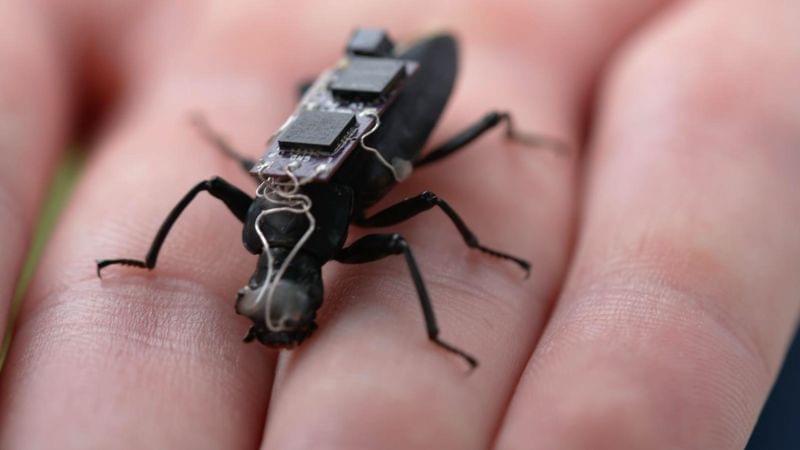
Fitzgerald says cyborg search and rescue beetles or cockroaches might be able to help in disaster situations by finding and reporting the location of survivors and delivering lifesaving drugs to them before human rescuers can get there.
But first, the Australian researchers must master the ability to direct the movements of the insects, which could take a while. Fitzgerald says that although the work might seem futuristic now, in a few decades, cyborg insects could be saving lives.
He’s not the only roboticist creating robots from living organisms. Academics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), for example, are implanting electronic pacemakers into jellyfish to control their swimming speed. They hope the bionic jellies could help collect data about the ocean far below the surface.