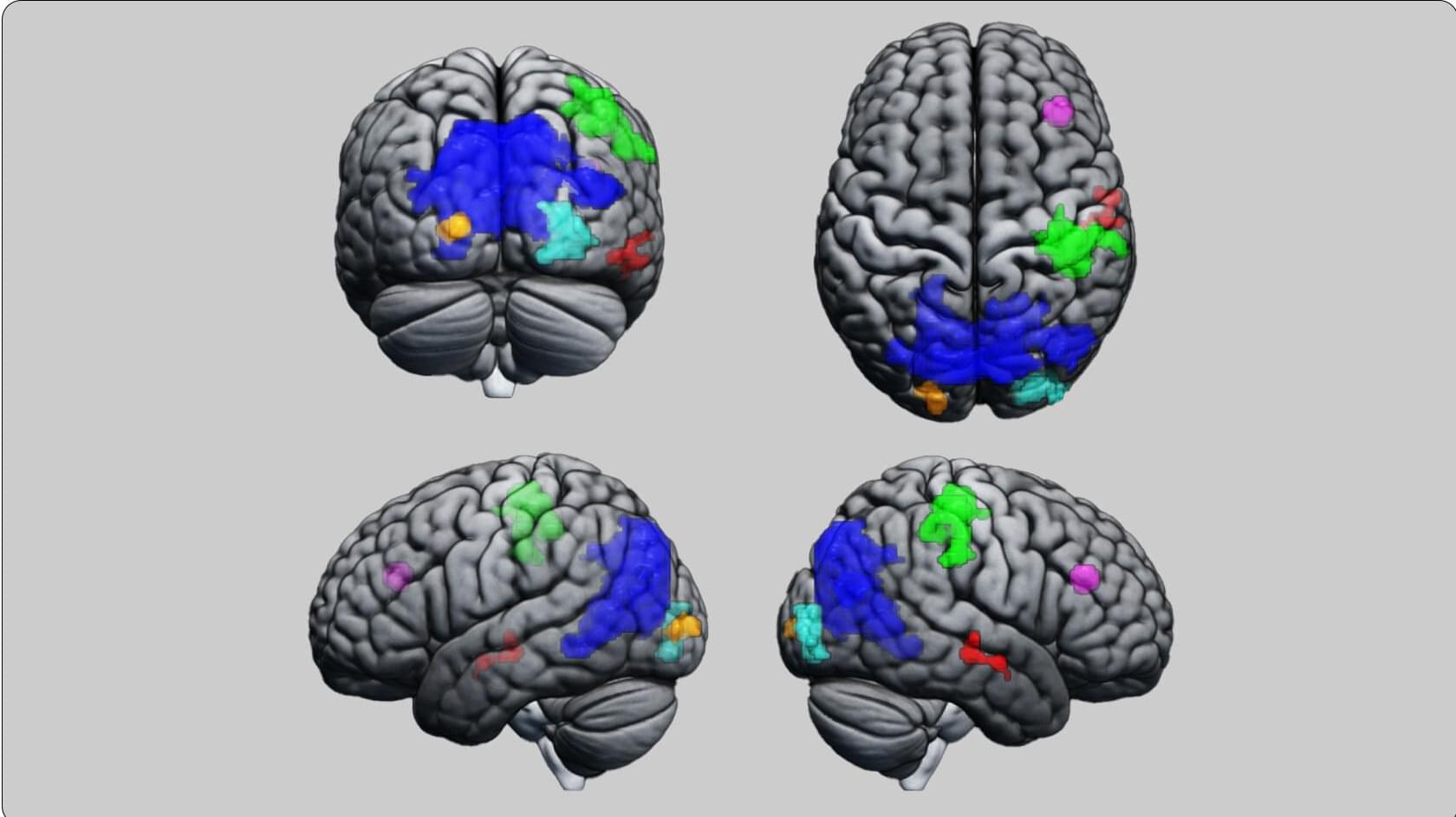
An international team of physicists has successfully measured the size of a certain type of neutrino to a certain degree. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes experiments they conducted that involved measuring the radioactive decay of the element beryllium.
Neutrinos are subatomic particles with a mass very close to zero. They also have a half-integral spin and rarely react with normal matter. To date, three kinds of neutrinos have been identified, each by association with an electron, muon or tau particle. Physicists have become more interested in neutrinos over the past several years because it is thought better understanding them may lead to a better understanding of why there is more matter than antimatter in the known universe.
One of the first questions that needs to be answered about neutrinos is their size. This is important because it allows building the right size and shape of neutrino detectors. Currently, they are very large, which allows for what is believed to be their largest possible theoretical size—several meters—though it is believed they are smaller. In this new effort, the research team conducted experiments with beryllium to measure the size of an electron-associated neutrino.