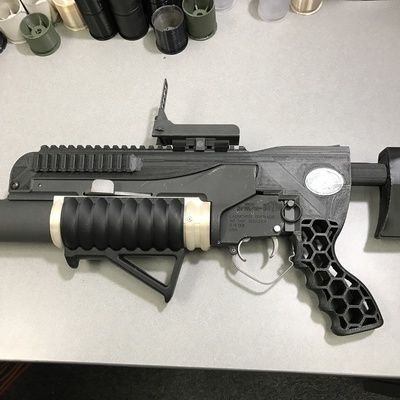
As this example shows, 3D printing has come a long way, quickly. In February 2011, when The Economist ran a story called “Print me a Stradivarius”, the idea of printing objects still seemed extraordinary. Now, it is well established. Additive manufacturing, as it is known technically, is speeding up prototyping designs and is also being used to make customised and complex items for actual sale.
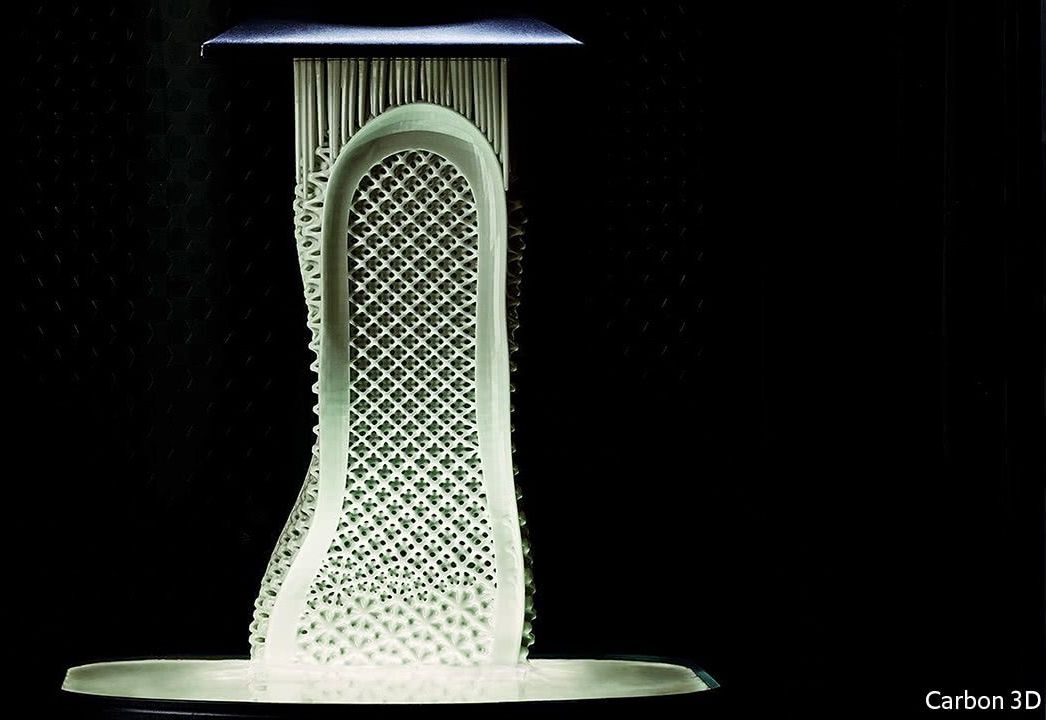
SLOWLY but surely the sole of a shoe emerges from a bowl of liquid resin, as Excalibur rose from the enchanted lake. And, just as Excalibur was no ordinary sword, this is no ordinary sole. It is light and flexible, with an intricate internal structure, the better to help it support the wearer’s foot. Paired with its solemate it will underpin a set of trainers from a new range planned by Adidas, a German sportswear firm.
Adidas intends to use the 3D-printed soles to make trainers at two new, highly automated factories in Germany and America, instead of producing them in the low-cost Asian countries to which most trainer production has been outsourced in recent years. The firm will thus be able to bring its shoes to market faster and keep up with fashion trends. At the moment, getting a design to the shops can take months. The new factories, each of which is intended to turn out up to 500,000 pairs of trainers a year, should cut that to a week or less.