Optimal culture conditions for cynomolgus monkey naive embryonic stem cells and improved procedures for chimeric embryo culture were developed to allow for high (20%–90%) donor cell contribution to chimeric monkeys.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 1,079
Advancing CAR-T Therapy Through Immunophenotyping
Adoptive cell therapy has emerged as a promising alternative treatment for hematological and solid cancers, with CAR-T therapy standing out as a prominent avenue. In this approach, T cells are genetically engineered with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) to enhance their targeting capabilities1–2. The outcome of CAR-T cell therapy hinges on a complex interplay of phenotype, activation, and functional profiling of these engineered cells. Immunophenotypic characterization of CAR-T cells assumes a pivotal role in ensuring treatment quality and facilitating continuous monitoring of treatment response1. In the process of immunophenotyping, engineered T cells are separated based on their markers to characterize the composition of the cell population within the sample. The strategic identification and isolation of specific CAR-T cell subsets is essential in augmenting therapy responses2.
Deciphering Cellular Composition, Defining CAR-T Therapy Efficacy
Immunophenotyping is a pivotal technique that combines specific antibodies with fluorescent compounds to reveal specific protein expression in cell populations to identify categorize the tagged cells. Immunophenotyping leverages the differences in surface markers among T cells, reflecting their differentiation, activation, and memory status2. These markers provide insights into immune cell development, function, proliferation potential, and long-term viability. The distinct surface marker profiles closely correlate with the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy3. Essential markers for immunophenotypic analysis, including CD3, CD4, CD8, CD45RA, CD34R0, CCR7, CD27, and CD95, are presented in Table 1.
Mind-Body Link Exposed: Unraveling the Physical Costs of Mental Disorders
Psychiatric patients almost twice as likely to have multiple physical ailments – new study.
A new study, conducted by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in collaboration with the University of Cambridge’s Biomedical Research Centre, has revealed significant findings about the physical health of psychiatric patients. This extensive analysis incorporated data from 19 different studies, involving 194,123 psychiatric patients globally, and compared them to 7,660,590 individuals in control groups.
Findings on Multimorbidity.

Maternal metabolic conditions linked to children’s neurodevelopmental risks, study shows
🤰 🧠 👶
Study investigates how maternal metabolic conditions like pregestational diabetes, gestational diabetes, and obesity mediate the risk of neurodevelopmental conditions in children. It highlights the significant role of obstetric and neonatal complications in this relationship, emphasizing the need for managing these complications to mitigate children’s risk of developing conditions like ADHD and autism.
The Impact of AI on Medical Records — The Medical Futurist
You requested a video exploring the future of medical records, and your wish is our command!
We’re aware that administrative tasks are often the bane of a physician’s work, contributing significantly to burnout. So, let’s embark on a journey together to discover how the future might unfold, and whether artificial intelligence has the potential to lighten this heavy burden.
New Gene Editing Treatment Cuts Dangerous Cholesterol in Small Study
So they volunteered for an experimental cholesterol-lowering treatment using gene editing that was unlike anything tried in patients before.
The result, reported Sunday by the company Verve Therapeutics of Boston at a meeting of the American Heart Association, showed that the treatment appeared to reduce cholesterol levels markedly in patients and that it appeared to be safe.
The trial involved only 10 patients, with an average age of 54. Each had a genetic abnormality, familial hypercholesterolemia, that affects around one million people in the United States. But the findings could also point the way for millions of other patients around the world who are contending with heart disease, which remains a leading cause of death. In the United States alone, more than 800,000 people have heart attacks each year.
BCM, Duke University to study surgery treatment for mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a highly fatal disease with a survival rate of under 10% at five years. New advances with immunotherapy have improved survival, but only 23% of patients are alive at three years when treated with immunotherapy alone. Surgery with chemotherapy has resulted in the longest survival. Baylor College of Medicine and Duke University will conduct a clinical trial for patients with mesothelioma to determine whether the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy prior to surgery is more effective in treating patients with mesothelioma.
Before surgery, the research team will give participants immunotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy. They plan to enroll 23 people in each arm between Baylor and Duke, and anyone with mesothelioma can participate. They will see participants in clinic to evaluate them prior to enrollment, prior to surgery and in follow-up continually.
“We will determine disease stage and make sure they’re physiologically strong enough for treatment. For patients who have disease that can be removed by surgery, we will randomize them to one of the two arms – either immunotherapy with two drugs, or immunotherapy with two chemotherapy agents. They will receive three cycles of each, then get reevaluated for surgery. They will then continue immunotherapy after surgery for one year,” said Dr. R. Taylor Ripley, associate professor of surgery in the Division of Thoracic Surgery and member of the Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center at Baylor.
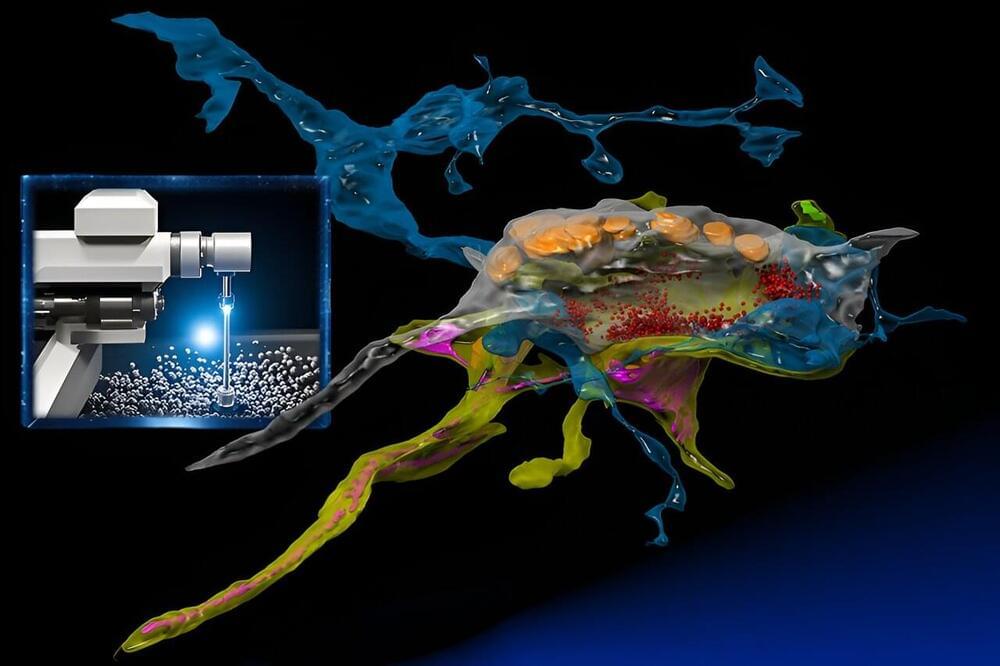
Using AI to optimize for rapid neural imaging
Connectomics, the ambitious field of study that seeks to map the intricate network of animal brains, is undergoing a growth spurt. Within the span of a decade, it has journeyed from its nascent stages to a discipline that is poised to (hopefully) unlock the enigmas of cognition and the physical underpinning of neuropathologies such as in Alzheimer’s disease.
At its forefront is the use of powerful electron microscopes, which researchers from the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and the Samuel and Lichtman Labs of Harvard University bestowed with the analytical prowess of machine learning. Unlike traditional electron microscopy, the integrated AI serves as a “brain” that learns a specimen while acquiring the images, and intelligently focuses on the relevant pixels at nanoscale resolution similar to how animals inspect their worlds.
“SmartEM” assists connectomics in quickly examining and reconstructing the brain’s complex network of synapses and neurons with nanometer precision. Unlike traditional electron microscopy, its integrated AI opens new doors to understand the brain’s intricate architecture. “SmartEM: machine-learning guided electron microscopy” has been published on the pre-print server bioRxiv.

Move Over, CRISPR: Algae and Snails Are Hiding Gene Editing Superpowers
New research finds RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule similar to DNA that is essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. Both are nucleic acids, but unlike DNA, RNA is single-stranded. An RNA strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (ribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases—adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine ©, or guanine (G). Different types of RNA exist in the cell: messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).