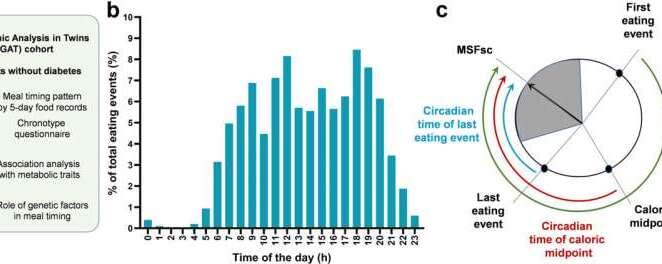
Our metabolic processes differ depending on the time of day and many of them are more active in the morning than in the evening. Although studies show that eating late in the day is associated with an increased risk of obesity and cardiovascular diseases, little is known about how the time we eat affects glucose metabolism and to what extent this is genetically defined.
Prof. Olga Ramich from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbrücke (DIfE) and her team recently investigated this using data from a twin cohort from 2009-10. Their article was published in the journal eBioMedicine.
The circadian system is a hierarchically structured 24-hour time control system in the body that regulates behavior and metabolism via a central clock in the brain and peripheral clocks in organs such as the liver or pancreas. As a result, our metabolic processes differ depending on the time when we eat, which leads to diurnal fluctuations in glucose metabolism and the release of hormones after a meal.