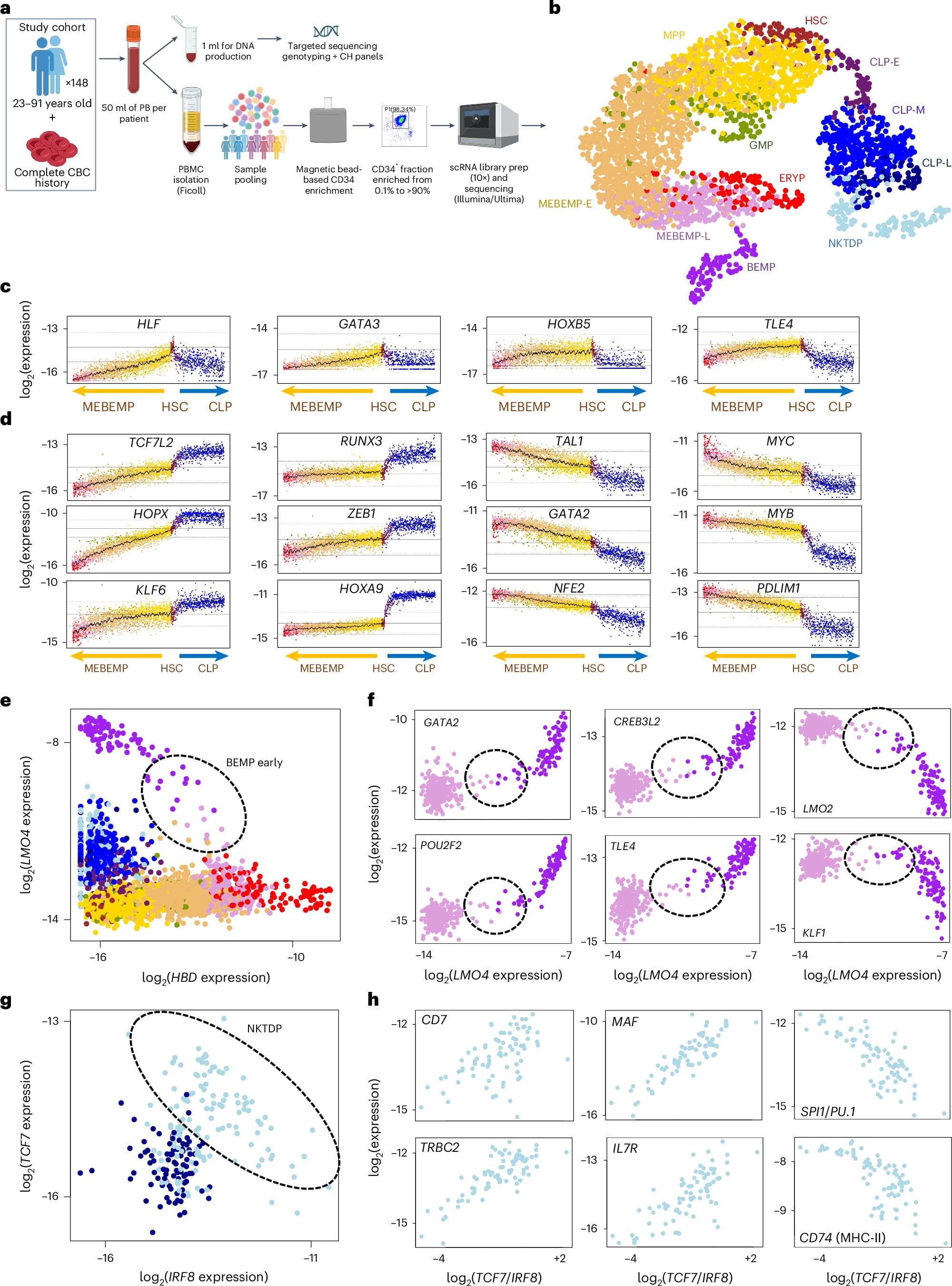
What if a blood test could reveal the pace of our aging—and the diseases that may lie ahead? The labs of Profs. Liran Shlush and Amos Tanay at the Weizmann Institute of Science have been conducting in-depth studies into the biology of blood to better understand the aging process and why some people become more susceptible to disease over the years.
Their research teams, made up of physicians, biologists and data scientists, have been tracking changes in the blood-forming stem cells, including the emergence of genetic changes in these cells in about one-third of people over the age of 40. These changes not only increase the risk of blood cancers such as leukemia, but have also been linked to heart disease, diabetes and other age-related conditions.
In a new study published today in Nature Medicine, Shlush and Tanay present findings that may lead to an innovative blood test for detecting a person’s risk of developing leukemia. This test may potentially replace the invasive diagnostic procedure of bone marrow sampling.