Unlocking Real-Time Inflammation Monitoring with Active-Reset Protein Sensors.
Imagine a tiny device that could continuously monitor your body’s inflammation levels, offering insights in real time to help manage diseases. While sensors for small molecules like glucose have existed for years, tracking proteins—a critical component in understanding inflammation—has been a major challenge. Proteins are present at much lower levels in the body, and traditional sensors struggle with slow response times due to their high-affinity binding to these molecules.
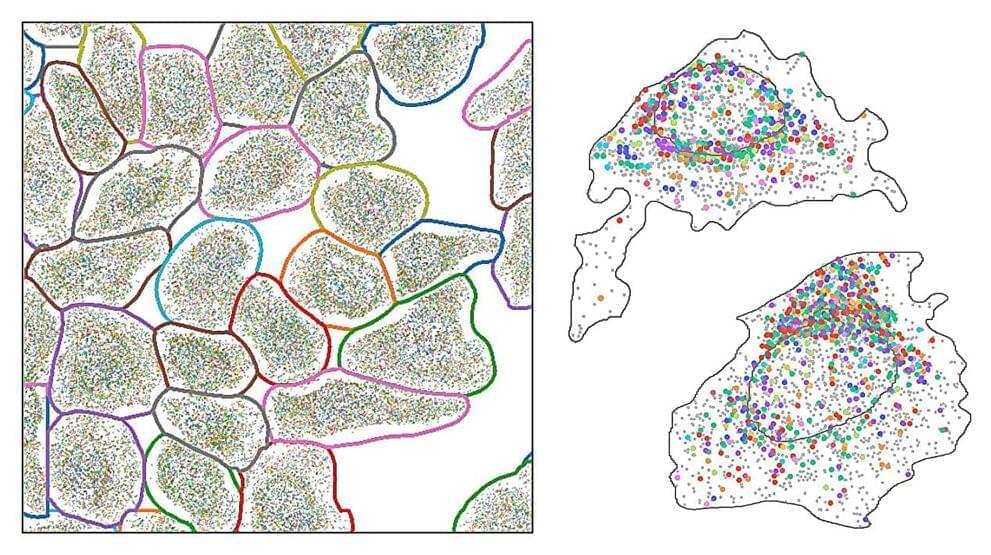
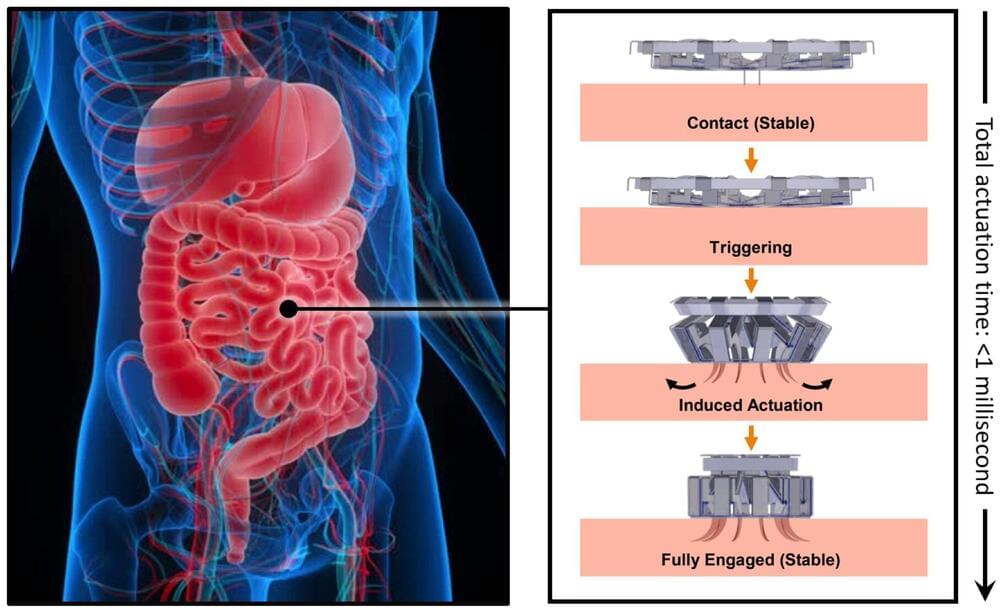
A team led by Zargartalebi has now overcome this barrier by introducing active-reset protein sensors. These sensors employ high-frequency oscillations of positive voltage to rapidly release bound protein molecules from their sensing electrodes. This breakthrough allows the sensors to reset in under a minute, enabling continuous tracking of protein levels.
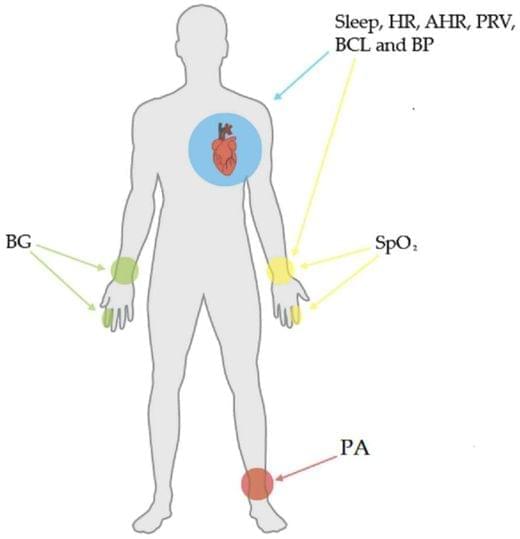
The researchers incorporated these sensors into a microneedle device, which was successfully tested in mice to monitor cytokines—key markers of inflammation associated with diabetes. Unlike previous approaches, this method is not only simple to implement but can also be adapted to various sensor designs, potentially revolutionizing how we monitor and respond to conditions like chronic inflammation.
By bringing real-time protein monitoring closer to reality, active-reset sensors could pave the way for more dynamic and responsive healthcare, ensuring better disease management and prevention.
[#biosensors](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/biosensors?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#invivo](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/invivo?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#sensing](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/sensing?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#inflammation](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/inflammation?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#Microneedle](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/microneedle?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R)
[#regenerativesensors](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/regenerativesensors?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#pointofcare](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/pointofcare?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#diagnostics](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/diagnostics?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R) [#cytokines](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/cytokines?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXpWTjqoXcElrcVMft-YBHF33SrUIfWG14SxebDv6jc7ayB9obklbDJ5BXDEcXMFhRK4gARwyDe24ko0Pjq0q5uSGpyaiia1YlxceB88HQ4AkLMRRKBaP_TJR0TQWWUQlYvZFrxBhxODGJhyWYo_RjJbdkcNE9A_kXuT2XJxXfpKD1LGhewSjGBaGndlInALDM&__tn__=*NK-R)