Within a tiny plankton, an even smaller cell has been found living an unexpectedly virus-like existence, challenging what it means to be alive.

5k words, 23 minutes reading time
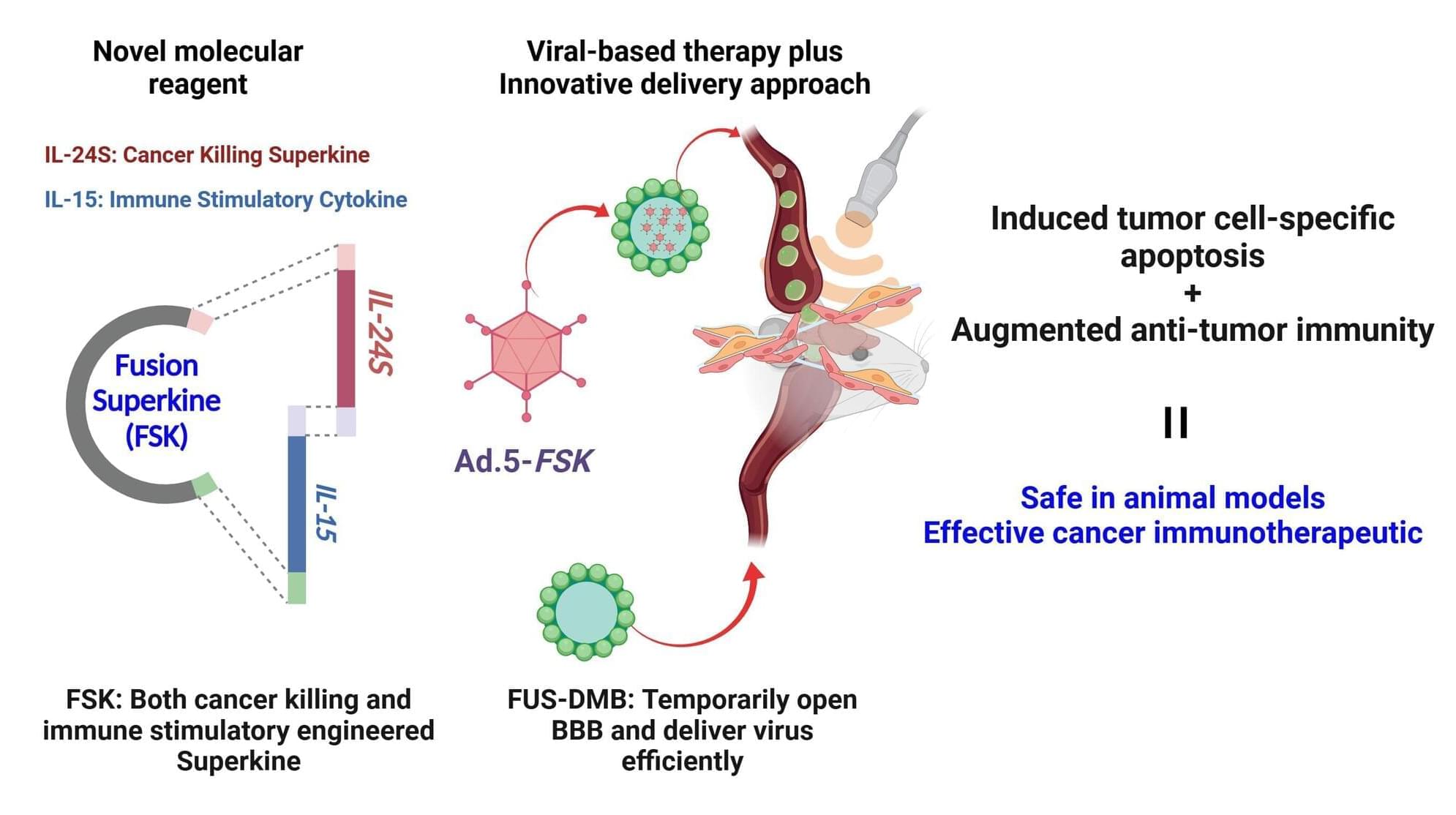
Researchers at VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center and the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM) have discovered a new and potentially revolutionary way to treat glioblastoma (GBM), the most aggressive type of brain cancer, which currently has no curative treatment options.
In a study led by Paul B. Fisher, MPh, Ph.D., FNAI, and Swadesh K. Das, Ph.D., recently published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, researchers created a new molecule that demonstrates the ability to introduce a combination of treatment outcomes—direct toxicity and immunotoxicity—to kill the tumor while exploiting immunotherapy to potentially prevent the recurrence of GBM. The new molecule, a fusion superkine (FSK), contains dual-acting therapeutic cytokines in a single molecule.
“This is the tip of the iceberg,” said Dr. Fisher, the Thelma Newmeyer Corman Endowed Chair in Cancer Research at Massey, director of the VIMM and professor in the Department of Cellular, Molecular and Genetic Medicine. “We’re optimistic that our first trial in brain cancer, planned for 2026, will show that the IL-24 gene and these therapeutic viruses are effective and safe. And [the FSK] will be the one knocking it out of the ballpark.
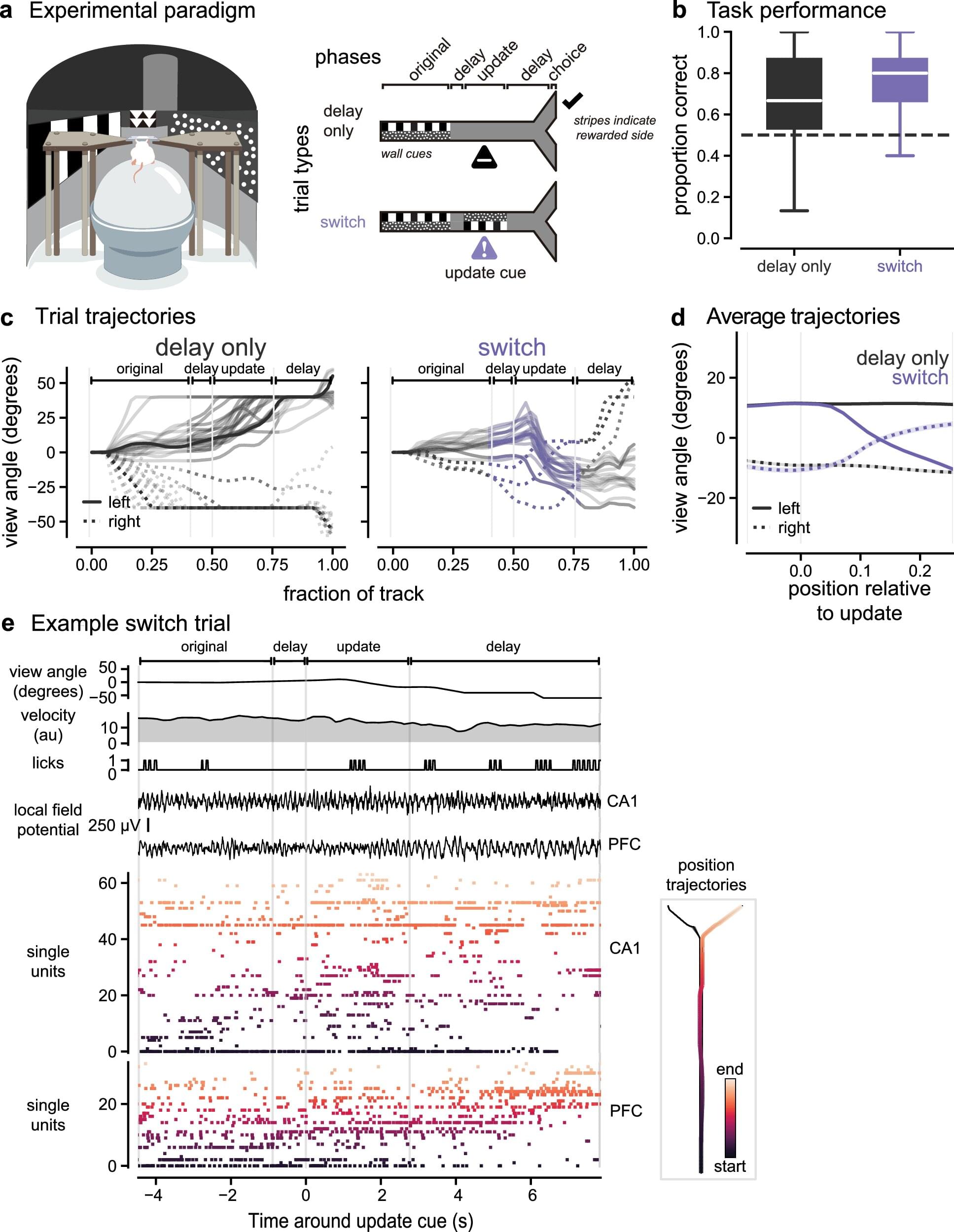
In a paper published in the journal Nature Communications, biomedical engineers have shown how two brain regions quickly adapt to shift focus from one planned destination to another.
Stephanie Prince explains her research with a scenario many Atlantans can relate to. Imagine you’re driving to the Atlanta airport to pick up a friend. They call to say they’re in the terminal—but they’re not sure which one. North, maybe? You head in that direction through the maze of roads around the airport.
Then they call back. They’re actually in the South Terminal. So you make a quick mental adjustment and switch your route to arrive at the correct side of the airport.
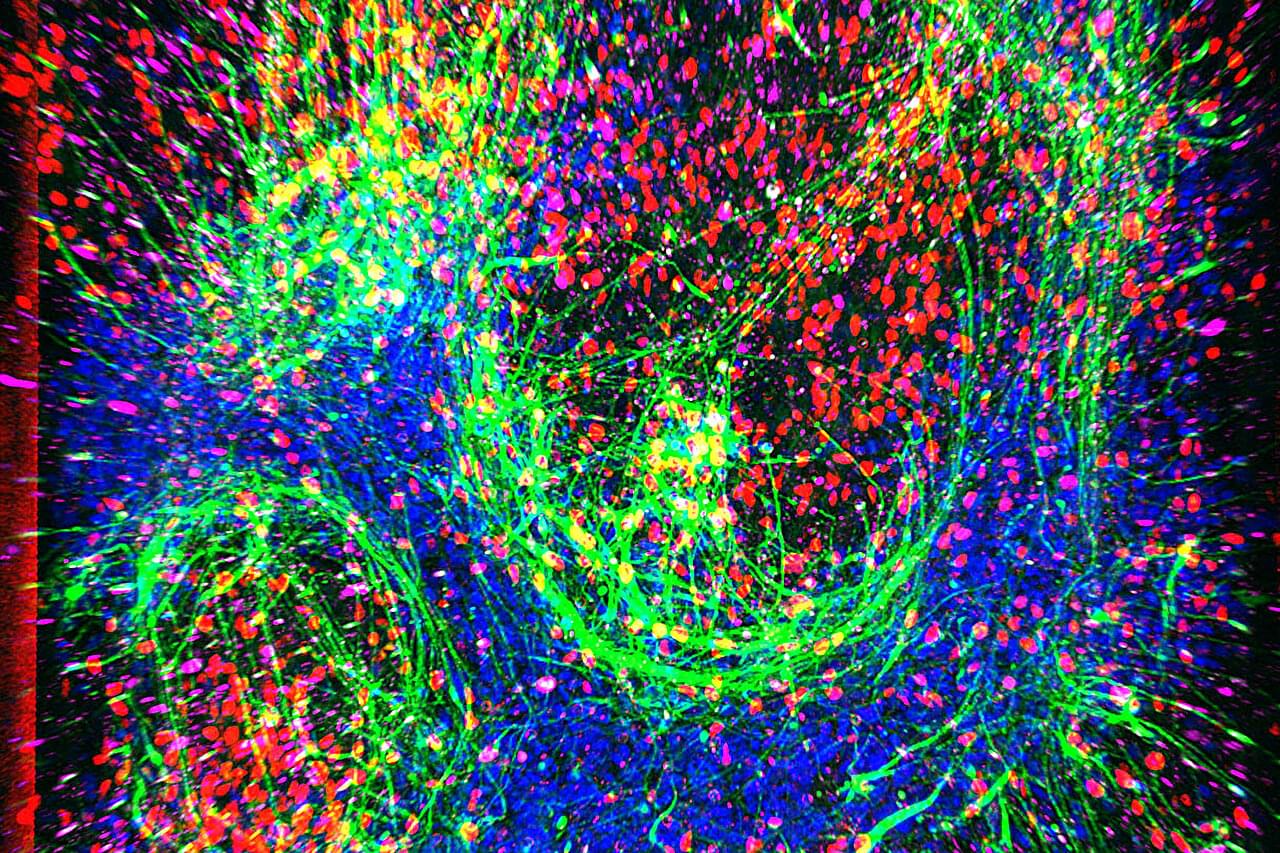
Using stem cells from patients with ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), Cedars-Sinai has created a lifelike model of the mysterious and fatal disease that could help identify a cause of the illness as well as effective treatments.
In a study published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, investigators detail how they created “ALS on a chip” and the clues the specialized laboratory chip has already produced about nongenetic causes of the disease, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease.
The work builds on previous studies where adult cells from ALS patients were reverted into stem cells. The cells were then pushed forward to produce motor neurons, which die in the disease, causing progressive loss of the ability to move, speak, eat and breathe.

Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) is a soil-borne virus showing a low percentage of ca. 3% soil-mediated infection when the soil contains root debris from a previous 30–50 day growth cycle of ToBRFV-infected tomato plants. We designed stringent conditions of soil-mediated ToBRFV infection by increasing the length of the pre-growth cycle to 90–120 days, adding a ToBRFV inoculum as well as truncating seedling roots, which increased seedling susceptibility to ToBRFV infection. These rigorous conditions were employed to challenge the efficiency of four innovative root-coating technologies in mitigating soil-mediated ToBRFV infection while avoiding any phytotoxic effect. We tested four different formulations, which were prepared with or without the addition of various virus disinfectants. We found that under conditions of 100% soil-mediated ToBRFV infection of uncoated positive control plants, root-coating with formulations based on methylcellulose (MC), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), silica Pickering emulsion and super-absorbent polymer (SAP) that were prepared with the disinfectant chlorinated-trisodium phosphate (Cl-TSP) showed low percentages of soil-mediated ToBRFV infection of 0%, 4.3%, 5.5% and 0%, respectively. These formulations had no adverse effect on plant growth parameters when compared to negative control plants grown under non ToBRFV inoculation conditions.
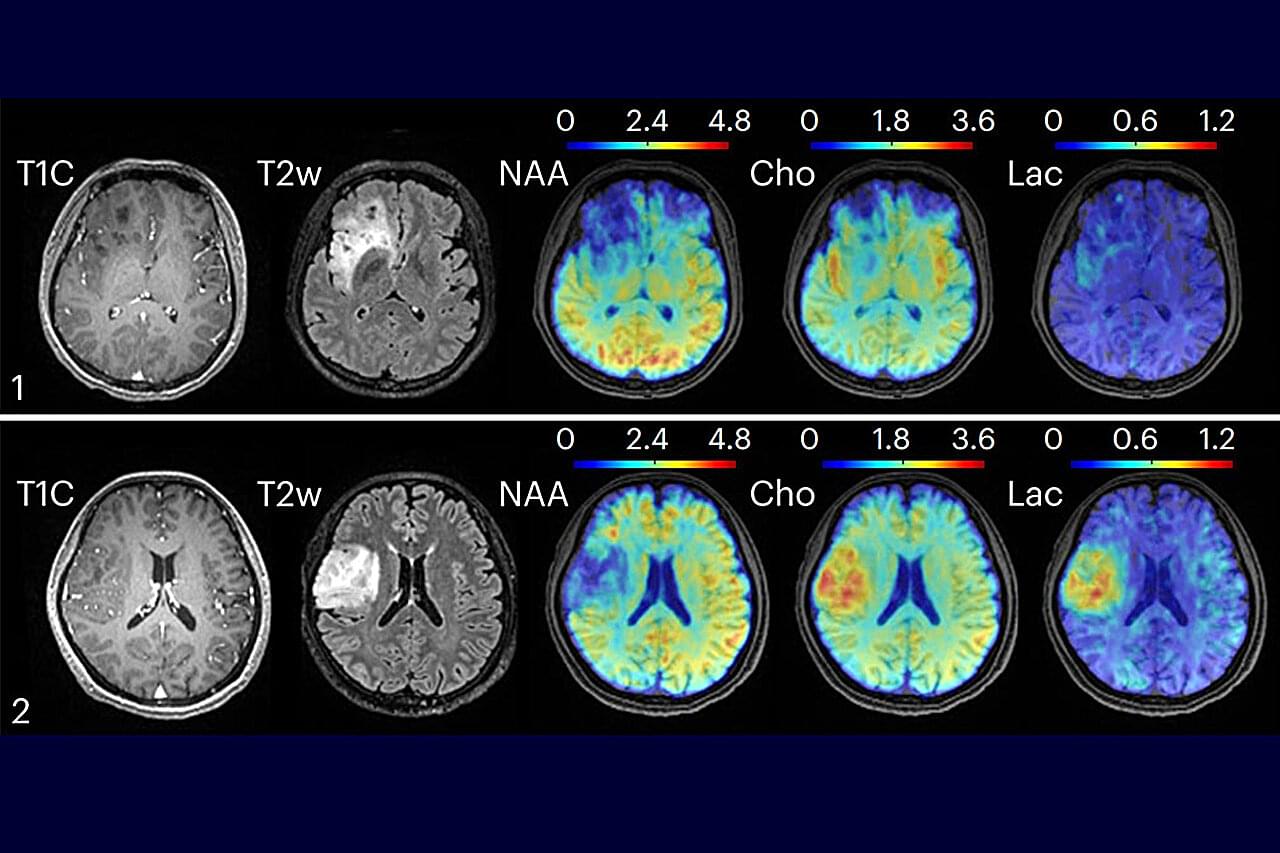
A new technology that uses clinical MRI machines to image metabolic activity in the brain could give researchers and clinicians unique insight into brain function and disease, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign report. The non-invasive, high-resolution metabolic imaging of the whole brain revealed differences in metabolic activity and neurotransmitter levels among brain regions; found metabolic alterations in brain tumors; and mapped and characterized multiple sclerosis lesions—with patients only spending minutes in an MRI scanner.
Led by Zhi-Pei Liang, a professor of electrical and computer engineering and a member of the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the U. of I., the team reported its findings in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“Understanding the brain, how it works and what goes wrong when it is injured or diseased is considered one of the most exciting and challenging scientific endeavors of our time,” Liang said. “MRI has played major roles in unlocking the mysteries of the brain over the past four decades. Our new technology adds another dimension to MRI’s capability for brain imaging: visualization of brain metabolism and detection of metabolic alterations associated with brain diseases.”
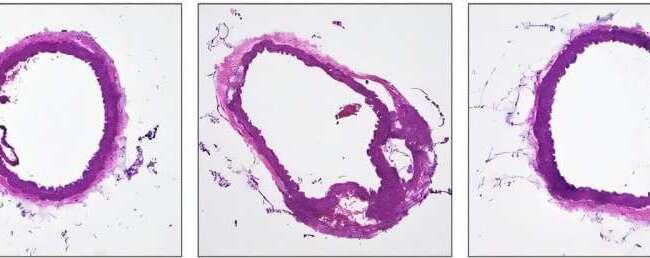
Using gene editing in a preclinical model, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center blocked the symptoms of a rare smooth muscle disease before they developed. Their findings, published in Circulation, could eventually lead to gene therapies for this and other genetic diseases affecting smooth muscle cells.
“Gene editing has been used in other disease contexts, but its application to inherited vascular diseases, particularly targeting smooth muscle cells in vivo, is still emerging. Our approach advances the field by demonstrating functional correction in a cell type that’s notoriously difficult to target,” said Eric Olson, Ph.D., Chair and Professor of Molecular Biology and a member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UT Southwestern.
Dr. Olson co-led the study with Ning Liu, Ph.D., Professor of Molecular Biology, and first author Qianqian Ding, Ph.D., postdoctoral researcher, both members of the Olson Lab.
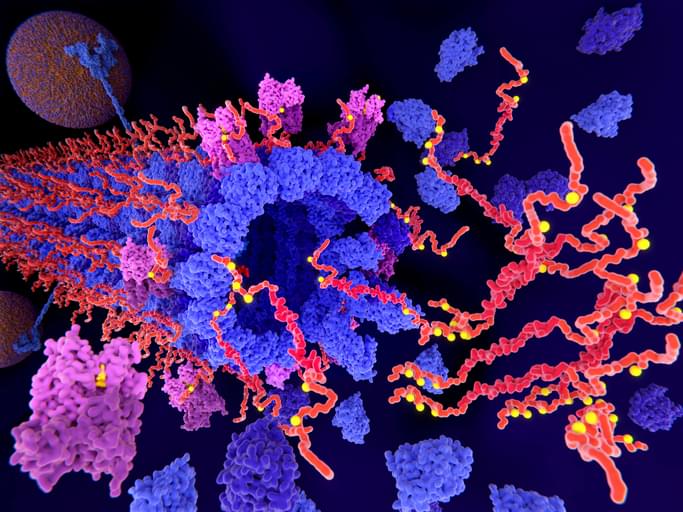
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine report that a rare gene mutation that delays Alzheimer’s disease does so by damping inflammatory signaling in brain-resident immune cells in a preclinical study. The finding adds to growing evidence that brain inflammation is a major driver of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s—and that it may be a key therapeutic target for these disorders.
In their study “The R136S mutation in the APOE3 gene confers resilience against tau pathology via inhibition of the cGAS-STING-IFN pathway,” in Immunity, the investigators examined the effects of the mutation APOE3-R136S—known as the “Christchurch mutation”—which was recently found to delay hereditary early-onset Alzheimer’s. The scientists showed that the mutation inhibits the cGAS-STING pathway, an innate immune signaling cascade that is abnormally activated in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. The researchers found that pharmacologically blocking the cGAS-STING pathway with a drug-like inhibitor replicated key protective effects of the mutation in a preclinical model.
“This is an exciting study because it suggests that inhibiting this cGAS-STING pathway could make the brain more resistant to the Alzheimer’s process, even in the face of significant tau accumulation,” said study senior author Li Gan, PhD, the Burton P. and Judith B. Resnick Distinguished Professor in Neurodegenerative Diseases and director of the Helen and Robert Appel Alzheimer’s Disease Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine.