A new study led by a pair of researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst turns long-held conventional wisdom about a certain type of polymer on its head, greatly expanding understanding of how some of biochemistry’s fundamental forces work. The study, released recently in Nature Communications, opens the door for new biomedical research running the gamut from analyzing and identifying proteins and carbohydrates to drug delivery.
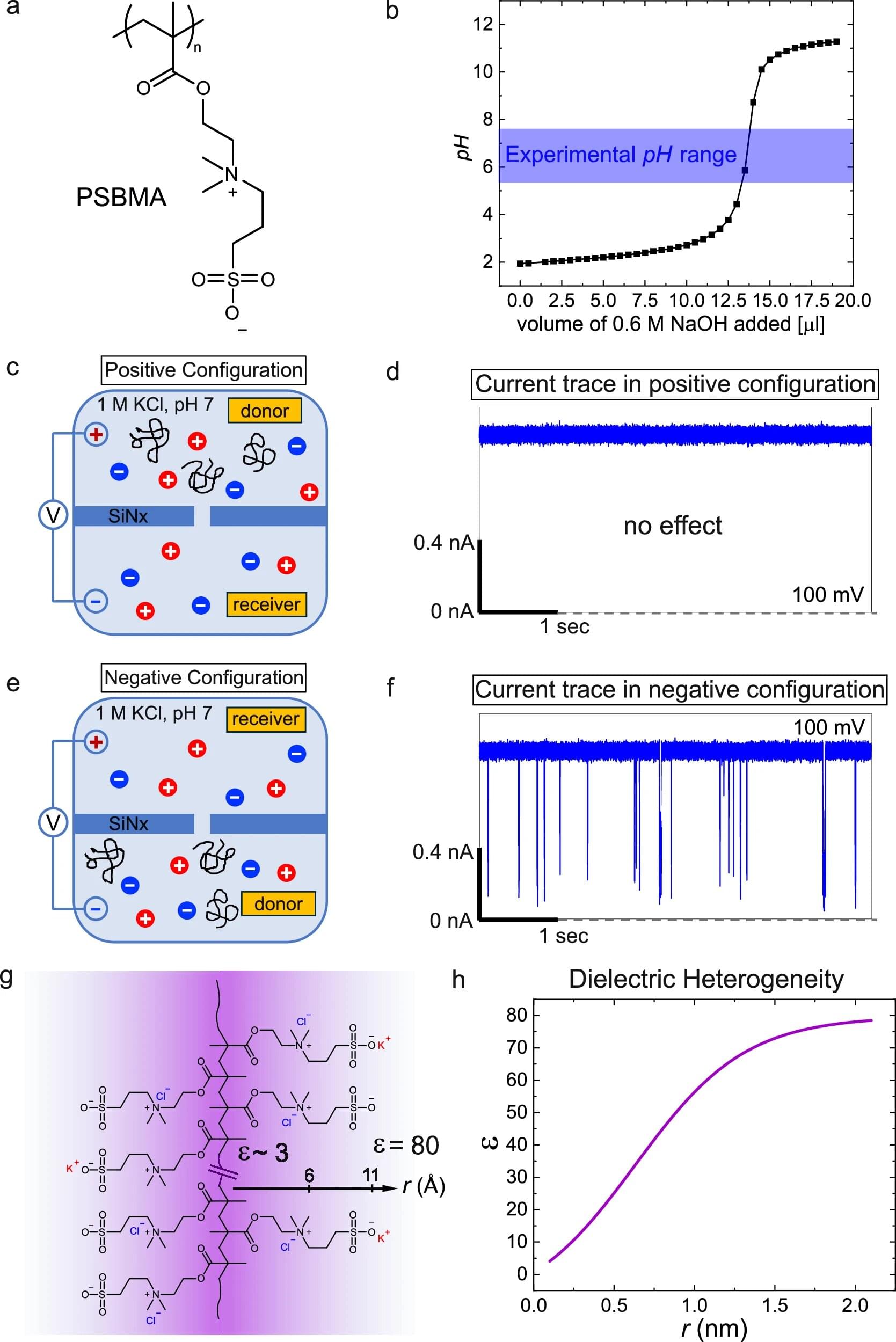
The work involves a kind of polymer made up of neutral polyzwitterions. Because they have a neutral electrical charge, polyzwitterions are not expected to respond to an electric field. However, the team found not only that certain neutral polyzwitterions behave as if they were charged, but also that the electric field surrounding polyzwitterions, once thought to be uniform, varies in strength.
“My interest is in the proteins and amino acids, which are the building blocks for protein, inside our body’s cells,” says Yeseul Lee, lead author and graduate student in polymer science and engineering at UMass Amherst.