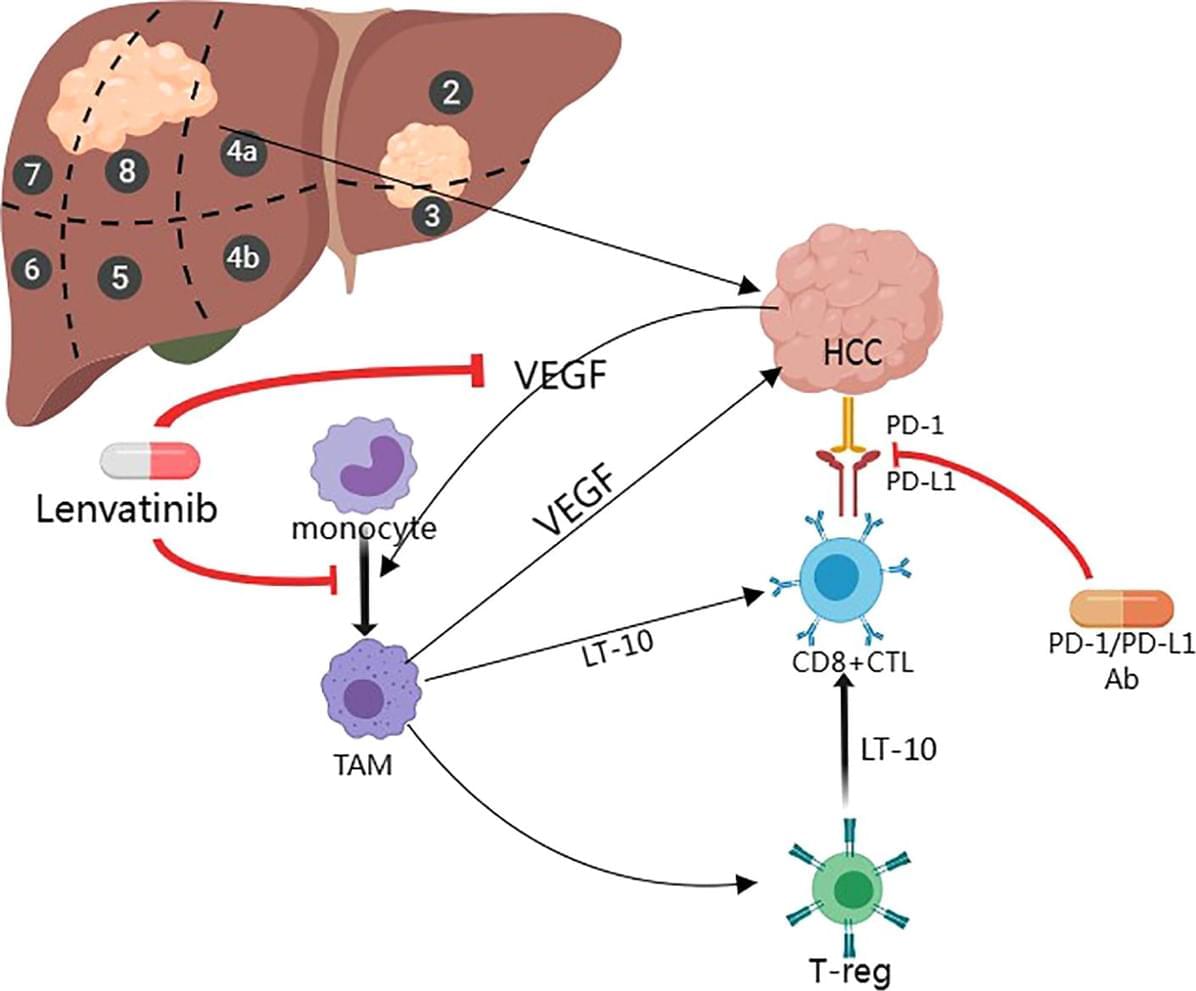
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer, affecting millions of people worldwide. Due to the complexity and variability of the disease, there are major challenges in the treatment of HCC in its intermediate and advanced stages; despite advances in various treatment modalities, there are still gaps in our understanding of effective therapeutic strategies. Key findings from several studies have shown that the combination of immunotherapy and targeted therapy has a synergistic anti-tumor effect, which can significantly enhance efficacy with a favorable safety profile. In addition, other studies have identified potential biomarkers of therapeutic response, such as tumor protein 53 (TP53) and CTNNB1 (encoding β-conjugated proteins), thus providing personalized treatment options for patients with intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. The aim of this article is to review the recent advances in the treatment of intermediate and advanced HCC, especially targeted immune-combination therapy, chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy (CAR-T cell therapy), and gene therapy for these therapeutic options that fill in the gaps in our knowledge of effective treatment strategies, providing important insights for further research and clinical practice.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignant tumor, ranking sixth and fifth in incidence globally and in China, respectively. It ranks among the top three in mortality and has long been recognized as a global challenge. HCC is the most common type of liver cancer, accounting for 75% to 80% of cases. Its incidence and mortality vary significantly across regions, which is closely related to risk factors such as viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis B and C), alcoholic and non-alcoholic cirrhosis, and fatty liver. Treatment options for HCC include surgical resection, percutaneous anhydrous ethanol injection, Transcatheter arterial embolization (TACE), ablative therapy, chemotherapy and liver transplantation. Early stage HCC can be completely cured by surgery, but about 70% of patients have progressed to an intermediate and advanced stage at the time of diagnosis and are unable to undergo surgery.