Disease diagnosis, drug discovery, robot delivery—artificial intelligence is already powering change in the pandemic’s wake. That’s only the beginning.


You might be interested in my latest interview with Natasha Vita-More, transhumanist writer and executive director of Humanity+, covering human augmentation, the world transhumanist movement and whole-body prosthetics.
Trying to grow my transhumanism related channel so super grateful for any subs: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCnVLqMgLDwO-aSk5YcYo1dA…
I interview Natasha Vita-More, a transhumanist thinker who wrote the ‘Transhumanist Statement’ and is the Executive Director of Humanity+, formerly the World Transhumanist Association.
We cover artificial intelligence, whole body prosthetics, radical life extension, upgrading the human body and the world transhumanist movement amongst other topics.
This week: Be The Match BioTherapies® (MN, USA) and NantKwest (CA, USA) collaborate to help progress a potential cell therapy for COVID-19-associated ARDS and a new platform from WuXi Advanced Therapies (PA, USA) may help accelerate cell and gene therapy development.
ECommunity, Future Science Group
If an unconscious person responds to smell through a slight change in their nasal airflow pattern — they are likely to regain consciousness. This is the conclusion from a new study conducted by Weizmann Institute scientists and colleagues at the Loewenstein Rehabilitation Hospital, Israel. According to the findings, published in the journal Nature, 100% of the unconscious brain-injured patients who responded to a “sniff test” developed by the researchers regained consciousness during the four-year study period. The scientists think that this simple, inexpensive test can aid doctors in accurately diagnosing and determining treatment plans according to the patients’ degree of brain injury. The scientists conclude that this finding once again highlights the primal role of the sense of smell in human brain organization. The olfactory system is the most ancient part of the brain, and its integrity provides an accurate measure of overall brain integrity.
Following severe brain injury, it is often difficult to determine whether the person is conscious or unconscious, and current diagnostic tests can lead to an incorrect diagnosis in up to 40% of cases. “Misdiagnosis can be critical as it can influence the decision of whether to disconnect patients from life support machines,” says Dr. Anat Arzi, who led the research. “In regard to treatment, if it is judged that a patient is unconscious and doesn’t feel anything, physicians may not prescribe them painkillers that they might need.” Arzi commenced this research during her doctoral studies in the group of Prof. Noam Sobel of the Weizmann Institute of Science’s Neurobiology Department and continued it as part of her postdoctoral research at the University of Cambridge’s Department of Psychology.
The “consciousness test” developed by the researchers — in collaboration with Dr. Yaron Sacher, Head of the Department of Traumatic Brain Injury Rehabilitation at Loewenstein Rehabilitation Hospital — is based on the principle that our nasal airflow changes in response to odor; for example, an unpleasant odor will lead to shorter and shallower sniffs. In healthy humans, the sniff-response can occur unconsciously in both wakefulness and sleep.
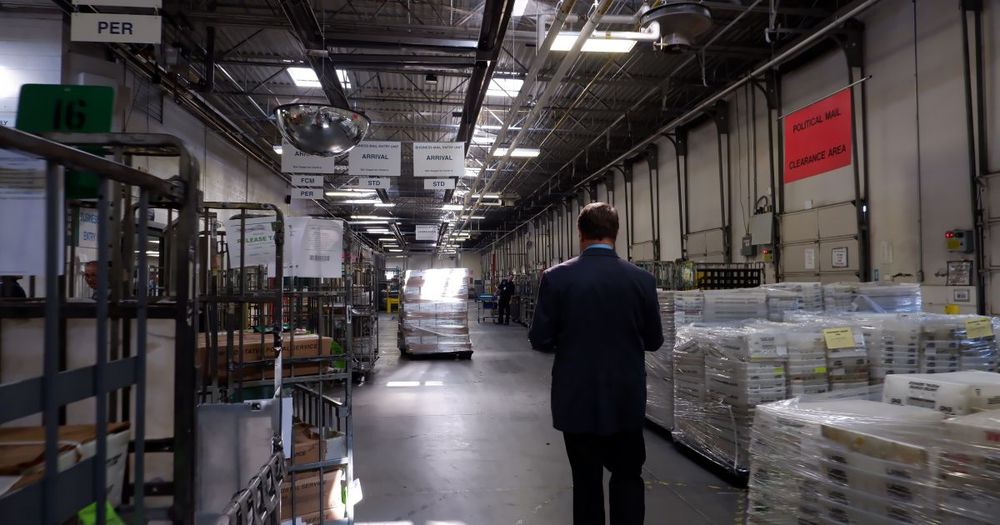

Denver Department of Public Health and Environment issued the order Thursday, the day after investigators said they were denied full access to the facility.
Denver health officials have ordered the closure of a United States Postal Service distribution center that handles all mail for Colorado and Wyoming, saying the facility has multiple confirmed cases of the coronavirus among its employees.

Last month, scientists at Oxford University began immunizing more than 1,000 volunteers with their vaccine candidate in a preliminary trial designed to test the shot’s safety. On Friday, the scientists announced they now aim to vaccinate 10,260 people across Britain, including older people and children.
“The clinical studies are progressing very well and we are now initiating studies to evaluate how well the vaccine induces immune responses in older adults and to test whether it can provide protection in the wider population,” said Andrew Pollard, head of the Oxford Vaccine Group.
British researchers testing an experimental vaccine against the new coronavirus are moving into advanced studies and aim to immunize more than 10,000 people to determine if the shot works.
Last month, scientists at Oxford University began vaccinating more than 1,000 volunteers in a preliminary study designed to test the shot’s safety. Those results aren’t in yet but on Friday, the scientists announced they’re expanding to 10,260 people across Britain, including older people and children.
If all goes smoothly, “it’s possible as early as the autumn or toward the end of the year, you could have results that allowed use of the vaccine on a wider scale,” predicted Andrew Pollard, head of the Oxford Vaccine Group.


“I do believe there’s great potential to bring in artificial intelligence to provide early warning of future problems” such as disease outbreaks, Air Force Lt. Gen. John N.T. “Jack” Shanahan, director of the Pentagon’s Joint Artificial Intelligence Center, said in an interview.
Artificial intelligence could spot and track earlier outbreaks of disease around the world, the Pentagon’s AI chief says as he retires from service.
In order to find and treat cancerous tumors, a team of scientists is working on an aggressive new approach that involves a swarm of tiny, cancer-killing robots.
The idea is to inject the nanobots, which are engineered to look and travel like white blood cells, into a patient’s veins and move them around inside the body with powerful magnets.
“Our vision was to create the next-generation vehicle for minimally invasive targeted drug delivery that can reach even deeper tissues inside the body with even more difficult access routes than what was previously possible,” Metin Sitti, Director of Physical Intelligence at the Max Planck Society, said in a press release.