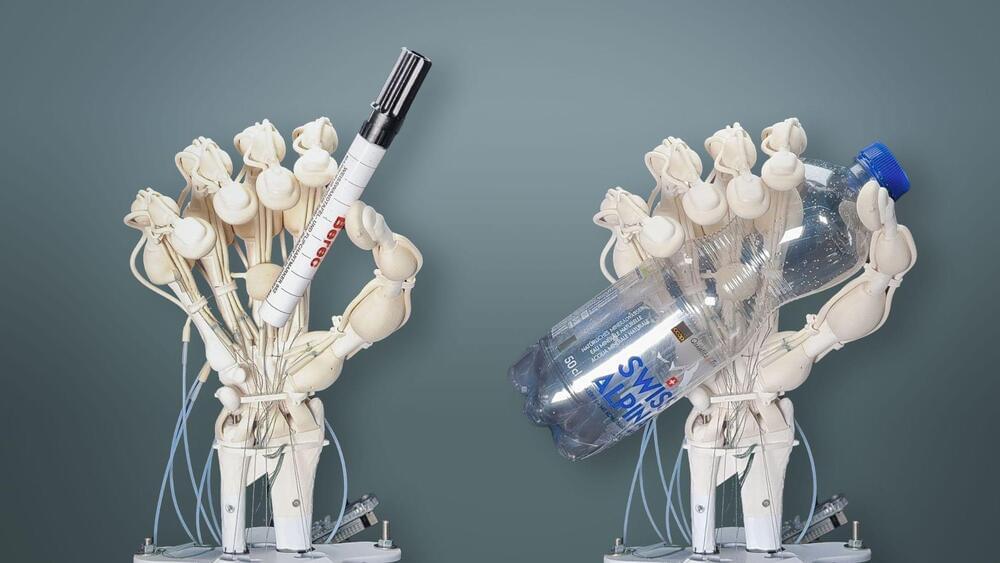
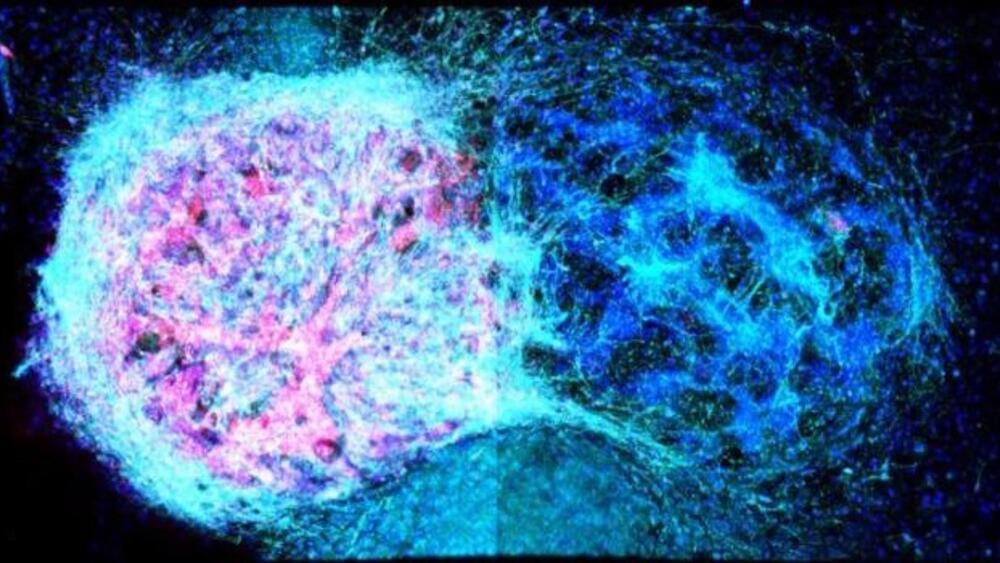
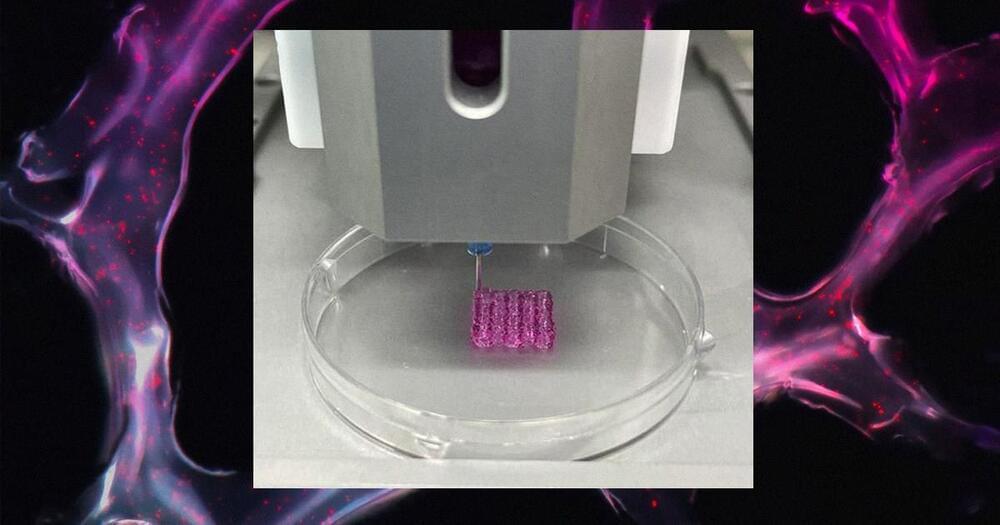
Here’s my latest Opinion piece just out for Newsweek…focusing on cyborg rights.
Over the past half-century, the microprocessor’s capacity has doubled approximately every 18–24 months, and some experts predict that by 2030, machine intelligence could surpass human capabilities. The question then arises: When machines reach human-level intelligence, should they be granted protection and rights? Will they desire and perhaps even demand such rights?
Beyond advancements in microprocessors, we’re witnessing breakthroughs in genetic editing, stem cells, and 3D bioprinting, all which also hold the potential to help create cyborg entities displaying consciousness and intelligence. Notably, Yale University’s experiments stimulating dead pig brains have ignited debates in the animal rights realm, raising questions about the ethical implications of reviving consciousness.
Amid these emerging scientific frontiers, a void in ethical guidelines exists, akin to the Wild West of the impending cyborg age. To address these ethical challenges, a slew of futurist-oriented bills of rights have emerged in the last decade. One of the most prominent is the Transhumanist Bill of Rights, which is in its third revision through crowdsourcing and was published verbatim by Wired in 2018.
These cyborg bills encompass a broad array of protections, including safeguards for thinking robots, gender recognition for virtual intelligences, regulations for genetically engineered sapient beings, and the defense of freedoms for biohackers modifying their bodies. Some also incorporate tech-driven rules to combat environmental threats like asteroids, pandemics, and nuclear war.