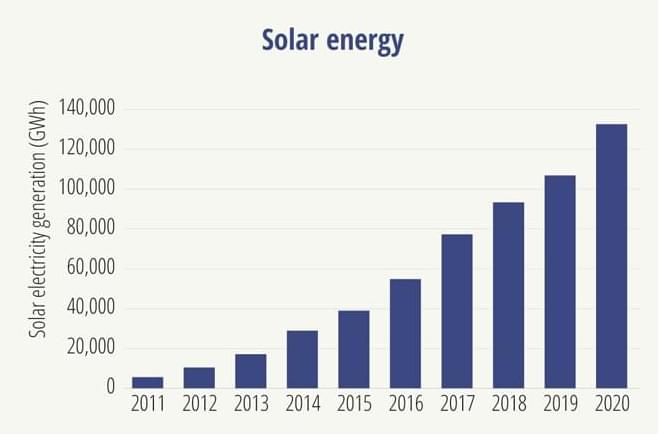
A new report, published this week, highlights the explosive growth in solar, wind, electric vehicles, and other clean tech in the United States.


Am I talking to a software robot or a human? It’s a question that many of us will have posed at some point when we are online interacting with a web interface chatbot with its chirpy ‘Hi! Can I help?’ message flags and discussion box.
Some of us deliberately try and second guess these bots in order to be able to work out whether we are talking to a machine or a person. We do this because we somehow hope that this knowledge will enable us to assess more accurately how much help we are likely to get — and so, perhaps, get an idea of how much effort we should put into explaining our customer issues or requests.
Right now, it is not necessarily that difficult to know if you are speaking to an Artificial Intelligence (AI) engine. The Turing test was of course established to rate the point at which people can’t tell the difference between a human and a machine. The AI software robot ‘bots’ that have passed the Turing test so far have been given quirky personality traits to mask the challenges that even the best AI engines have when dealing with human conversational challenges.

With the proliferation of AI programs into the strategy gaming spaces, should human players bother competing at all? In a world where artificial intelligence (AI) learns from its mistakes and progresses with every match, it’s hard to tell. A computer can learn from its mistakes in an instant and play millions of hands in seconds.
While it might take a human a lifetime to master the game of poker, an AI could become unbeatable overnight. This reality has raised a lot of questions in the world of strategy games.
AI is an ever-evolving field that can be difficult to understand. One of the most common ways for non-techies to get introduced to AI is through online poker, where humans are pitted against artificial intelligence in a game of cards. Which raises the question: when does one become indistinguishable from the other?
Becoming Immortal through Mind Uploading sounds like something that’ll only be possible around the 2100’s. But amazingly, a group of scientists at Nectome are working on giving us the ability to live forever inside of a computer simulation by the end of this decade for around 10000$.
Ray Kurzweil, director of engineering at Google, has long predicted that people will be able to upload their entire brains to computers and become digitally immortal by 2045. Kurzweil made this claim for many years, e.g. during his speech in 2013 at the Global Futures 2045 International Congress in New York, which claims to subscribe to a similar set of beliefs. Mind uploading has also been advocated by a number of researchers in neuroscience and artificial intelligence, such as the late Marvin Minsky.
–
If you enjoyed this video, please consider rating this video and subscribing to our channel for more frequent uploads. Thank you! smile
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 The Future is near.
01:46 How this procedure works.
03:31 The development of this technology.
04:24 Is this actually possible to achieve?
06:58 The ethical concerns.
07:40 Last Words.
–
#longevity #minduploading #bci
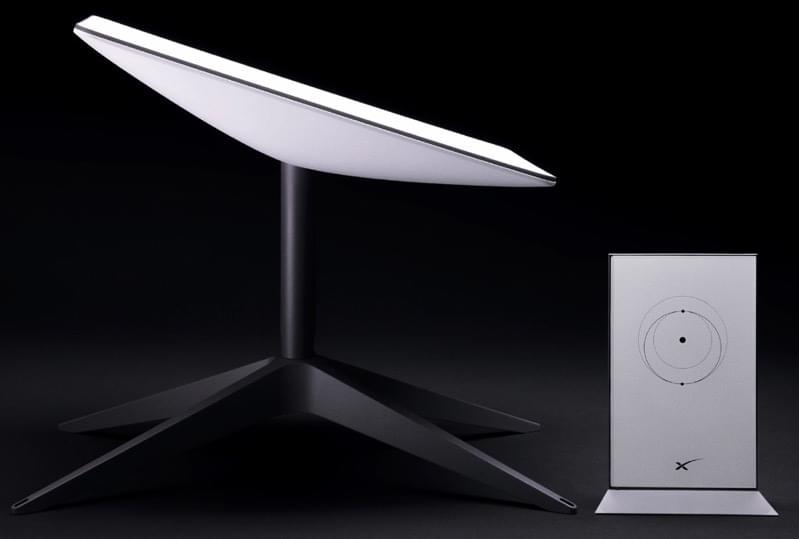

It is interesting to see Starlink evolve and move towards massive expansion. Currently, Starlink has only launched 64 laser satellites but this number should grow dramatically in the coming months. (All future Starlink satellites will include lasers.)
Their new Starlink dish will be a lot cheaper to produce which is important as originally the first Starlink dish cost $3,000 to make and SpaceX was selling it for $500. It has already gone through multiple generations and this rectangular dish should cost around $650 to make. (With the original dish, if they had sold a million of them, they would have lost 2.5 billion dollars which would have been painful.)
SpaceX has unveiled a new Starlink satellite dish, sporting a new rectangular design for customers in the United States. The company’s website is showing the new design for visitors showing U.S. IP addresses.
Canadian visitors, for example, are still seeing the old design, as the new dish is not available outside the U.S. yet.

O,.o.
A near-Earth asteroid known as Kamo‘oalewa might be made of a stray chunk of the Moon, scientists have said.
Kamo‘oalewa is one of a mysterious and little-understood set of objects called quasi-satellites. It is an asteroid that orbits around the Sun but remains close to the Earth.
As with all objects of that type, Kamo‘oalewa is difficult to observe. Though it is relatively close to the Earth – it comes as close as 9 million mile away – it is also very faint, about 4 million times darker than the faintest star humans can see in the sky.
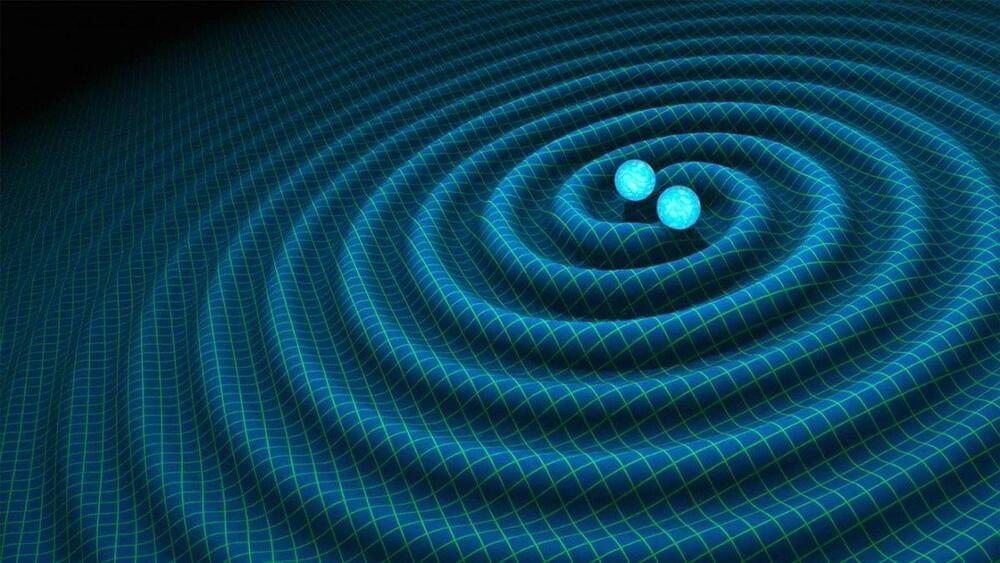
Scientists have released the largest catalog of gravitational wave detections to date, shedding new light on interactions between the most massive objects in the universe, black holes and neutron stars.
The catalog was compiled by three groundbreaking detectors: the two Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detectors located in Hanford, Washington, and Livingston, Louisiana, and the European Virgo gravitational wave antenna in Pisa, Italy.
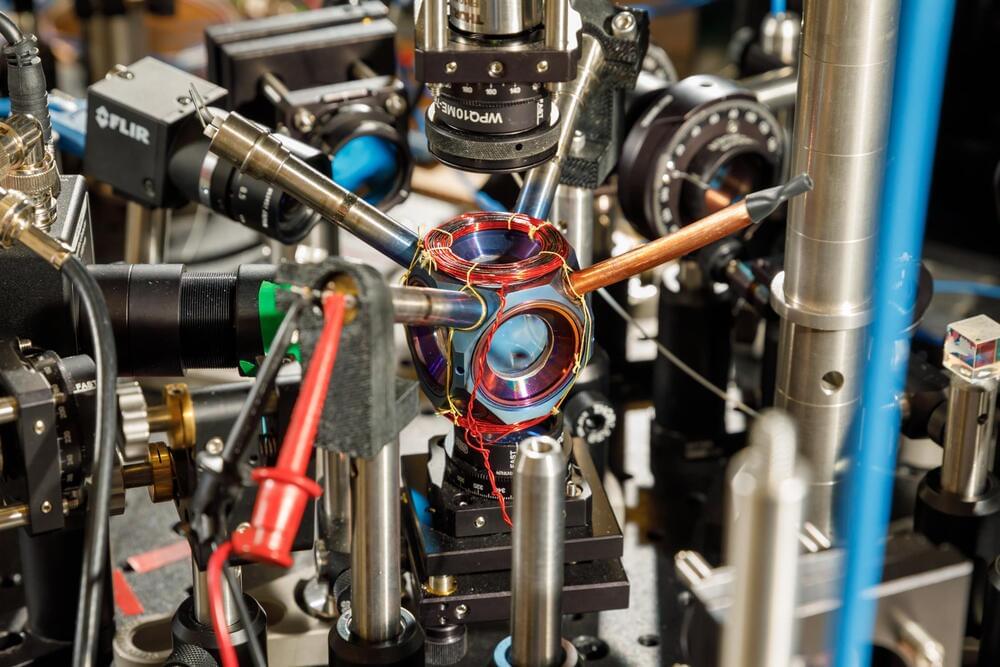
Sandia National Laboratories is developing an avocado-sized vacuum chamber made out of titanium and sapphire that could one day use quantum mechanical sensors to provide GPS-grade navigation without the need for satellites.
In only a few short decades, GPS has gone from a military technology to finding so many everyday applications that modern society is now dependent on it. However, GPS is not always available in places like high polar latitudes or in deep mountain valleys, and it can be jammed or spoofed.
The vulnerability of GPS and similar systems lies in their dependence on constellations of satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites emit time-stamped signals that are synced to atomic clocks. Using these signals, a GPS receiver in something as small as a wristwatch can use the Doppler effect on the satellite signals as they pass overhead to make an extremely precise fix on the receiver’s position and velocity. If these signals are interrupted or corrupted, the system fails.
*To date, most studies have focused on understanding how much carbon is stored above ground (in trees and other plants, for example). This research, however, revealed that when you look below ground and get into deeper levels of soil, there are massive deposits of carbon.*
Canada’s first-ever national carbon map reveals the location of billions — yes, billions — of tonnes of carbon stored in ecosystems across the country. This data, and how we use it, could alter the pace of climate change.
Over the span of two years, researchers fed data from existing soil samples collected from across the country, as well as long-term satellite data and topographic and climate variables, into a machine-learning algorithm. Researchers were able to estimate carbon at a 250-metre spatial resolution in different carbon pools (soils and plant biomass), as well as at multiple depths (1−2 metres).
Tens of thousands of field measurements were fed into a machine-learning algorithm to train satellite observations, including space-based laser scanning data, to estimate carbon stocks in plant biomass and soils across Canada. The resulting national carbon map will have a huge impact on the way conservation activities and policies are approached to prioritize nature-based climate solutions.
## ORIGINAL PAPER
Large soil carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of Canada