Researchers develop DVAP, a groundbreaking 3D printing technique using sono-ink and ultrasound waves for deep-tissue biomedical applications.

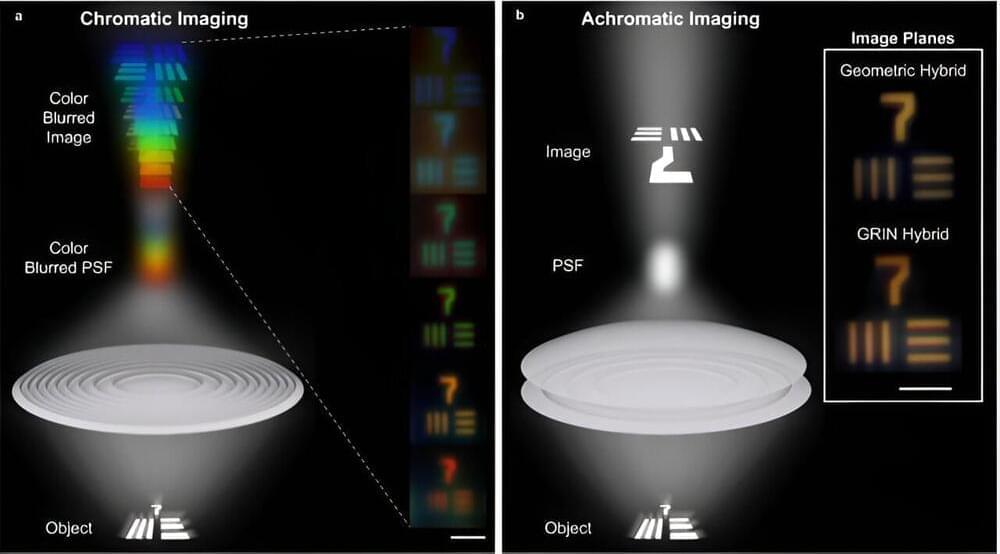
Using 3D printing and porous silicon, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed compact, visible wavelength achromats that are essential for miniaturized and lightweight optics. These high-performance hybrid micro-optics achieve high focusing efficiencies, while minimizing volume and thickness. Further, these microlenses can be constructed into arrays to form larger area images for achromatic light-field imagers and displays.
This study was led by materials science and engineering professors Paul Braun and David Cahill, electrical and computer engineering professor Lynford Goddard and former graduate student Corey Richards. The results of this research were published in Nature Communications.
“We developed a way to create structures exhibiting the functionalities of classical compound optics but in highly miniaturized thin from, via non-traditional fabrication approaches,” says Braun.
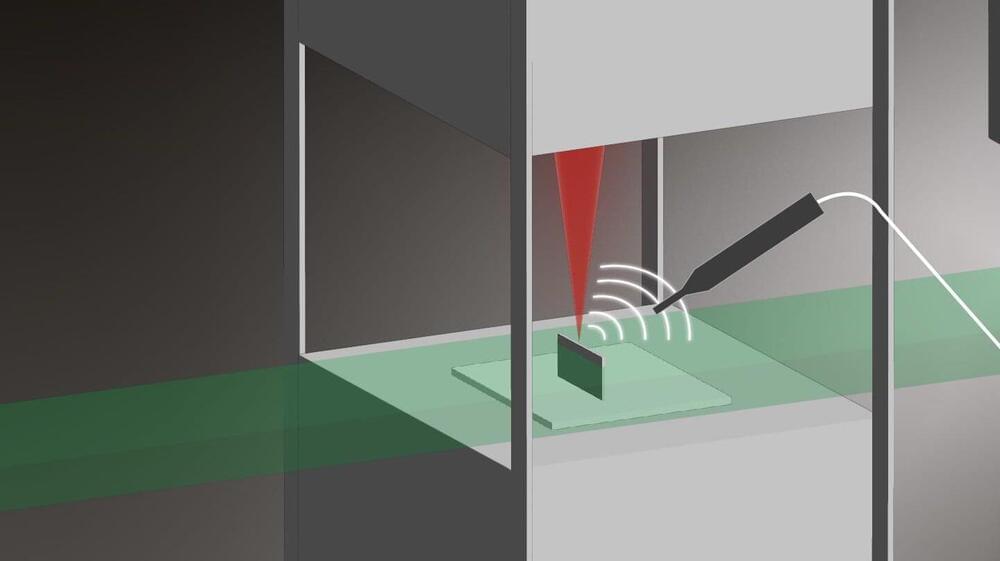
Researchers from EPFL have resolved a long-standing debate surrounding laser additive manufacturing processes with a pioneering approach to defect detection.
The progression of laser additive manufacturing —which involves 3D printing of metallic objects using powders and lasers—has often been hindered by unexpected defects. Traditional monitoring methods, such as thermal imaging and machine learning algorithms, have shown significant limitations. They often either overlook defects or misinterpret them, making precision manufacturing elusive and barring the technique from essential industries like aeronautics and automotive manufacturing.
But what if it were possible to detect defects in real-time based on the differences in the sound the printer makes during a flawless print and one with irregularities? Up until now, the prospect of detecting these defects this way was deemed unreliable. However, researchers at the Laboratory of Thermomechanical Metallurgy (LMTM) at EPFL’s School of Engineering have successfully challenged this assumption.
Good telescope that I’ve used to learn the basics: https://amzn.to/35r1jAk.
Get a Wonderful Person shirt: https://teespring.com/stores/whatdamath.
Alternatively, PayPal donations can be sent here: http://paypal.me/whatdamath.
Hello and welcome! My name is Anton I’m away for a few days due to voice issues, so enjoy this older video where we talk about the incredible invention of 3D printed bio ink that could be used to print any biological tissue (in theory). 3D printed heart anyone?
Links:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26791-x.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-666X/12/8/865
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/09/210921134345.htm.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibrin.
Bladder grown from 3D bioprinted tissue continues to function after 14 years
https://www.ascb.org/science-news/bioprinting-ethical-and-societal-implications/
Biocomputing: https://youtu.be/nszcPNhYRzI
Artificial cell: https://youtu.be/0MRGJNKACYs.
Synthethic genome: https://youtu.be/OxVZPKmm58M
0:00 History of 3D printing organs.
2:00 Why this is important for medical studies.
2:45 Bioink invention.
3:40 How this works.
5:30 Results from the study are quite incredible.
6:30 Future of medical 3D printing.
Support this channel on Patreon to help me make this a full time job:
https://www.patreon.com/whatdamath.
Bitcoin/Ethereum to spare? Donate them here to help this channel grow!
bc1qnkl3nk0zt7w0xzrgur9pnkcduj7a3xxllcn7d4
or ETH: 0x60f088B10b03115405d313f964BeA93eF0Bd3DbF
Space Engine is available for free here: http://spaceengine.org.
Researchers report that they have developed a new composite material designed to change behaviors depending on temperature in order to perform specific tasks. These materials are poised to be part of the next generation of autonomous robotics that will interact with the environment.
The new study conducted by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign civil and environmental engineering professor Shelly Zhang and graduate student Weichen Li, in collaboration with professor Tian Chen and graduate student Yue Wang from the University of Houston, uses computer algorithms, two distinct polymers, and 3D printing to reverse engineer a material that expands and contracts in response to temperature change with or without human intervention.
The study findings are reported in the journal Science Advances.

The technique represents an important step in engineering skin grafts, drug testing. A team led by scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute has 3D-printed hair follicles in human skin tissue cultured in the lab. This marks the first time researchers have used the technology to generate hair follicles, which play an important role in skin healing and function.
The finding, published in the journal Science Advances, has potential applications in regenerative medicine and drug testing, though engineering skin grafts that grow hair are still several years away.
“Our work is a proof-of-concept that hair follicle structures can be created in a highly precise, reproducible way using 3D-bioprinting. This kind of automated process is needed to make future biomanufacturing of skin possible,” said Pankaj Karande, Ph.D., an associate professor of chemical and biological engineering and a member of Rensselaer’s Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies, who led the study.

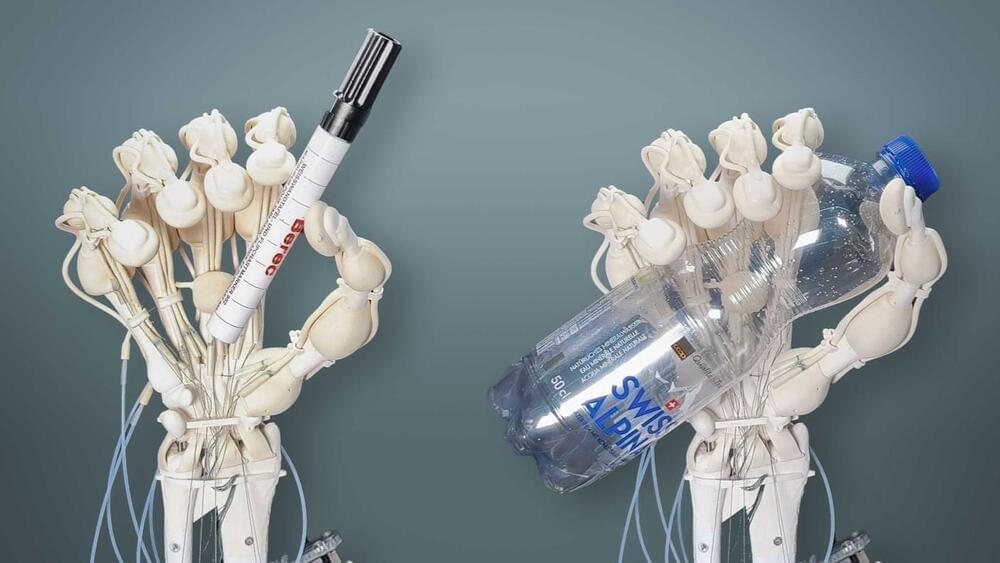
With 3D inkjet printing systems, engineers can fabricate hybrid structures that have soft and rigid components, like robotic grippers that are strong enough to grasp heavy objects but soft enough to interact safely with humans.
These multimaterial 3D printing systems utilize thousands of nozzles to deposit tiny droplets of resin, which are smoothed with a scraper or roller and cured with UV light. But the smoothing process could squish or smear resins that cure slowly, limiting the types of materials that can be used.
Researchers from MIT, the MIT spinout Inkbit, and ETH Zurich have developed a new 3D inkjet printing system that works with a much wider range of materials. Their printer utilizes computer vision to automatically scan the 3D printing surface and adjust the amount of resin each nozzle deposits in real time to ensure no areas have too much or too little material.
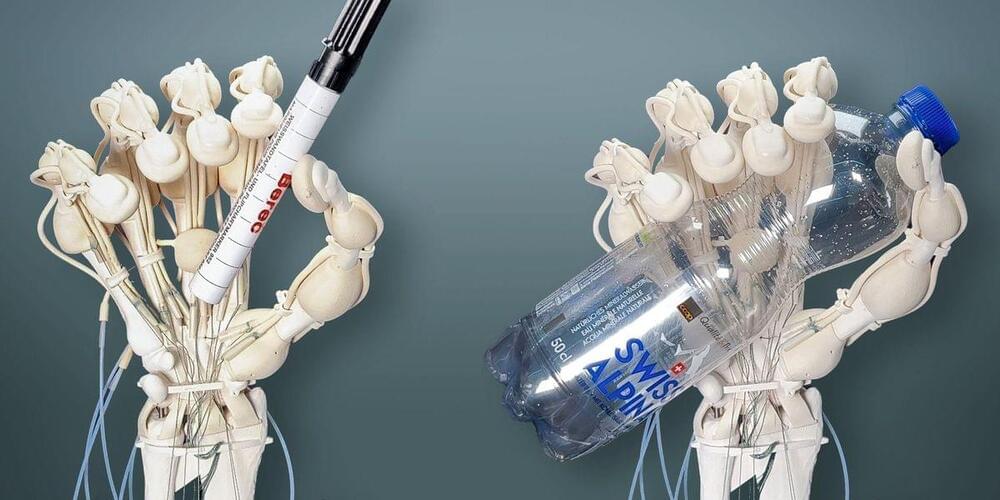
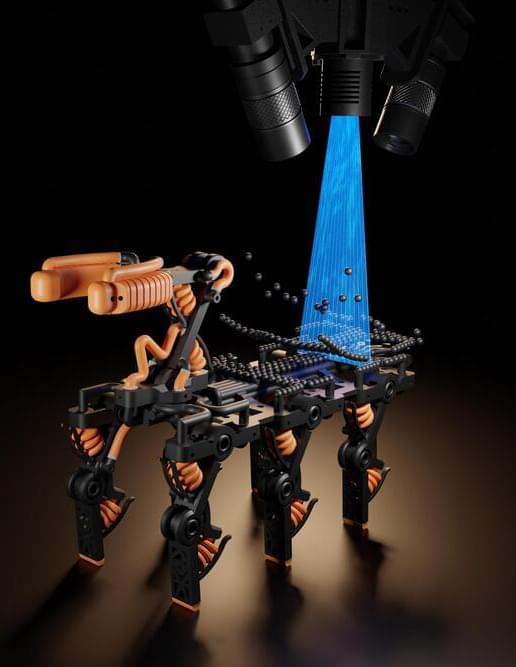
3D printing is advancing rapidly, and the range of materials that can be used has expanded considerably. While the technology was previously limited to fast-curing plastics, it has now been made suitable for slow-curing plastics as well. These have decisive advantages as they have enhanced elastic properties and are more durable and robust.
The use of such polymers is made possible by a new technology developed by researchers at ETH Zurich and a US start-up. As a result, researchers can now 3D print complex, more durable robots from a variety of high-quality materials in one go. This new technology also makes it easy to combine soft, elastic, and rigid materials. The researchers can also use it to create delicate structures and parts with cavities as desired.