Nice.
(Phys.org)—A team of researchers with Harvard University and the University of Cambridge has successfully improved the accuracy of a synthetic clock known as a repressilator. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the team describes the steps they took to reduce the amount of noise in the biological system and how well it worked. Xiaojing Gao and Michael Elowitz with the California Institute of Technology offer a News & Views piece on the work done by the team and explain how their results could improve understanding of natural gene circuits.
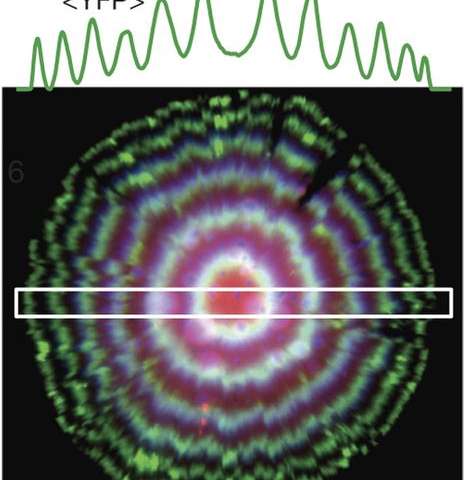
Scientists have noted the high precision that some living cells demonstrate in keeping track of time, such as those that are part of the circadian clock, and have tried to duplicate the process. Sixteen years ago, Michael Elowitz and Stanislas Leibler developed what is now known as the repressilator—a synthetic oscillating genetic circuit. Their results demonstrated that it was possible for genetic circuits to be designed and built in the lab. The resulting circuit functioned, but was noisy, and therefore much less accurate than natural cell clocks. In this new effort, the researchers improved several of the design steps of the repressilator, each greatly reducing the amount of noise, and in so doing, increased the precision.
The repressilator was made using repressor proteins that would bind to DNA sequences that were adjacent to a gene to be targeted for inhibition. Three repressors were created such that each one represented the expression of the next cycle—when the protein in one repressor increased, it caused a decrease in the expression of the second, which in turn caused an increase in expression of the third, and so on, resulting in oscillations—the actions were monitored by reporters. Unfortunately, each was bothered by random fluctuations known as noise. To reduce the noise, the researchers integrated the reporters into the repressilator, engineered the repressor proteins to degrade in order to reduce the number of copies made, and increased the binding threshold between one of the repressors and the DNA sequence.