Rice and Baylor researchers have used Rice’s “drug factory” implants to eradicate advanced-stage mesothelioma tumors in mice.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 352
Cellular “switch” discovered that could reverse type 2 diabetes
The researchers identified a stress response that emerges from damaged mitochondria. By interrupting this stress response with a compound known as ISRIB, their results showed a marked improvement in blood sugar handling in mice.
A β-cell in the pancreas is responsible for releasing insulin, the hormone that regulates blood sugar.
These cells need high energy output from mitochondria to carry out their job. Weak energy conversion can disrupt insulin release, fueling the symptoms associated with type 2 diabetes.

Chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules, one carbon at a time
A team of chemists at the University of Cambridge has developed a powerful new method for adding single carbon atoms to molecules more easily, offering a simple one-step approach that could accelerate drug discovery and the design of complex chemical products.
The research, recently published in the journal Nature under the title “One-carbon homologation of alkenes,” unveils a breakthrough method for extending molecular chains—one carbon atom at a time. This technique targets alkenes, a common class of molecules characterized by a double bond between two carbon atoms. Alkenes are found in a wide range of everyday products, from anti-malarial medicines like quinine to agrochemicals and fragrances.
Led by Dr. Marcus Grocott and Professor Matthew Gaunt from the Yusuf Hamied Department of Chemistry at the University of Cambridge, the work replaces traditional multi-step procedures with a single-pot reaction that is compatible with a wide range of molecules.

New technologies help wood-burning stoves burn more efficiently, produce less smoke
Oregon State University researchers are gaining a more detailed understanding of emissions from wood-burning stoves and developing technologies that allow stoves to operate much more cleanly and safely, potentially limiting particulate matter pollution by 95%.
The work has key implications for human health as wood-burning stoves are a leading source of PM2.5 emissions in the United States. PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or smaller that can be inhaled deeply into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream. Exposure to PM2.5 is a known cause of cardiovascular disease and is linked to the onset and worsening of respiratory illness.
Even though a relatively small number of households use wood stoves, they are the U.S.’s third-largest source of particulate matter pollution, after wildfire smoke and agricultural dust, said Nordica MacCarty of the OSU College of Engineering.

Genetic mutation linked to iron deficiency in Crohn’s disease patients
A study led by biomedical scientists at the University of California, Riverside School of Medicine shows how a genetic mutation associated with Crohn’s disease can worsen iron deficiency and anemia—one of the most common complications experienced by patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD.
While IBD—a group of chronic inflammatory disorders that includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis—primarily affects the intestines, it can have effects beyond the gut. Iron deficient anemia is the most prevalent of these effects, contributing to chronic fatigue and reduced quality of life, particularly during disease flare-ups.
The study, performed on serum samples from IBD patients, reports that patients carrying a loss-of-function mutation in the gene PTPN2 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2) exhibit significant disruption in blood proteins that regulate iron levels. This mutation is found in 14–16% of the general population and 19–20% of the IBD population. A loss-of-function mutation is a genetic change that reduces or eliminates the normal function of a gene or its product, a protein.
Resisting Age-Related Blood Pressure Changes: 336 Days Of Testing
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
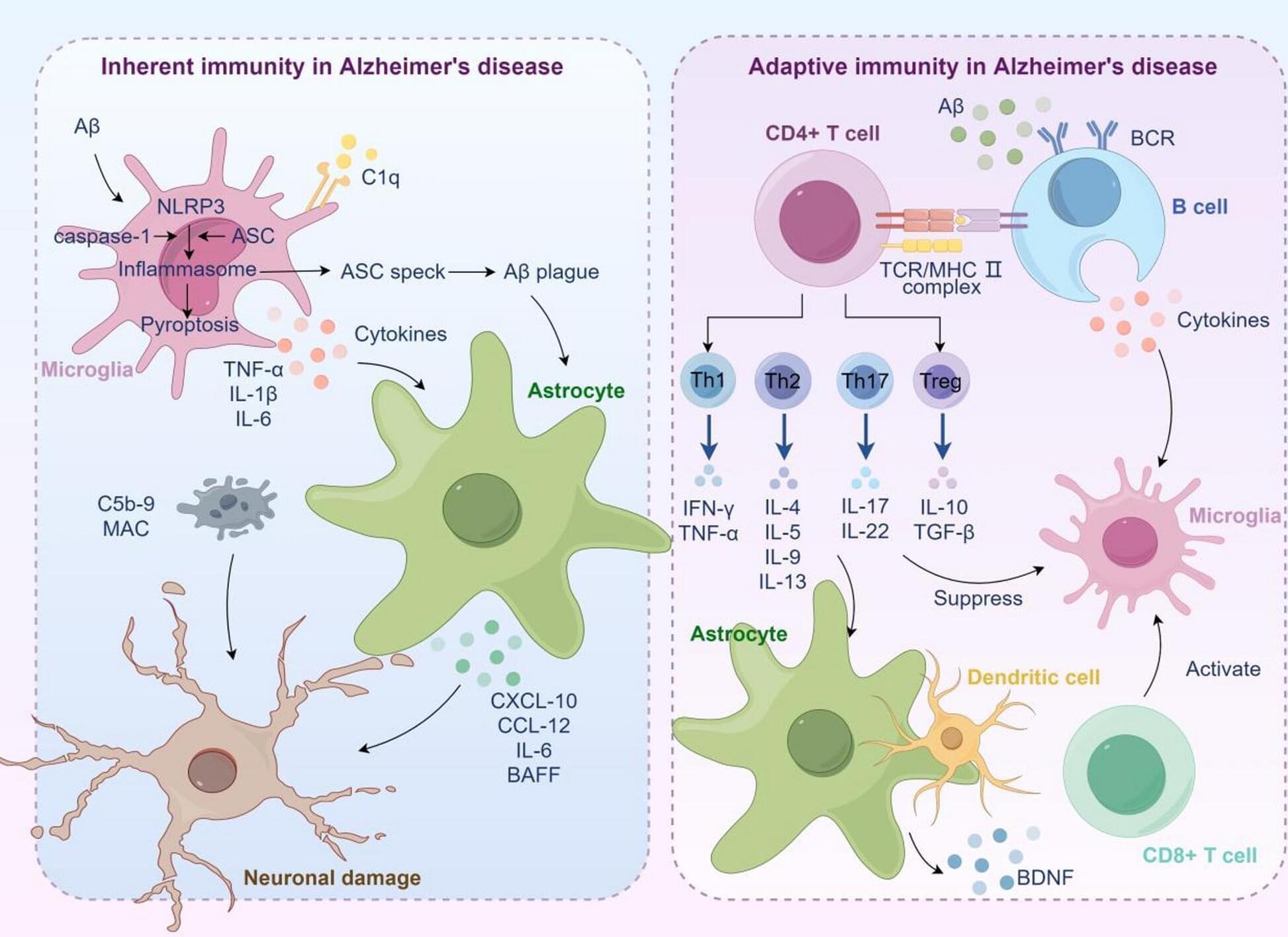
Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: standing at the crossroad of lipid metabolism and immune response
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by macroscopic features such as cortical atrophy, narrowing of the gyri, widening of the sulci, and enlargement of the ventricles. At the cellular level, the pathological characteristics include the extracellular aggregation of β-amyloid (Aβ) forming senile plaques, and the intracellular accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau proteins forming neurofibrillary tangles. AD leads to the progressive decline of cognitive, behavioral, and social abilities, with no effective treatment available currently. The pathophysiology of AD is complex, involving mechanisms such as immune dysregulation and lipid metabolism alterations. Immune cells, such as microglia, can identify and clear pathological aggregates like Aβ early in the disease.

A more realistic look at DNA in action
The background
Most biochemistry labs that study DNA isolate it within a water-based solution that allows scientists to manipulate DNA without interacting with other molecules. They also tend to use heat to separate strands, heating the DNA to over 150 degrees Fahrenheit, a temperature a cell would never naturally reach. By contrast, in a living cell DNA lives in a very crowded environment, and special proteins attach to DNA to mechanically unwind the double helix and then pry it apart.