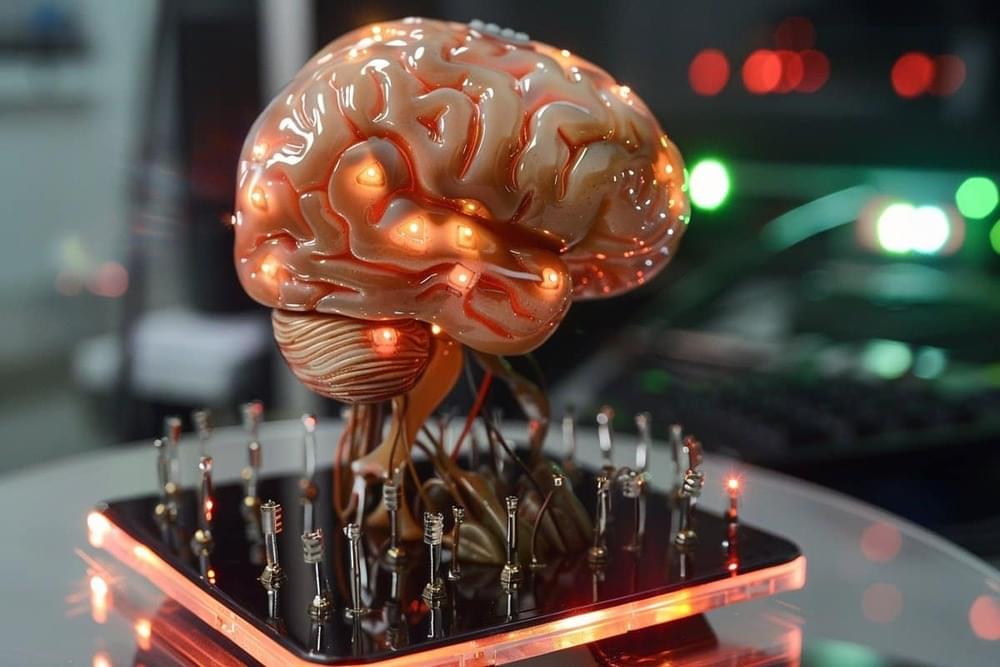
Summary: Researchers developed a groundbreaking pea-sized brain stimulator, the Digitally Programmable Over-brain Therapeutic (DOT), capable of wireless operation through magnetoelectric power transfer. This implantable device promises to revolutionize treatment for neurological and psychiatric disorders by enabling less invasive and more autonomous therapeutic options compared to traditional neurostimulation methods.
The DOT’s ability to stimulate the brain through the dura without implanted batteries represents a significant advancement in medical technology, offering potential treatments for conditions like drug-resistant depression directly from the comfort of one’s home. This innovation could change the landscape of how brain-related disorders are managed, emphasizing patient comfort and control.