Normally, T cells naturally identify cancer cells by recognizing specific protein fragments, known as peptides, presented on the cell surface by molecules called pMHCs. It is a slow and challenging process to utilize this knowledge for therapy, often because the variation in the body’s own T-cell receptors makes it challenging to create a personalized treatment.
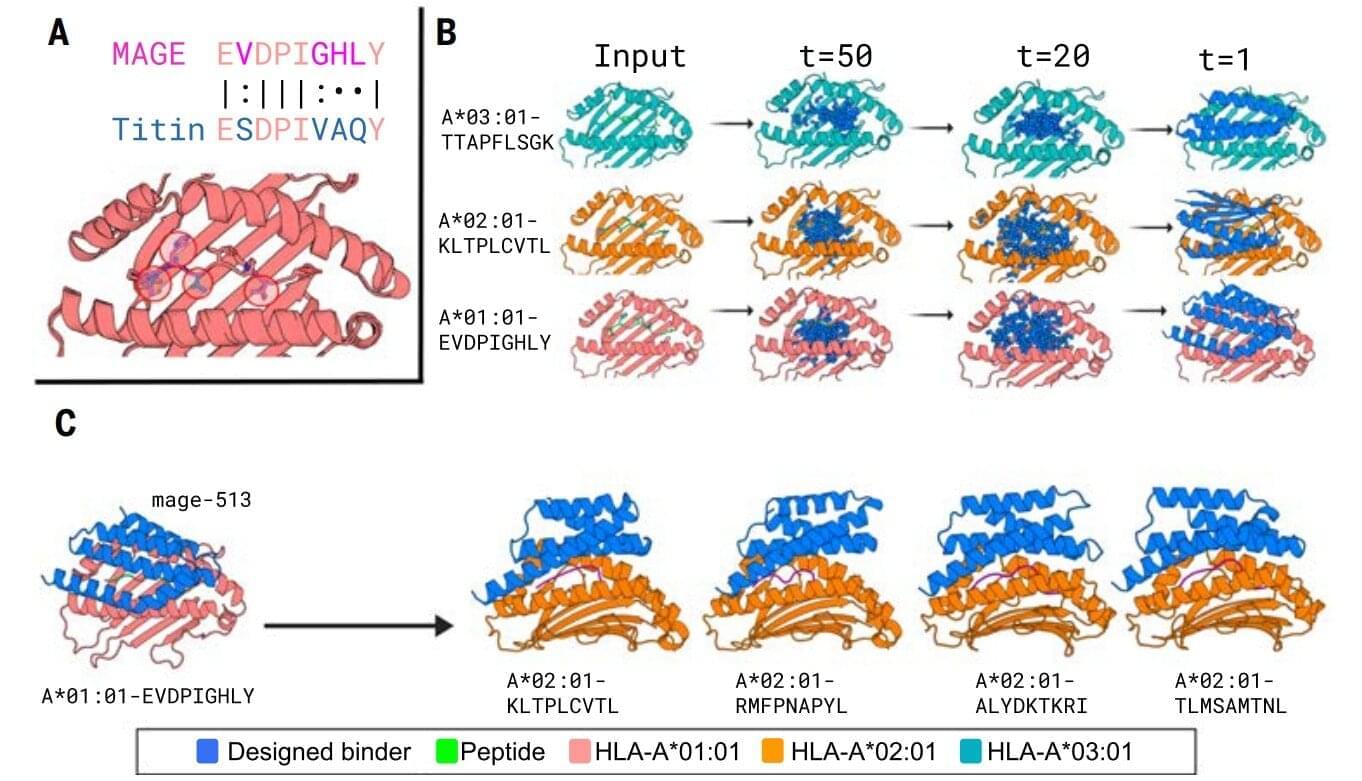
In the study, the researchers tested the strength of the AI platform on a well-known cancer target, NY-ESO-1, which is found in a wide range of cancers. The team succeeded in designing a minibinder that bound tightly to the NY-ESO-1 pMHC molecules. When the designed protein was inserted into T cells, it created a unique new cell product named ‘IMPAC-T’ cells by the researchers, which effectively guided the T cells to kill cancer cells in laboratory experiments.
“It was incredibly exciting to take these minibinders, which were created entirely on a computer, and see them work so effectively in the laboratory,” says a co-author of the study.
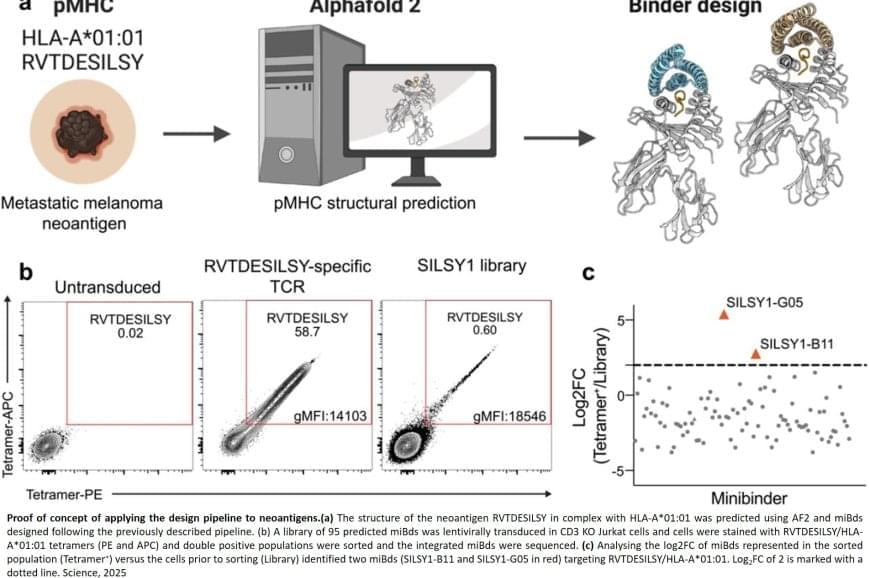
The researchers also applied the pipeline to design binders for a cancer target identified in a metastatic melanoma patient, successfully generating binders for this target as well. This documented that the method also can be used for tailored immunotherapy against novel cancer targets.
A crucial step in the researchers’ innovation was the development of a ‘virtual safety check’. The team used AI to screen their designed minibinders and assess them in relation to pMHC molecules found on healthy cells. This method enabled them to filter out minibinders that could cause dangerous side effects before any experiments were carried out.
Precision cancer treatment on a larger scale is moving closer after researchers have developed an AI platform that can tailor protein components and arm the patient’s immune cells to fight cancer. The new method, published in the scientific journal Science, demonstrates for the first time, that it is possible to design proteins in the computer for redirecting immune cells to target cancer cells through pMHC molecules.