, and the ongoing HERIZON-BTC-302 phase 3 trial is assessing zanidatamab alongside first-line standard care in this setting.
This follow-up analysis of the phase 2 HERIZON-BTC-01 trial evaluates the efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and safety profile of zanidatamab in patients with ERBB2-amplified biliary tract cancer with a HER2 immunohistochemistry score of 3+ or 2+ after 33 months of follow-up.

Read “” by Myk Eff on Medium.
When a patient in a clinical trial experiences genuine pain relief from an inert sugar pill, something remarkable occurs that contemporary medicine awkwardly labels the placebo effect — a term that simultaneously acknowledges the phenomenon while dismissing it as mere illusion. Yet what if this dismissal represents not scientific rigor but ontological timidity? What if the placebo effect, rather than being a confounding variable to be controlled away, is actually nature’s clearest demonstration of a quantum interface between consciousness and physiology, hiding in plain sight within the very architecture of our clinical trials? The question is not whether belief heals, but what belief actually is when we take seriously the contemporary understanding that information itself possesses physical reality.
The empirical robustness of placebo effects has become impossible to ignore. In their comprehensive meta-analysis published in The Lancet, Hróbjartsson and Gøtzsche (2001) examined 114 clinical trials and found that while placebo effects vary considerably across conditions, they demonstrate genuine clinical significance in pain reduction, with effect sizes rivaling those of established pharmaceutical interventions. More provocatively, Benedetti’s research on placebo analgesia has revealed that the effect operates through identifiable neurochemical pathways — placebo-induced pain relief can be blocked by naloxone, an opioid antagonist, demonstrating that the patient’s belief literally triggers the release of endogenous opioids (Benedetti, Mayberg, Wager, Stohler, & Zubieta, 2005). This is not imagination overriding reality; this is imagination as a physical force, translating expectation into molecular cascade.
Yet the standard neurobiological explanation, while accurate, remains curiously incomplete. Yes, belief activates specific neural circuits; yes, these circuits trigger biochemical responses; yes, measurable physiological changes occur. But this mechanistic account merely pushes the mystery one level deeper. How does the abstract informational content of a belief — the semantic meaning this pill will relieve my pain — couple to the physical substrate of neurons and neurotransmitters? The conventional answer invokes learning, conditioning, and expectation, but these terms describe the phenomenon without explaining the fundamental ontological transition from meaning to matter, from information to effect.
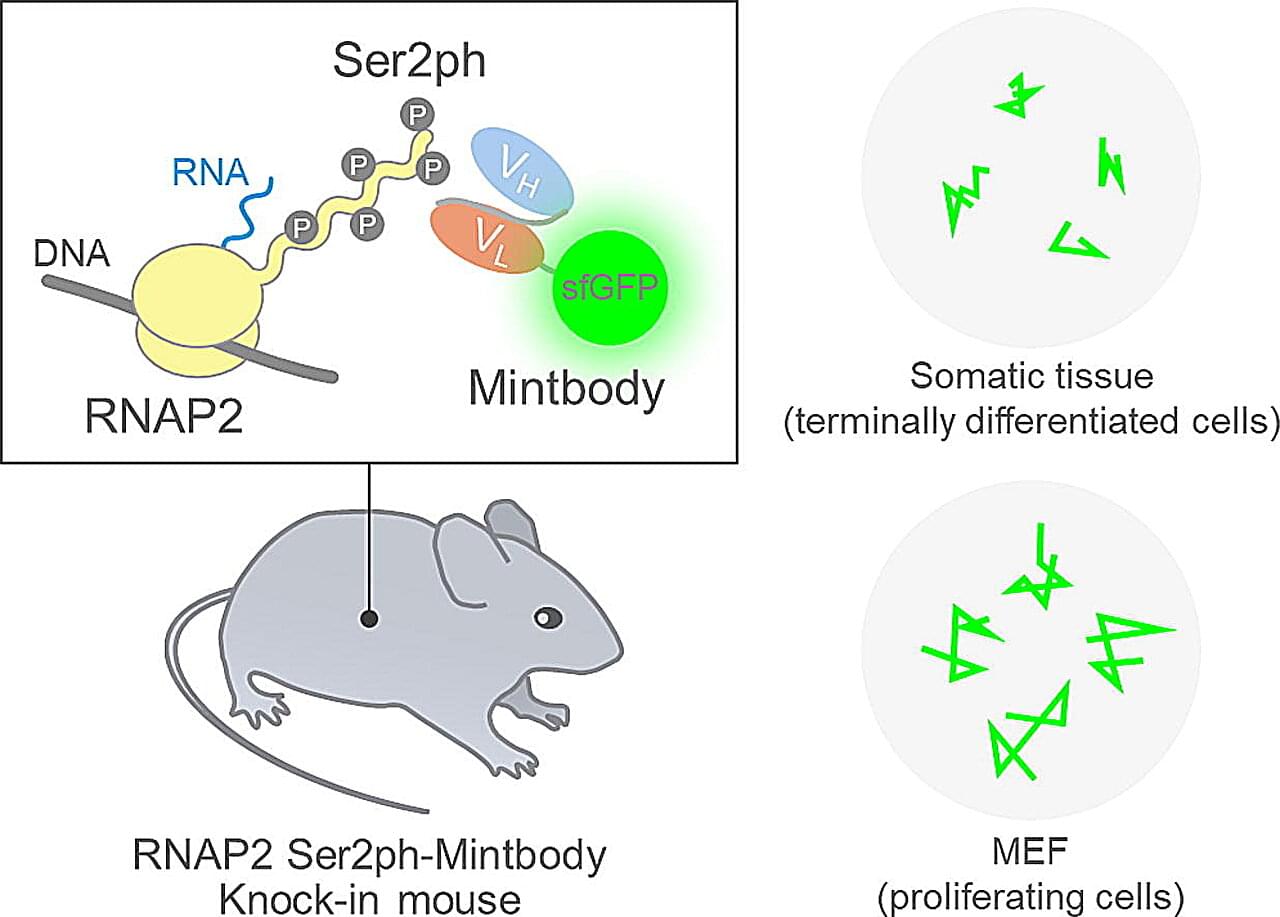
DNA can be thought of as a vast library that stores all genetic information. Cells do not use this information all at once. Instead, they copy only the necessary parts into RNA, which is then used to produce proteins—the essential building blocks of life. This copying process is called transcription, and it is carried out by a molecule known as RNA polymerase II.
When RNA polymerase II begins actively transcribing DNA, a specific site called Ser2 on its tail region is marked with a small chemical group known as a phosphate. This phosphate acts as a sign that transcription is in progress. Until now, observing this sign required stopping cellular activity and chemically treating the cells to visualize the phosphate. As a result, it was impossible to see how transcription changes dynamically in living cells.
To overcome this limitation, a research team led by Professor Hiroshi Kimura at Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) chose a different approach. Instead of freezing cells at a single moment, they aimed to track transcription continuously without stopping cellular activity.
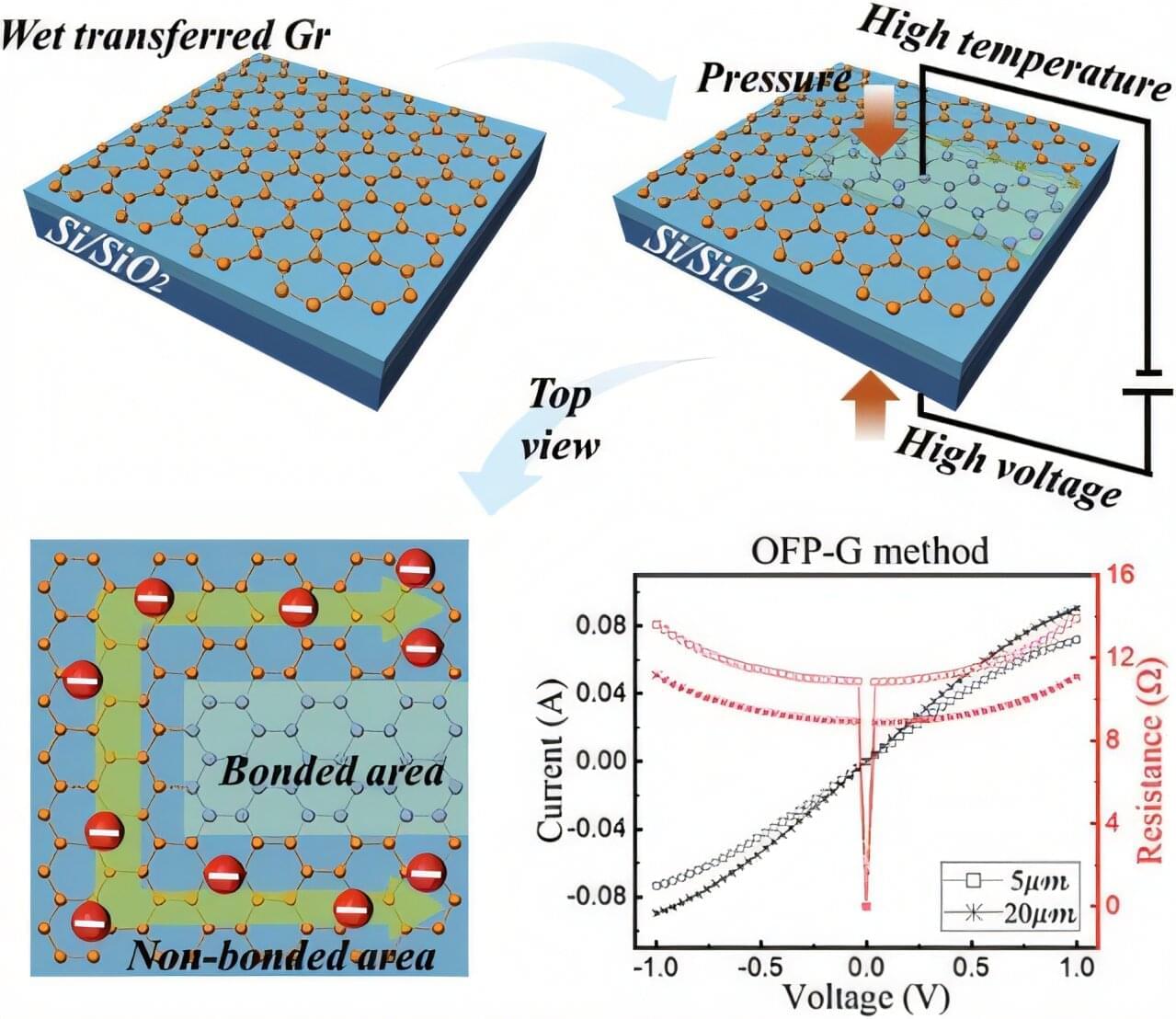
Transparent electrodes transmit light while conducting electricity and are increasingly important in bioelectronic and optoelectronic devices. Their combination of high optical transparency, low electrical resistance, and mechanical flexibility makes them well suited for applications such as displays, solar cells, and wearable or implantable technologies.
In a significant advancement, researchers led by Professor Wonsuk Jung at Chungnam National University in the Republic of Korea have introduced a new fabrication technique called one-step free patterning of graphene, or OFP-G, which enables high-resolution patterning of large-area monolayer graphene with feature sizes smaller than 5 micrometers, without the use of photoresists or chemical etching.
Published Microsystems & Nanoengineering, the method addresses a key limitation of conventional microelectrode fabrication, where lithographic processes often damage graphene and degrade its electrical performance.
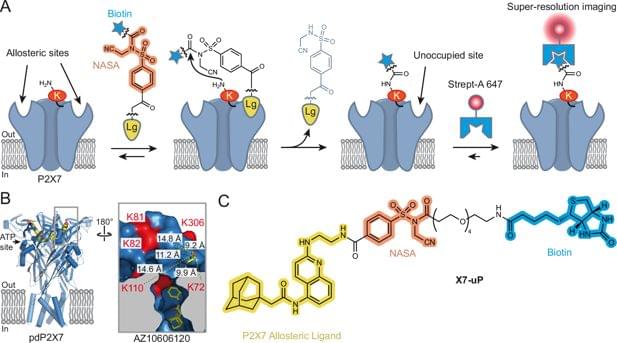
A new chemical labelling tool lets researchers watch the inflammatory receptor P2X7 reorganise and cluster on immune cells at the nanoscale, revealing how inflammatory signals reshape receptor behaviour in real time.
An affinity-guided chemical strategy enabling highly specific biotinylation of P2X7 receptors reveals, by super-resolution microscopy, how the nanoscale organization of endogenous P2X7 in BV2 microglial cells dynamically changes upon activation.
Newlypublished by gennady verkhivker, et al.
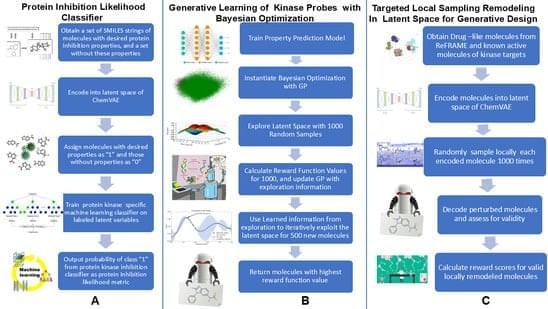
🔍 Key findings: Novel generative framework integrates ChemVAE-based latent space modeling with chemically interpretable structural similarity metric (Kinase Likelihood Score) and Bayesian optimization for SRC kinase ligand design, demonstrating kinase scaffolds spanning 37 protein kinase families spontaneously organize into low-dimensional manifold with chemically distinct carboxyl groups revealing degeneracy in scaffold encoding — local sampling successfully converts scaffolds from other kinase families into novel SRC-like chemotypes accounting for ~40% of high-similarity cutoffs.
Read now ➡️
Scaffold-aware artificial intelligence (AI) models enable systematic exploration of chemical space conditioned on protein-interacting ligands, yet the representational principles governing their behavior remain poorly understood. The computational representation of structurally complex kinase small molecules remains a formidable challenge due to the high conservation of ATP active site architecture across the kinome and the topological complexity of structural scaffolds in current generative AI frameworks. In this study, we present a diagnostic, modular and chemistry-first generative framework for design of targeted SRC kinase ligands by integrating ChemVAE-based latent space modeling, a chemically interpretable structural similarity metric (Kinase Likelihood Score), Bayesian optimization, and cluster-guided local neighborhood sampling.
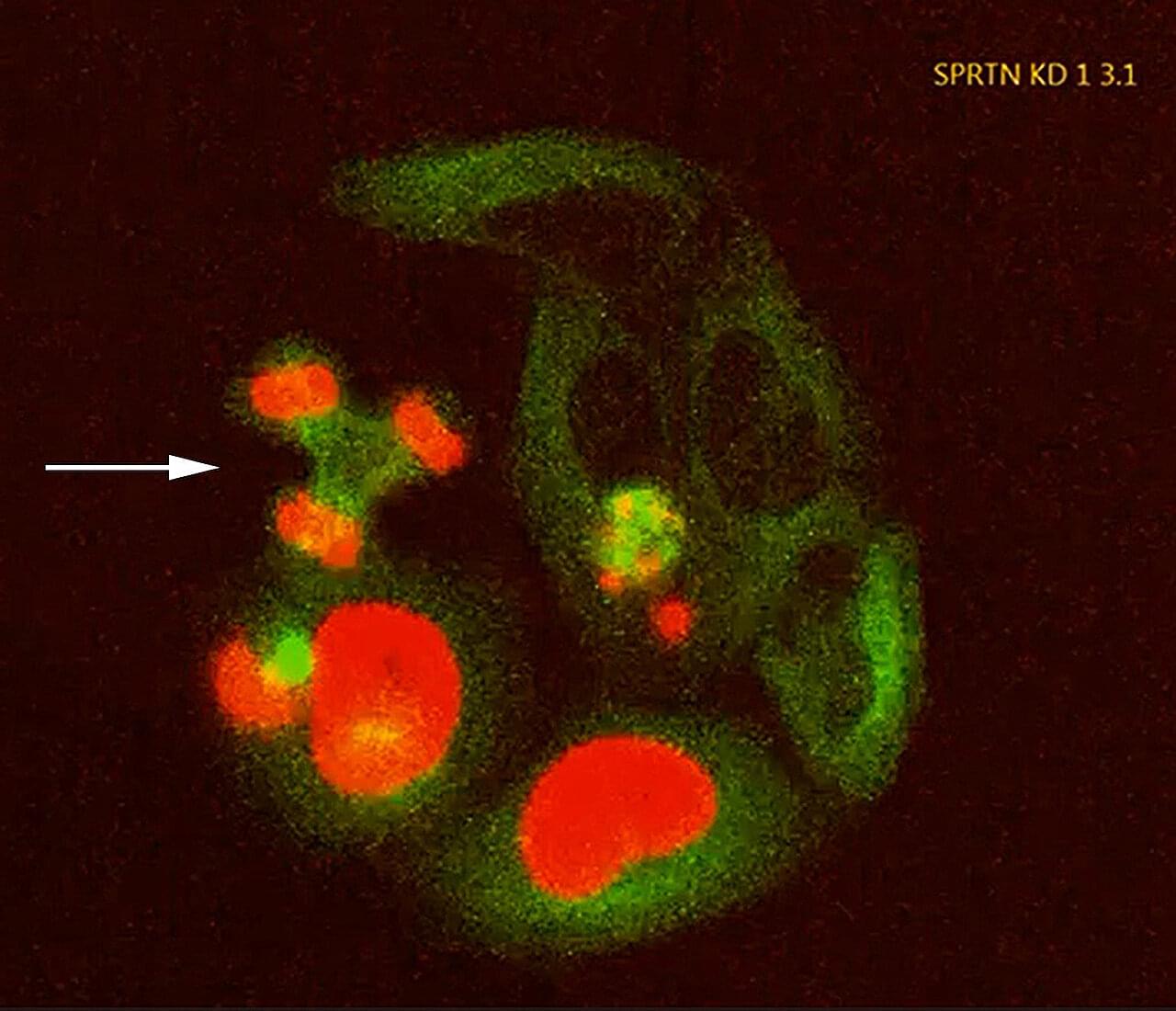
Although DNA is tightly packed and protected within the cell nucleus, it is constantly threatened by damage from normal metabolic processes or external stressors such as radiation or chemical substances. To counteract this, cells rely on an elaborate network of repair mechanisms. When these systems fail, DNA damage can accumulate, impair cellular function, and contribute to cancer, aging, and degenerative diseases.
One particularly severe form of DNA damage are the so-called DNA–protein crosslinks (DPCs), in which proteins become attached to DNA. DPCs can arise from alcohol consumption, exposure to substances such as formaldehyde or other aldehydes, or from errors made by enzymes involved in DNA replication and repair. Because DPCs can cause serious errors during cell division by stalling DNA replication, DNA–protein crosslinks pose a serious threat to genome integrity.
The enzyme SPRTN removes DPCs by cleaving the DNA-protein crosslinks. SPRTN malfunctions, for example as a result of mutations, may predispose individuals to developing bone deformities and liver cancer in their teenage years. This rare genetic disorder is known as Ruijs-Aalfs syndrome. Its underlying mechanism remains poorly understood, and there are no specific therapies.

Researchers are continually looking for new ways to hack the cellular machinery of microbes like yeast and bacteria to make products that are useful for humans and society. In a new proof-of-concept study, a team from the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology showed they can expand the biosynthetic capabilities of these microbes by using light to help access new types of chemical transformations.
The paper, published in Nature Catalysis, demonstrates how the bacteria Escherichia coli can be engineered to produce these new molecules in vivo, using light-driven enzymatic reactions. This framework sets the foundation for future development in the emerging field of photobiocatalysis.
“Photobiocatalysis is basically light-activated catalysis by enzymes. Without light, the target enzyme cannot catalyze a reaction. When light is added, the target enzyme will be activated,” said Huimin Zhao (BSD leader/CAMBERS/CGD/MMG), Steven L. Miller Chair of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. “We have published many papers showing that it is possible to combine photocatalysis with enzyme catalysis to create a new class of photoenzymes. These artificial photoenzymes can catalyze selective reactions that cannot be achieved by natural enzymes and are also very difficult, or sometimes even not possible, with chemical catalysis.”
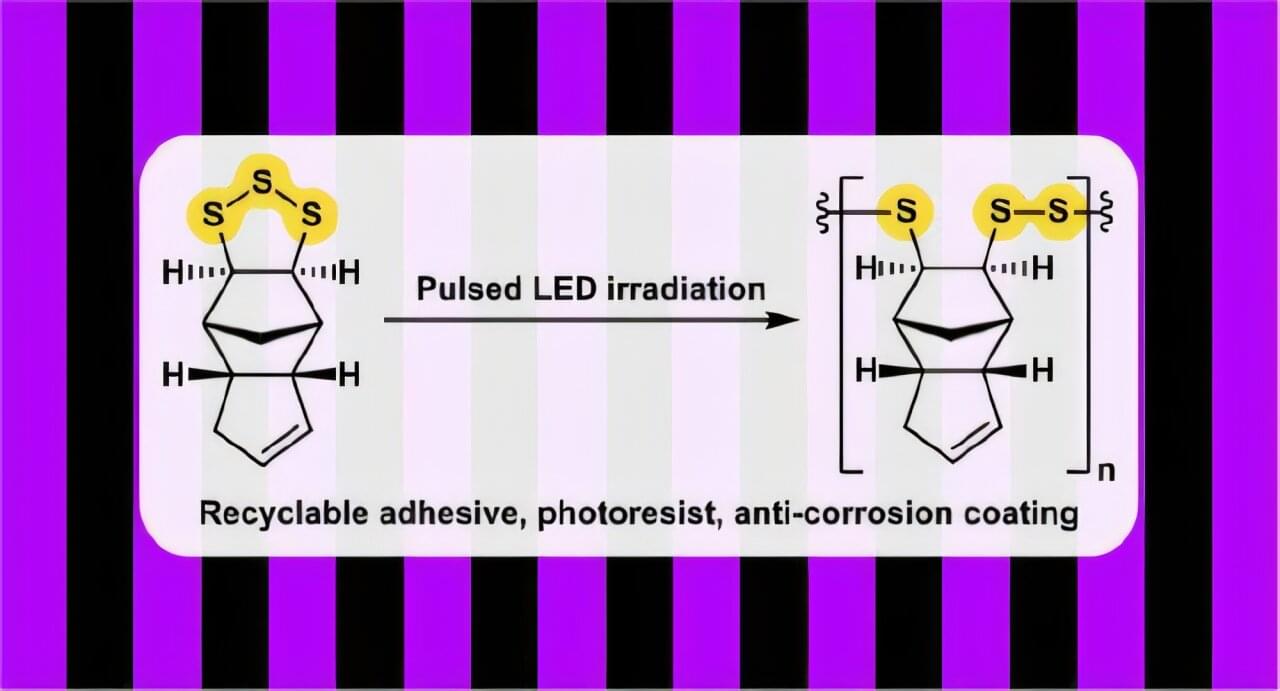
For the first time, scientists have used ultraviolet (UV) light, a low-cost and readily available energy source, to successfully synthesize more sustainable and recyclable polymer materials. Led by green chemistry experts at Flinders University, the development is a major step in making polymers high in sulfur content for more sustainable plastic alternatives using waste materials.
Their paper, “Making and Unmaking Poly(trisulfides) with Light: Precise Regulation of Radical Concentrations via Pulsed LED Irradiation” is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.