A new study shows that combining heavy alcohol use with burn trauma causes severe disruptions in the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and a weakened gut barrier.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 353
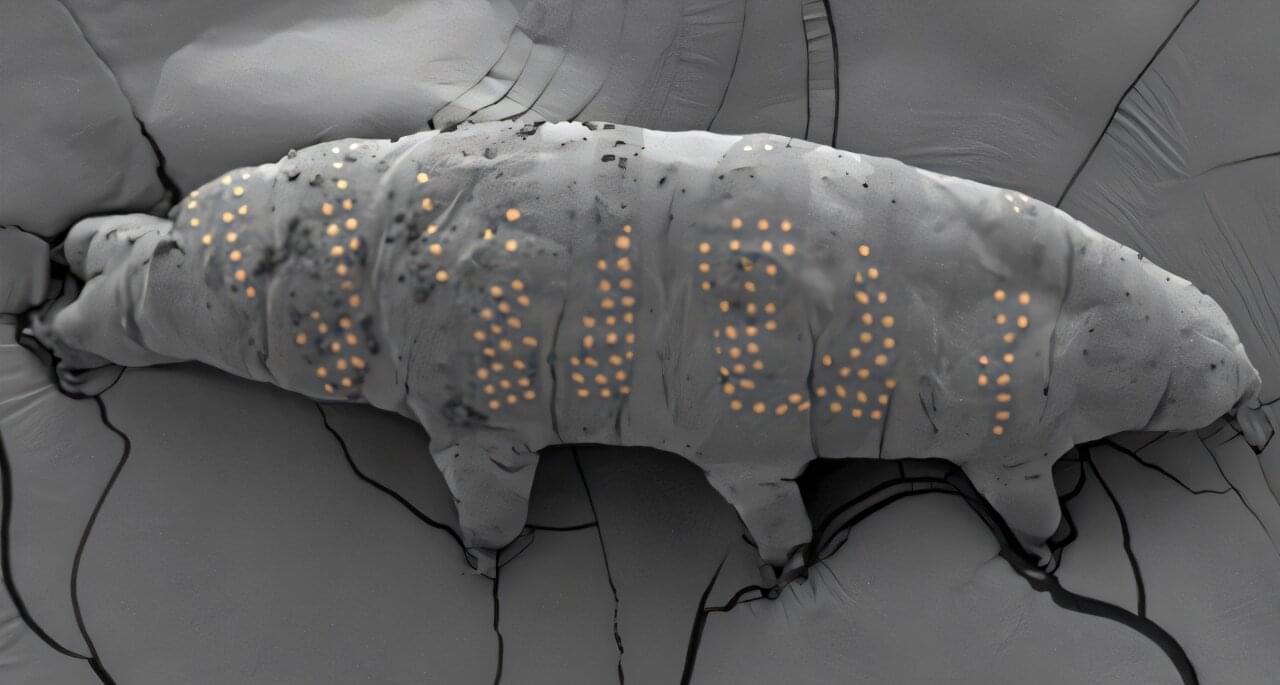
Scientists have found a way to ‘tattoo’ tardigrades
If you haven’t heard of a tardigrade before, prepare to be wowed. These clumsy, eight-legged creatures, nicknamed water bears, are about half a millimeter long and can survive practically anything: freezing temperatures, near starvation, high pressure, radiation exposure, outer space and more. Researchers reporting in the journal Nano Letters took advantage of the tardigrade’s nearly indestructible nature and gave the critters tiny “tattoos” to test a microfabrication technique to build microscopic, biocompatible devices.
“Through this technology, we’re not just creating micro-tattoos on tardigrades—we’re extending this capability to various living organisms, including bacteria,” explains Ding Zhao, a co-author of the paper.
Microfabrication has revolutionized electronics and photonics, creating micro-and nanoscale devices ranging from microprocessors and solar cells to biosensors that detect food contamination or cancerous cells. But the technology could also advance medicine and biomedical engineering, if researchers can adapt microfabrication techniques to make them compatible with the biological realm.
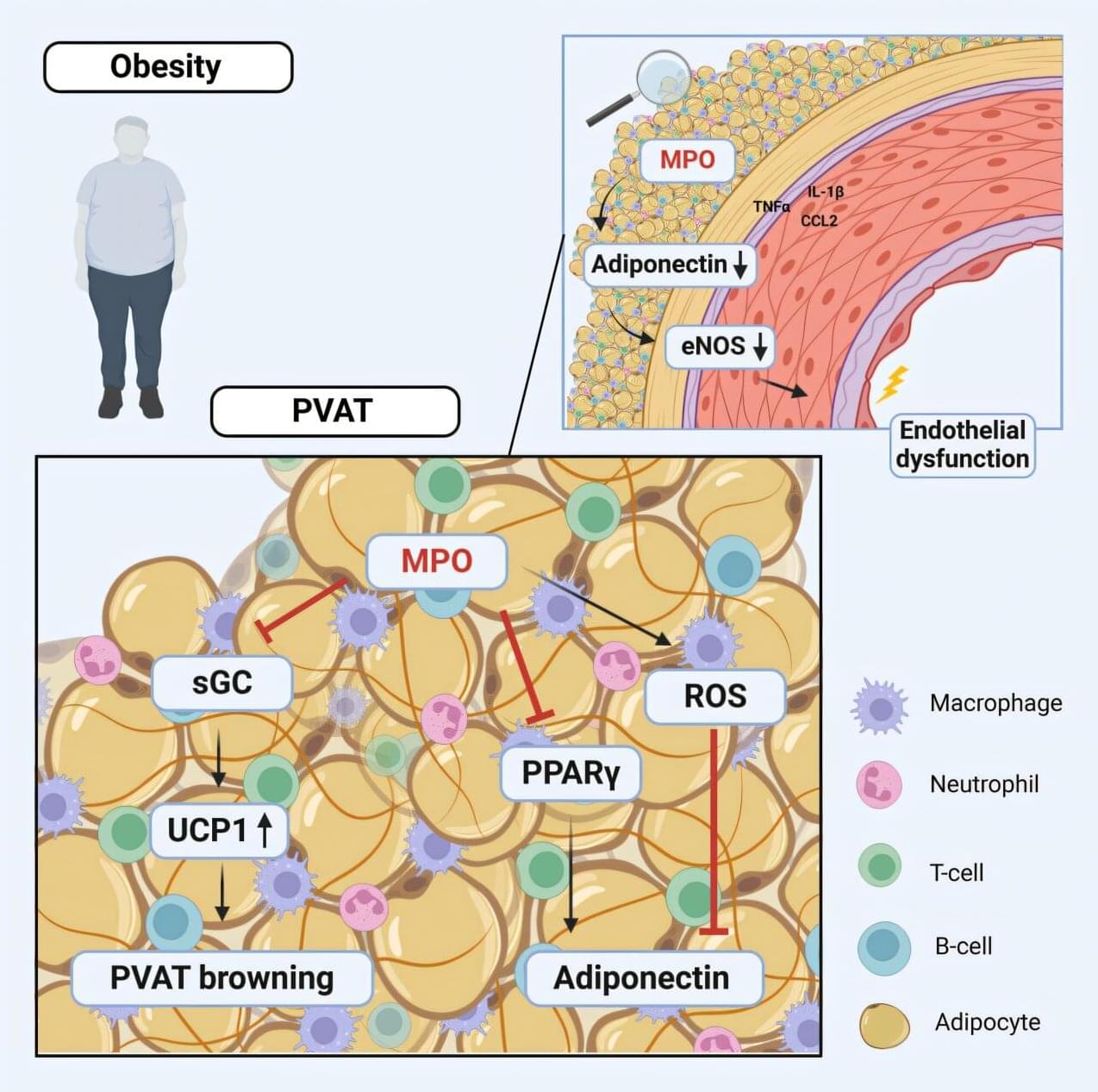
Inhibition of an enzyme that promotes inflammation may reduce cardiovascular risk in obese people
A research team led by Dr. Martin Mollenhauer from the Heart Center at University Hospital Cologne has investigated the link between obesity and the risk of cardiovascular disease in greater detail. The researchers have discovered that in obese patients and in mouse models, increased levels of the oxidative enzyme myeloperoxidase (MPO) are associated with poorer vascular function.
The results of the research have been published under the title “Myeloperoxidase impacts vascular function by altering perivascular adipocytes’ secretome and phenotype in obesity” in Cell Reports Medicine.
In people suffering from obesity, MPO is active in a particular form of fatty tissue surrounding the aorta. This fatty tissue is called perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT). MPO promotes inflammatory processes in PVAT and at the same time inhibits protective mechanisms that normally keep the blood vessels elastic and healthy.
The Big Bang Never Happened? Eric Lerner, DemystifySci #337
Eric Lerner is a popular science writer, plasma physicist, and long-time collaborator of the late Nobel laureate Hannes Alfvén. He’s also one of the featured speakers at our Beyond the Big Bang event this summer in Sesimbra, Portugal. For over thirty years, Lerner has been a leading voice in plasma cosmology and a critic of Big Bang cosmology, who argued for a non-expanding, steady state universe as the central claim of his landmark book The Big Bang Never Happened (affiliate link to puchase: https://amzn.to/4jEez8H). Our conversation dives into the history and foundations of plasma cosmology, from early Birkeland current experiments in the Arctic that revealed the electrical nature of the aurora, to the role of plasma dynamics in the shape and behavior of galaxies. All the hits are in here — from Halton Arp, whose Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies seriously challenged the way that mainstream cosmologists interpret redshift, to the electromagnetic forces often overlooked in mainstream cosmology, to the filamentary plasma structures and cosmic-scale currents that strain the limits of the standard model. This is a deep exploration of alternative cosmology, electric universe theories, and the scientists behind them — from Fred Hoyle to Anthony Peratt — who refused to patch a dying theory and instead asked instead if the universe might be eternal.
MAKE HISTORY WITH US THIS SUMMER:
https://demystifysci.com/demysticon-2025
PATREON
/ demystifysci.
PARADIGM DRIFT
https://demystifysci.com/paradigm-dri… Go! 00:05:59 – The Cosmological Pendulum 00:14:09 – Knowledge and Societal Progress 00:22:18 – Big Bang Origins & Ideological Influence 00:29:04 – Technological Stagnation Since the 1970s 00:32:02 – Ideology Replacing Empiricism in Science 00:36:14 – Gravity vs. Electromagnetism in Cosmology 00:41:02 – Evolution of Scientific Funding Models 00:51:11 – Birkeland Currents & Plasma Discoveries 00:56:25 – Centralization of Postwar Science 01:00:18 – Orthodoxy in Medicine 01:00:59 – Decline of Fundamental Research 01:04:39 – Plasma Cosmology vs. Dark Matter 01:08:52 – Capitalism and Research Priorities 01:14:22 – Sustaining Independent Science 01:15:16 – Birkeland, Alfvén & Plasma History 01:22:24 – Einstein’s Rise & Cultural Legacy 01:31:05 – General Relativity and Elitism 01:34:44 – Chapman’s Math vs. Empirics 01:37:12 – Alfvén’s Plasma Breakthroughs 01:43:39 – Plasma Physics vs. Big Bang Theories 01:47:39 – Nobel Prize & MHD’s Hidden Flaws 01:58:00 – Filamentary Plasmas vs. MHD 02:00:47 – Pseudoplasmas and MHD Limits 02:02:58 – Defining Plasma as a State of Matter 02:06:00 – Where Plasma Exists in Nature 02:11:17 – The Myth of Mathematical Models 02:21:10 – Scientific vs. Aesthetic Cosmology 02:29:55 – Failed Big Bang Predictions 02:36:01 – Alternatives to the Expanding Universe 02:43:09 – Large-Scale Structures and Cosmic Age 02:50:10 – Public Science and Open Debate 02:55:16 – Toward a New Cosmological Paradigm #plasma #bigbang #darkmatter #electricuniverse, #cosmology, #astrophysics, #scientificrevolution, #fusionenergy, #philosophypodcast, #sciencepodcast, #longformpodcast ABOUS US: Anastasia completed her PhD studying bioelectricity at Columbia University. When not talking to brilliant people or making movies, she spends her time painting, reading, and guiding backcountry excursions. Shilo also did his PhD at Columbia studying the elastic properties of molecular water. When he’s not in the film studio, he’s exploring sound in music. They are both freelance professors at various universities. PATREON: get episodes early + join our weekly Patron Chat https://bit.ly/3lcAasB MERCH: Rock some DemystifySci gear : https://demystifysci.myspreadshop.com… AMAZON: Do your shopping through this link: https://amzn.to/3YyoT98 DONATE: https://bit.ly/3wkPqaD SUBSTACK: https://substack.com/@UCqV4_7i9h1_V7h… BLOG: http://DemystifySci.com/blog RSS: https://anchor.fm/s/2be66934/podcast/rss MAILING LIST: https://bit.ly/3v3kz2S SOCIAL:
- Discord:
/ discord
- Facebook:
/ demystifysci
- Instagram:
/ demystifysci
- Twitter:
/ demystifysci
MUSIC:-Shilo Delay: https://g.co/kgs/oty671
00:00 Go!
00:05:59 – The Cosmological Pendulum.
00:14:09 – Knowledge and Societal Progress.
00:22:18 – Big Bang Origins & Ideological Influence.
00:29:04 – Technological Stagnation Since the 1970s.
00:32:02 – Ideology Replacing Empiricism in Science.
00:36:14 – Gravity vs. Electromagnetism in Cosmology.
00:41:02 – Evolution of Scientific Funding Models.
00:51:11 – Birkeland Currents & Plasma Discoveries.
00:56:25 – Centralization of Postwar Science.
01:00:18 – Orthodoxy in Medicine.
01:00:59 – Decline of Fundamental Research.
01:04:39 – Plasma Cosmology vs. Dark Matter.
01:08:52 – Capitalism and Research Priorities.
01:14:22 – Sustaining Independent Science.
01:15:16 – Birkeland, Alfvén & Plasma History.
01:22:24 – Einstein’s Rise & Cultural Legacy.
01:31:05 – General Relativity and Elitism.
01:34:44 – Chapman’s Math vs. Empirics.
01:37:12 – Alfvén’s Plasma Breakthroughs.
01:43:39 – Plasma Physics vs. Big Bang Theories.
01:47:39 – Nobel Prize & MHD’s Hidden Flaws.
01:58:00 – Filamentary Plasmas vs. MHD
02:00:47 – Pseudoplasmas and MHD Limits.
02:02:58 – Defining Plasma as a State of Matter.
02:06:00 – Where Plasma Exists in Nature.
02:11:17 – The Myth of Mathematical Models.
02:21:10 – Scientific vs. Aesthetic Cosmology.
02:29:55 – Failed Big Bang Predictions.
02:36:01 – Alternatives to the Expanding Universe.
02:43:09 – Large-Scale Structures and Cosmic Age.
02:50:10 – Public Science and Open Debate.
02:55:16 – Toward a New Cosmological Paradigm.
#plasma #bigbang #darkmatter #electricuniverse, #cosmology, #astrophysics, #scientificrevolution, #fusionenergy, #philosophypodcast, #sciencepodcast, #longformpodcast.
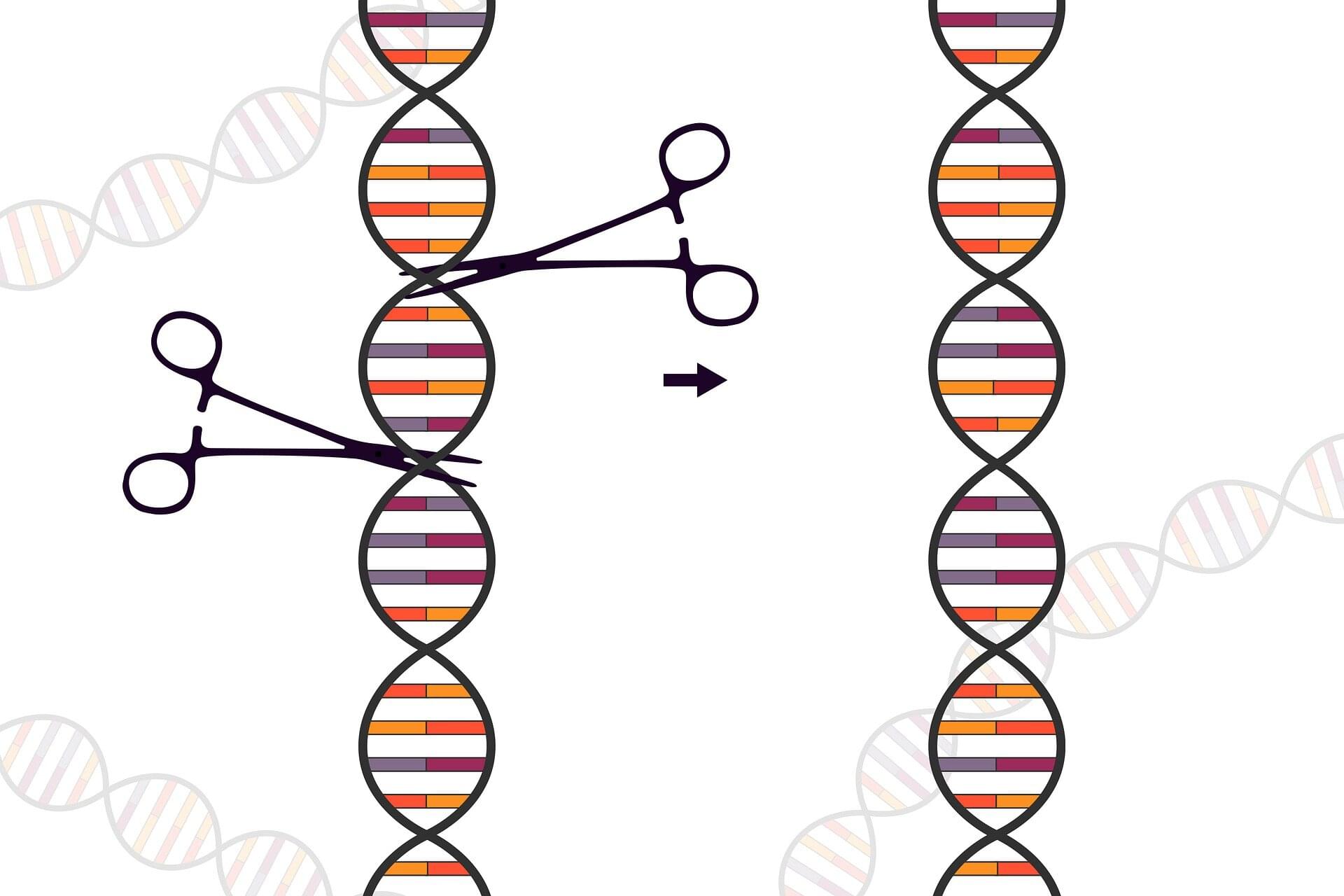
Engineering ‘bespoke enzymes’: Machine learning expands CRISPR toolbox
Genome editing has advanced at a rapid pace with promising results for treating genetic conditions—but there is always room for improvement. A new paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham showcases the power of scalable protein engineering combined with machine learning to boost progress in the field of gene and cell therapy.
In their study, the authors developed a machine learning algorithm—known as PAMmla—that can predict the properties of approximately 64 million genome-editing enzymes. The work could help reduce off-target effects and improve editing safety, enhance editing efficiency, and enable researchers to predict customized enzymes for new therapeutic targets. The results are published in Nature.
“Our study is a first step in dramatically expanding our repertoire of effective and safe CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes. In our manuscript, we demonstrate the utility of these PAMmla-predicted enzymes to precisely edit disease-causing sequences in primary human cells and in mice,” said corresponding author Ben Kleinstiver, Ph.D., Kayden-Lambert MGH Research Scholar associate investigator at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH).
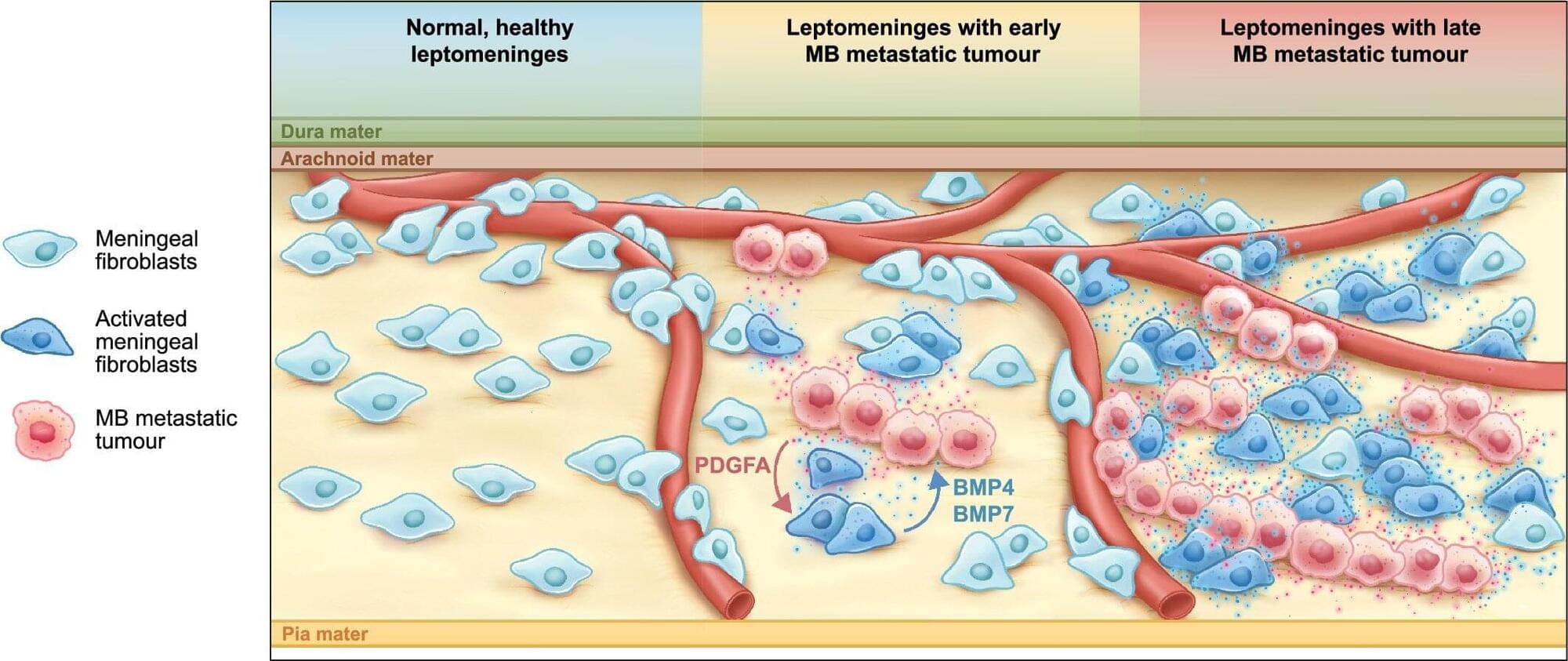
New research points out a promising strategy for treating metastatic medulloblastoma
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital, the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and collaborating institutions reveal in Nature Cell Biology a strategy that helps medulloblastoma, the most prevalent malignant brain tumor in children, spread and grow on the leptomeninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
They discovered a novel line of communication between metastatic medulloblastoma and leptomeningeal fibroblasts that mediates recruitment and reprogramming of the latter to support tumor growth. The findings suggest that disrupting this communication offers a potential opportunity to treat this devastating disease.
“Metastases, the spreading of a tumor away from its original site, are the most common and most important cause of illness and death for children with medulloblastoma,” said co-first author Dr. Namal Abeysundara, a postdoctoral fellow who was working in the lab of Dr. Michael D. Taylor at the Arthur and Sonia Labatt Brain Tumor Research Center and the Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Program at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Canada during this project.