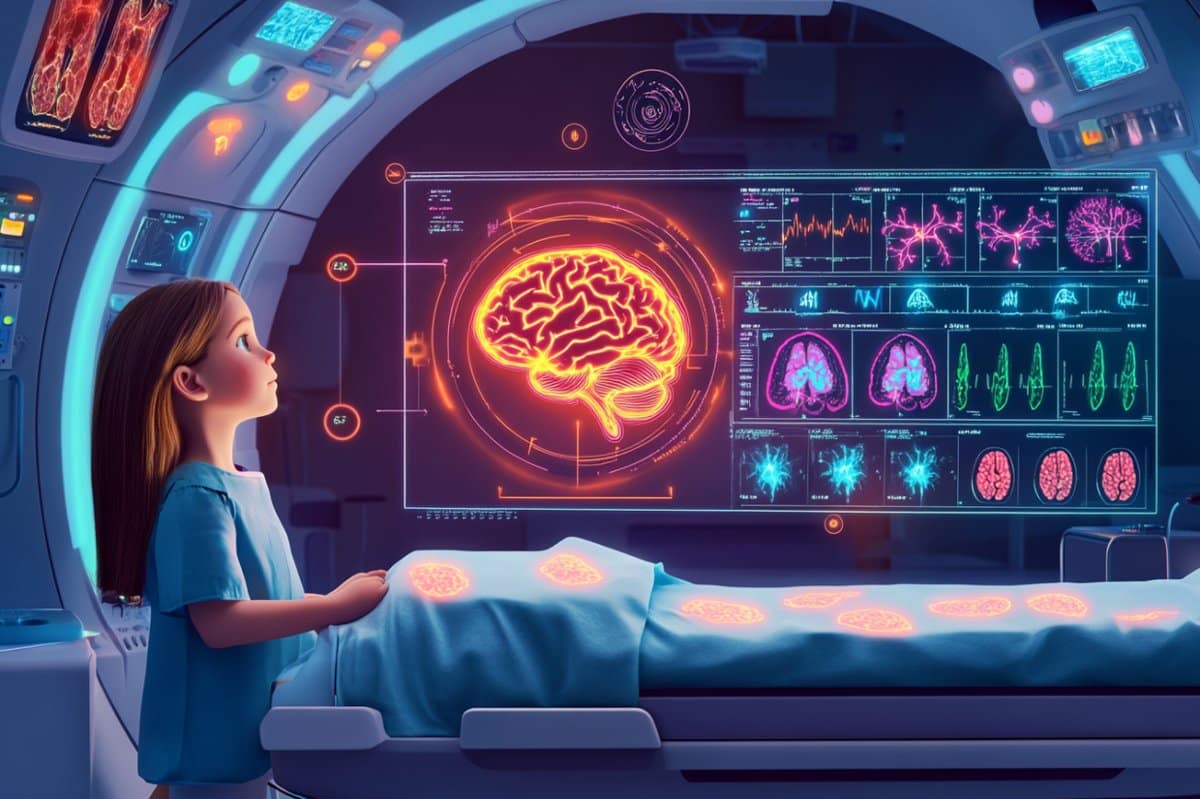
Researchers have developed an AI model that analyzes sequences of brain scans to accurately predict tumor recurrence in children with gliomas.

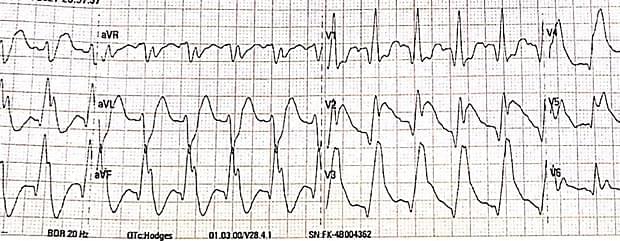
Shark fin electrocardiographic (ECG) pattern, also known as ‘Lambda-wave’, ‘giant R waves’, or ‘triangular QRS-ST-T waveform’ is a dangerous ECG pattern associated with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It is formed by the fusion of QRS, ST, and T waves and predicts the high risk of mortality due to cardiogenic shock and ventricular fibrillation. The management should be aggressive with reperfusion via thrombolysis or percutaneous intervention, ideally in the intensive care unit with ventricular assist devices. This ECG pattern may be misdiagnosed as wide complex tachycardia or the ECG changes of hyperkalemia. Thus, differentiating it from other conditions causing similar ECG changes and prompt management is highly important to save the patient from serious complications.
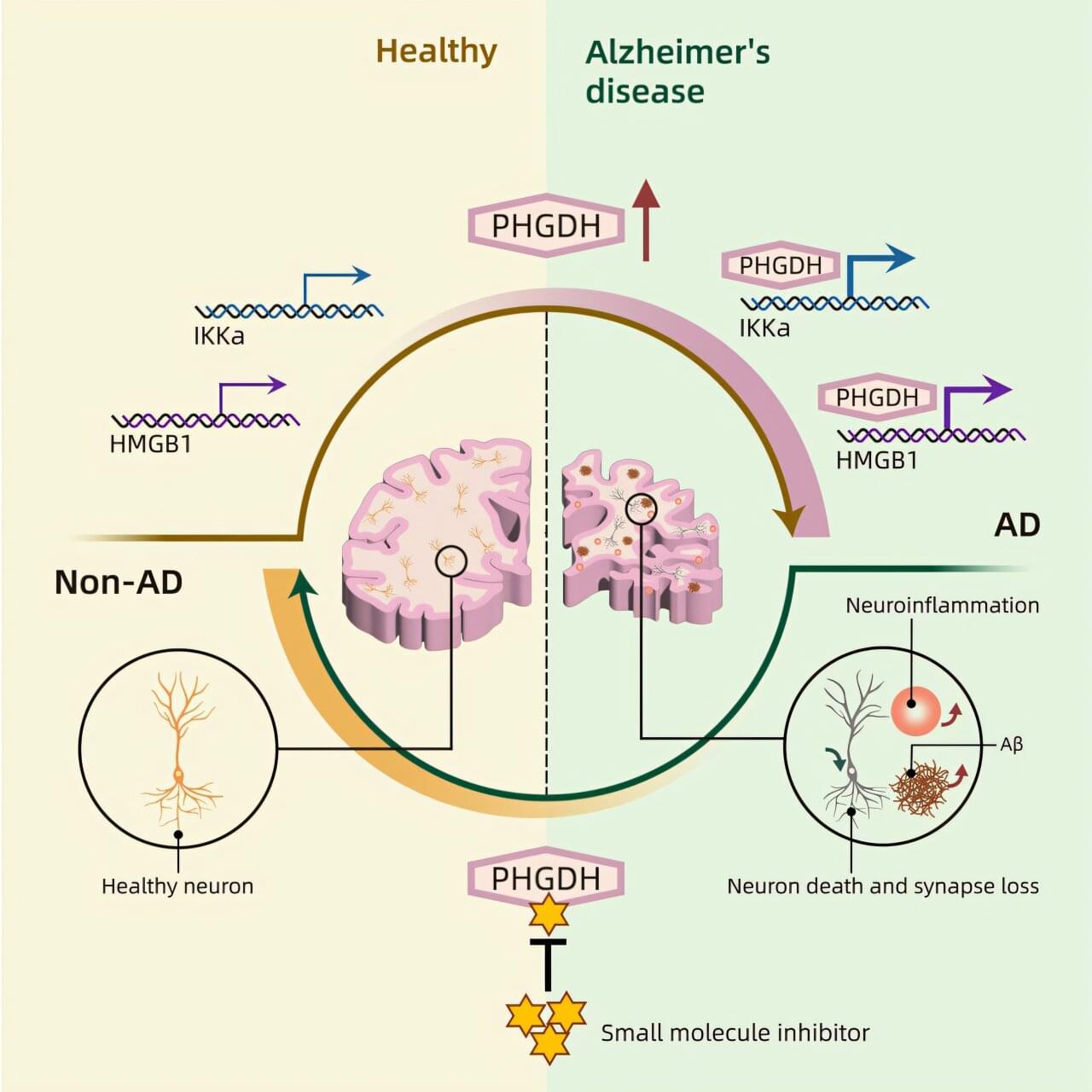
A new study found that a gene recently recognized as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease is actually a cause of it, due to its previously unknown secondary function. Researchers at the University of California San Diego used artificial intelligence to help both unravel this mystery of Alzheimer’s disease and discover a potential treatment that obstructs the gene’s moonlighting role.
The research team published their results on April 23 in the journal Cell.
About one in nine people aged 65 and older has Alzheimer’s disease, the most common cause of dementia. While some particular genes, when mutated, can lead to Alzheimer’s, that connection only accounts for a small percentage of all Alzheimer’s patients. The vast majority of patients do not have a mutation in a known disease-causing gene; instead, they have “spontaneous” Alzheimer’s, and the causes for that are unclear.
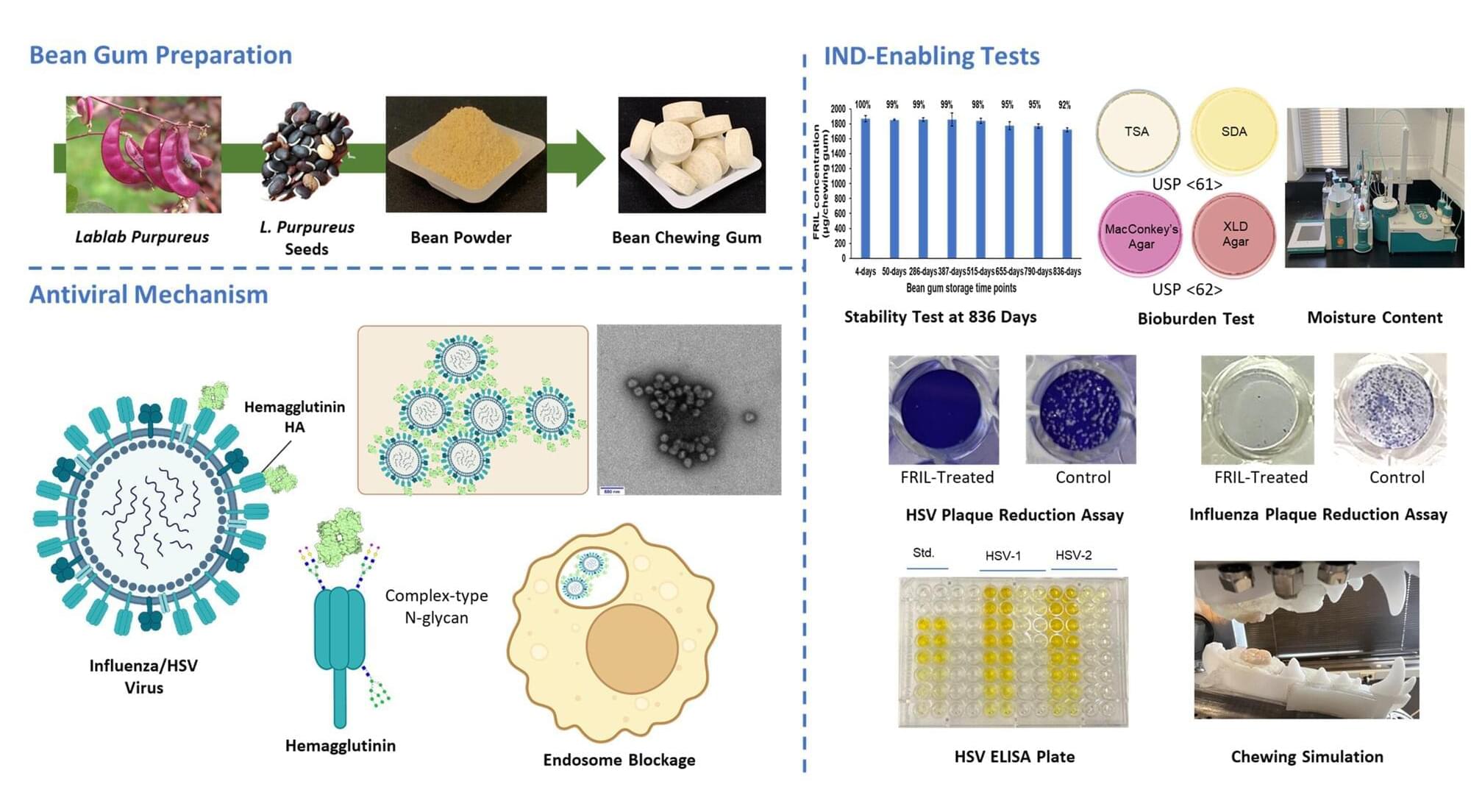
In today’s interconnected world, infectious diseases pose an escalating threat, as demonstrated by the coronavirus pandemic and outbreaks of H1N1, SARS, Ebola, Zika, and H5N1 (bird flu) viruses—all of which have had significant global health and economic impacts.
But more common viral diseases also contribute to global health challenges and economic costs. For example, seasonal influenza epidemics occur annually, causing a substantial global disease burden and economic losses exceeding $11.2 billion each year in the United States alone. Meanwhile, herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), spread primarily through oral contact, infects over two-thirds of the global population and is the leading cause of infectious blindness in Western countries.
Low vaccination rates for influenza viruses and the lack of an HSV vaccine underscore the need for a new approach—one that targets reducing viral loads at the sites where transmission occurs. And for viruses like these, which are transmitted more efficiently through the mouth than the nose, this means focusing on the oral cavity.
In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have successfully created stem cells that are better at developing into other cell types, like a younger, fitter version of themselves—by changing their diet. These stem cells are better than normal stem cells at creating specialized cells like liver, skin or nerve cells, which is a core trait of stem cells.
The study, “Altering metabolism programs cell identity via NAD+-dependent deacetylation” has been published in The EMBO Journal.
“We show that by changing their diet, the stem cells can rejuvenate and turn into ‘super stem cells.’ It forces them to metabolize their energy in a different way than they normally would, and that process essentially reprograms the stem cells,” says first author Robert Bone, Assistant Professor at the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Stem Cell Medicine, also known as reNEW.
CINCINNATI (WKRC) — A commonly prescribed sleeping pill could be a powerful tool in preventing Alzheimer’s disease, according to recently published research.
The study, published in Annals of Neurology, was born from the long-standing scientific belief that poor sleep increases a person’s risk of Alzheimer’s. This belief came from the fact that sleep clears out wasteful proteins like amyloid-beta and tau, which Alzheimer’s patients often have a high build up of.
The study examined suvorexant, a sleeping pill regularly prescribed for insomnia, and observed its effects on clearing those waste proteins.

Should you step away from the chicken wings?
For years, the conventional wisdom has been to swap out red meat for white meats like chicken and poultry to help reduce health risks like increased cholesterol, cancer, and inflammation —not to mention get a more budget-friendly protein source. But a new study links eating chicken and other poultry with a significantly increased risk of dying from gastrointestinal cancer and all other causes.
But before you put down the chicken—or roll your eyes and get back to your chicken Caesar—check out the details of the study, and what a dietitian says you should do if you’re concerned.
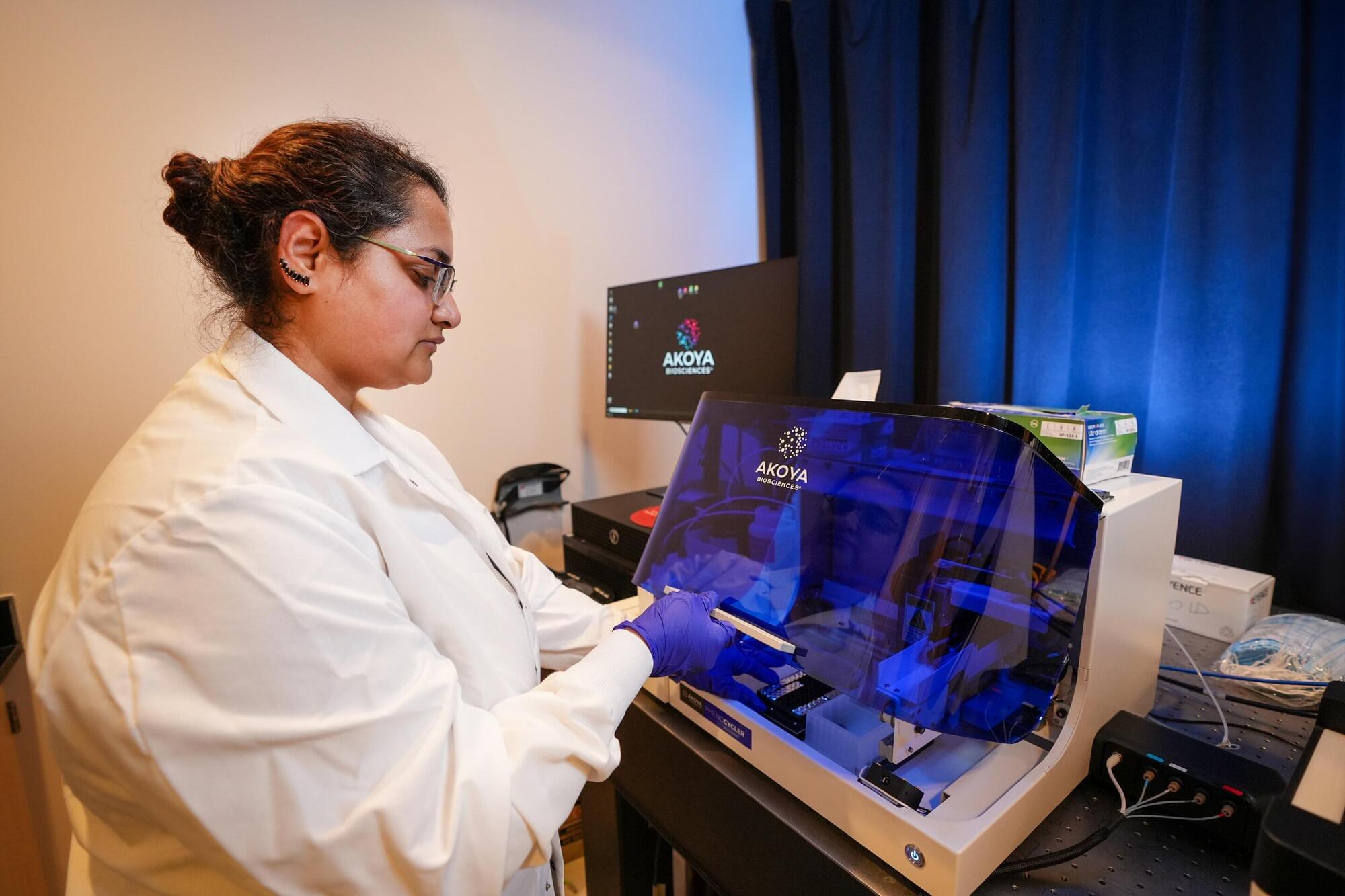

Indiana University School of Medicine scientists have developed a powerful new imaging technique to study bone marrow in mouse models. By overcoming key challenges unique to imaging this complex tissue, this advancement could support future drug development and therapies for conditions involving bone marrow, including cancers, autoimmune diseases and musculoskeletal disorders.
The new method was made possible by the multiplex imaging tool Phenocycler 2.0, which enabled researchers to visualize a record number of cellular markers within intact bone marrow tissue from mice. The findings are published in Leukemia.
“Bone marrow is difficult to study because it is gelatinous and encased in hard bone,” said Sonali Karnik, Ph.D., assistant research professor of orthopedic surgery at the IU School of Medicine and co-lead author of the study. “Since bone marrow plays an important role in blood and immune cell formation and houses valuable stem cells, our unique imaging approach offers a useful tool for a variety of research applications.”