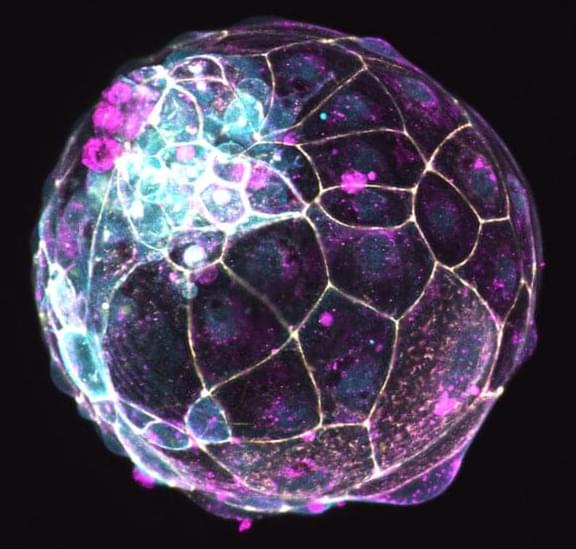
An influential scientific panel is pumping the brakes on stem cell-based embryo models — an umbrella term for the increasingly complex structures researchers are building from stem cells and growing in the lab to mimic aspects of embryonic development. In new guidelines released Monday, the International Society for Stem Cell Research called for stricter oversight of studies involving such models and the establishment of red lines against using them for certain activities.
Specifically, the latest guidelines say that researchers should not use any stem cell-based embryo models to try to start a pregnancy in a person or animal or grow them in an artificial womb to the point of viability, because of broad consensus that such experiments would be unethical. The new restrictions also extend to purposes beyond research, including commercial and reproductive.
Although the models that scientists have built thus far remain too primitive to reach that developmental milestone, the updated guidance is aimed at addressing an explosion of rapid advances in the field over the past several years that are already raising thorny ethical dilemmas.