Discover how Oxford Nanopore offers a single-platform solution that supports leading companies all the way through the drug development pathway — from discovery to clinical trials and manufacturing.





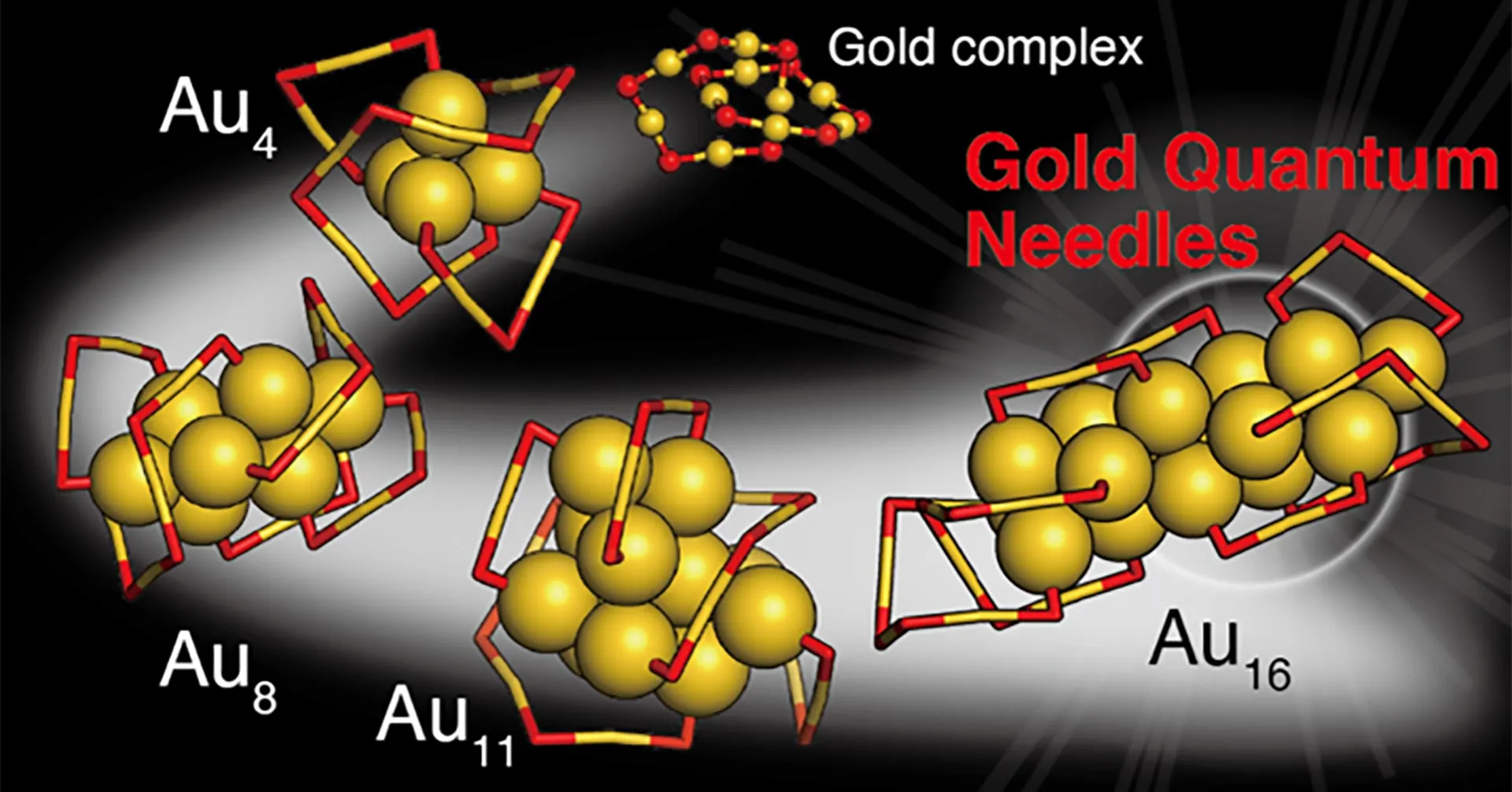
Scientists at the University of Tokyo have unveiled “gold quantum needles,” a newly discovered nanocluster structure formed under unusual synthesis conditions. Unlike typical spherical clusters, these elongated, pencil-shaped formations display unique quantum behaviors and respond to near-infrared light, making them promising tools for biomedical imaging and energy applications.

Edward Chang is a neurosurgeon, scientist, and a pioneering leader in functional neurosurgery and brain-computer interface technology, whose work spans the operating room, the research lab, and the engineering bench to restore speech and movement for patients who have lost these capabilities. In this episode, Edward explains the evolution of modern neurosurgery and its dramatic reduction in collateral damage, the experience of awake brain surgery, real-time mapping to protect critical functions, and the split-second decisions surgeons make. He also discusses breakthroughs in brain-computer interfaces and functional electrical stimulation systems, strategies for improving outcomes in glioblastoma, and his vision for slimmer, safer implants that could turn devastating conditions like ALS, spinal cord injury, and aggressive brain tumors into more manageable chronic illnesses.
View show notes here: https://bit.ly/46uJXlh.
Become a member to receive exclusive content: https://peterattiamd.com/subscribe/
Sign up to receive Peter’s email newsletter: https://peterattiamd.com/newsletter/
We discuss:
0:00:00 — Intro.
0:01:17 — The evolution of neurosurgery and the shift toward minimally invasive techniques.
0:10:58 — Glioblastomas: biology, current treatments, and emerging strategies to overcome its challenges.
0:17:39 — How brain mapping has advanced from preserving function during surgery to revealing how neurons encode language and cognition.
0:24:22 — How awake brain surgery is performed.
0:29:02 — How brain redundancy and plasticity allow some regions to be safely resected, the role of the corpus callosum in epilepsy surgery, and the clinical and philosophical implications of disconnecting the hemispheres.
0:43:46 — How neural engineering may restore lost functions in neurodegenerative disease, how thought mapping varies across individuals, and how sensory decline contributes to cognitive aging.
0:54:40 — Brain–computer interfaces explained: EEG vs. ECoG vs. single-cell electrodes and their trade-offs.
1:09:02 — Edward’s clinical trial using ECoG to restore speech to a stroke patient.
1:20:41 — How a stroke patient regained speech through brain–computer interfaces: training, AI decoding, and the path to scalable technology.
1:41:10 — Using brain-computer interfaces to restore breathing, movement, and broader function in ALS patients.
1:47:56 — The 2030 outlook for brain–computer interfaces.
1:52:35 — The potential of stem cell and cell-based therapies for regenerating lost brain function.
1:57:54 — Edward’s vision for how neurosurgery and treatments for glioblastoma, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease may evolve by 2040
2:00:43 — The rare but dangerous risk of vertebral artery dissections from chiropractic neck adjustments and high-velocity movements.
2:02:31 — How Harvey Cushing might view modern neurosurgery, and how the field has shifted from damage avoidance to unlocking the brain’s functions.
——-
About:
The Peter Attia Drive is a deep-dive podcast focusing on maximizing longevity, and all that goes into that from physical to cognitive to emotional health. With over 90 million episodes downloaded, it features topics including exercise, nutritional biochemistry, cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, mental health, and much more.
Peter Attia is the founder of Early Medical, a medical practice that applies the principles of Medicine 3.0 to patients with the goal of lengthening their lifespan and simultaneously improving their healthspan.

Many industrial products—from car bumpers to aerospace panels and medical implants—owe their performance to lightweight, cellular materials. These hard-working synthetics are engineered to meet specific functionality goals, but too often, defects introduced during the fabrication process can lead to subpar performance or even catastrophic failure.
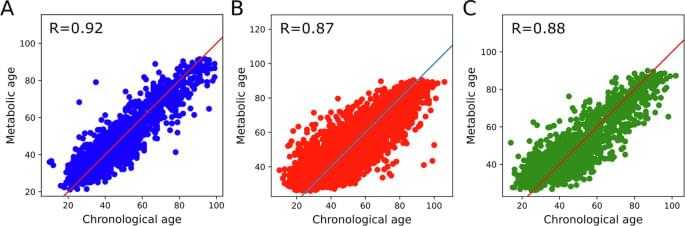
npj Metabolic Health and Disease volume 3, Article number: 35 (2025) Cite this article.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/