This Video Explains The DNA Double Strand Breaks And Homologous Recombination (HR) Repair System Versus Non-homologous End-Joining (NHEJ)
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,288
Nearly 100 common drugs linked to increased risk of thinking and memory problems
MINNEAPOLIS — A new study is sounding the alarm for patients taking dozens of common prescription and over-the-counter drugs. Researchers find that taking a particular class of drug, anticholinergics, increases the risk of developing mild thinking and memory problems.
The study shows there are about 100 of these types of drugs in widespread use. These medications treat everything from colds to high blood pressure to depression.
The research, published in the journal Neurology, finds that people with genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease are particularly susceptible to these issues. Overall, scientists reveal patients with no cognitive issues are 47 percent more likely to develop a mental impairment if they’re taking at least one anticholinergic drug.
Take a Free Course on COVID-19 From MIT
Beginning September 1 at 11:30 a.m. ET (8:30 a.m. PT), MIT is offering a course on “COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 and the Pandemic.” The course’s lectures will be livestreamed every Tuesday and are free to the public. (Only enrolled students can ask questions, but everyone can watch.)

Insights into the structure and function of Est3 from the Hansenula polymorpha telomerase
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme, which maintains genome integrity in eukaryotes and ensures continuous cellular proliferation. Telomerase holoenzyme from the thermotolerant yeast Hansenula polymorpha, in addition to the catalytic subunit (TERT) and telomerase RNA (TER), contains accessory proteins Est1 and Est3, which are essential for in vivo telomerase function. Here we report the high-resolution structure of Est3 from Hansenula polymorpha (HpEst3) in solution, as well as the characterization of its functional relationships with other components of telomerase. The overall structure of HpEst3 is similar to that of Est3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human TPP1. We have shown that telomerase activity in H. polymorpha relies on both Est3 and Est1 proteins in a functionally symmetrical manner. The absence of either Est3 or Est1 prevents formation of a stable ribonucleoprotein complex, weakens binding of a second protein to TER, and decreases the amount of cellular TERT, presumably due to the destabilization of telomerase RNP. NMR probing has shown no direct in vitro interactions of free Est3 either with the N-terminal domain of TERT or with DNA or RNA fragments mimicking the probable telomerase environment. Our findings corroborate the idea that telomerase possesses the evolutionarily variable functionality within the conservative structural context.
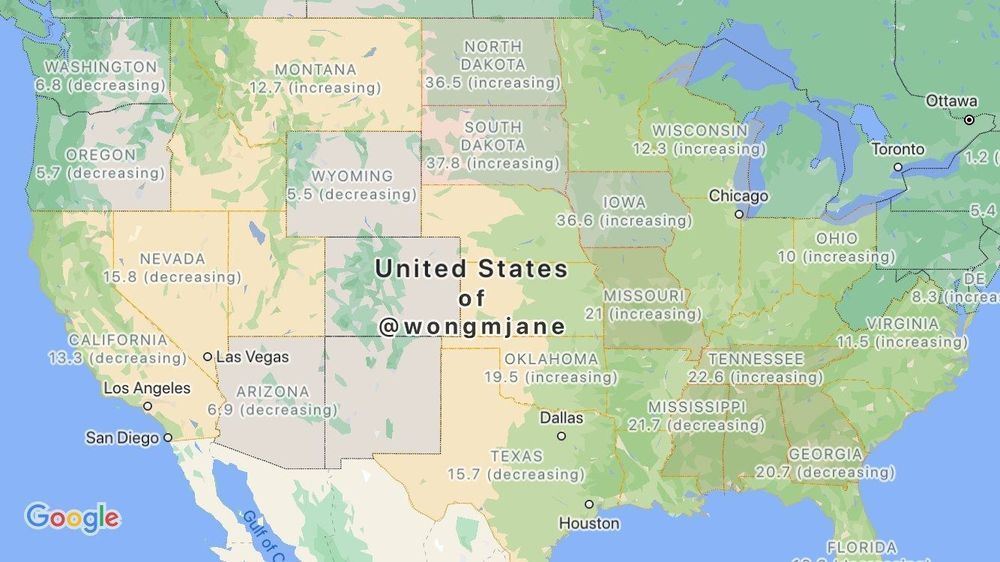
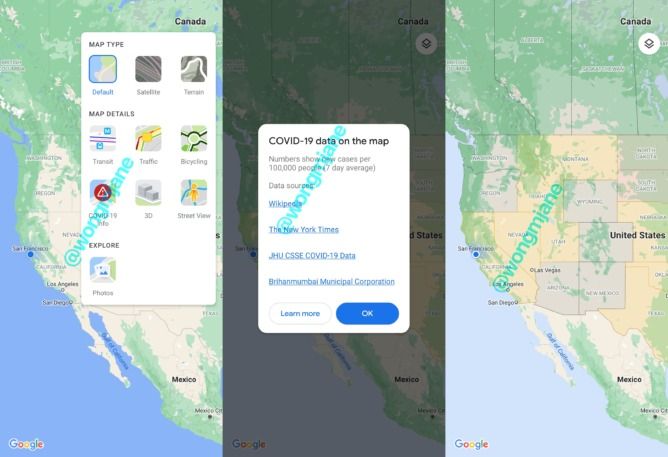
Google appears to be working on a COVID-19 outbreak overlay for Maps
Google has been placing COVID-19 reminders, warnings, and information in many of its services for some time now. You can’t use a Google service without being reminded to wear a mask, or of where to go for screening. It’s even added various tips to Maps, including where to get takeout during the pandemic. With a possible new overlay feature, it looks like we might soon be able to add Google Maps to our list of COVID tracing apps.
Jane Wong has shared screenshots she was able to trigger in Maps, showcasing the new feature. The pictures detail the COVID-19 tracking option alongside the other map overlays, like Traffic and Transit. The feature apparently sources data from Wikipedia, The New York Times, Johns Hopkins University, and Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Using this information, the overlay colors impacted states, countries, and their borders. The map also displays whether the current numbers for each area are increasing or decreasing.
Nano particles for healthy tissue
“Eat your vitamins” might be replaced with “ingest your ceramic nano-particles” in the future as space research is giving more weight to the idea that nanoscopic particles could help protect cells from common causes of damage.
Oxidative stress occurs in our bodies when cells lose the natural balance of electrons in the molecules that we are made of. This is a common and constant occurrence that is part of our metabolism but also plays a role in the aging process and several pathological conditions, such as heart failure, muscle atrophy and Parkinson’s disease.
The best advice for keeping your body in balance and avoiding oxidative stress is still to have a healthy diet and eat enough vitamins, but nanoparticles are showing promising results in keeping cells in shape.
Researchers Identify Possible New Entry Points for SARS-CoV-2 / COVID-19 Into the Human Body
“Hotspots” of Coronavirus Infections in Human Bodies
An infection with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 can affect multiple organs. With this in mind, researchers of the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Cornell University in the US have investigated cellular factors that could be significant for an infection. To this end, they analyzed the activity of 28 specific genes in a wide range of human tissues. Their findings, which provide a map of potentially disease-relevant factors across the human body, are published in the journal Cell Reports.
“SARS-CoV-2 not just infects the respiratory system, it has the potential to affect many other organs in the body. Even if the virus infects the respiratory system first, it is essential to be able to predict where it might go next. This aids to develop therapies. Our goal was thus to learn more about what makes the different organs susceptible to infection,” explained Dr. Vikas Bansal, a data scientist at the DZNE’s Tuebingen site. “Therefore, we looked at different tissues to see which components of the cellular machinery might be relevant for infection and also which cell types appear to be particularly susceptible.” Bansal co-authored the current paper with Manvendra Singh, a Cornell presidential fellow, and with Cedric Feschotte, professor in the Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics at Cornell University.
The genetics of blood: A global perspective
What’s the risk of different human populations to develop a disease? To find out, a team led by Université de Montréal professor Guillaume Lettre created an international consortium to study the blood of hundreds of thousands of people worldwide.
In one of the largest studies of its kind, published today in Cell, close to 750,000 participants from five major populations—European, African, Hispanic, East Asian and South Asian—were tested to see the effect of genetic mutations on characteristics in their blood.
These characteristics include such things as hemoglobin concentration and platelet counts.

Sleep ‘cleans’ the brain
Sleep has critical roles in health and regeneration, and one of those is clearing the brain of metabolic waste, according to researchers from the US and Denmark.
Now, as reported in the journal Nature Communications, they’ve discovered in mice that the time of day matters, suggesting the process is controlled by circadian rhythms.
“Our group has shown that just being awake or asleep drastically changes how well the brain can clear waste,” says lead author Lauren Hablitz from the University of Rochester Medical Centre.