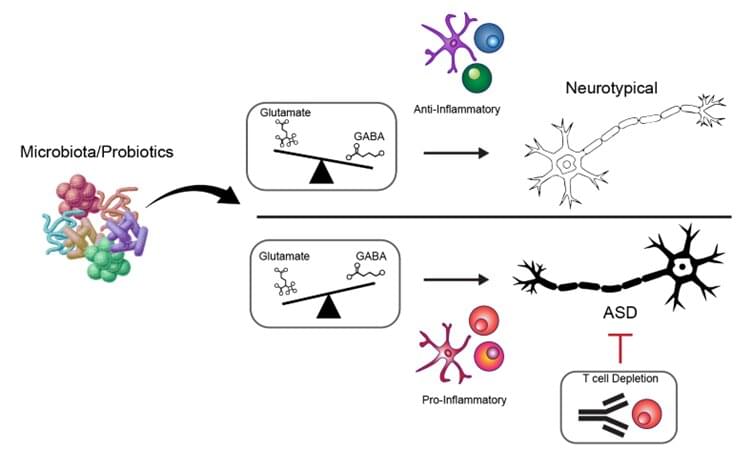
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) affects an estimated 1 in 31 children in the United States by 2025, and prevalence in East Asian countries, such as South Korea, Singapore, and Japan, may be even higher than those in the United States. Despite its increasing prevalence, the underlying causes of ASD remain poorly understood, and there are currently no curative, preventive, or treatment options available.
A research team from POSTECH and ImmunoBiome in Korea, led by Professor Sin-Hyeog Im, who also serves as the CEO of ImmunoBiome, has made a discovery that reveals a multi-faceted mechanism behind ASD. This study, published in the July issue of Nature Communications, in collaboration with Dr. John C. Park and Prof. Tae-Kyung Kim, demonstrates that the gut microbiota and host immune system together can influence the progression of ASD in a genetic mouse model.
ASD has long been regarded as a genetically driven disorder. However, growing evidence suggests that environmental and microbial factors also play a role. The human gut harbors more than ten times as many microbial cells as human cells, and these microbes play vital roles in metabolism and the development of the immune system.