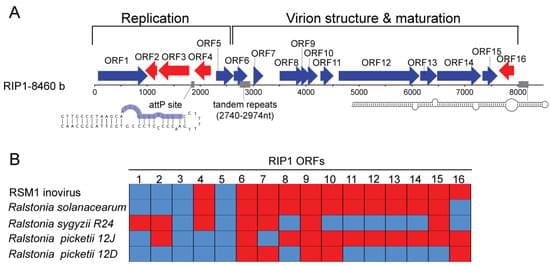
Viruses infecting bacteria (bacteriophages) represent the most abundant viral particles in the human body. They participate in the control of the human-associated bacterial communities and play an important role in the dissemination of virulence genes. Here, we present the identification of a new filamentous single-stranded DNA phage of the family Inoviridae, named Ralstonia Inoviridae Phage 1 (RIP1), in the human blood. Metagenomics and PCR analyses detected the RIP1 genome in blood serum, in the absence of concomitant bacterial infection or contamination, suggesting inovirus persistence in the human blood. Finally, we have experimentally demonstrated that the RIP1-encoded rolling circle replication initiation protein and serine integrase have functional nuclear localization signals and upon expression in eukaryotic cells both proteins were translocated into the nucleus. This observation adds to the growing body of data suggesting that phages could have an overlooked impact on the evolution of eukaryotic cells.
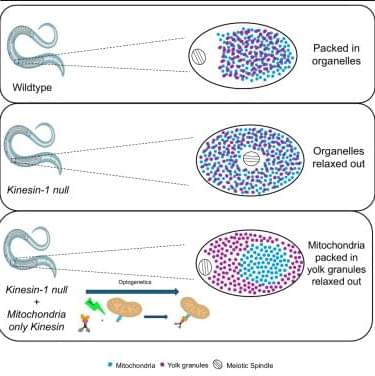
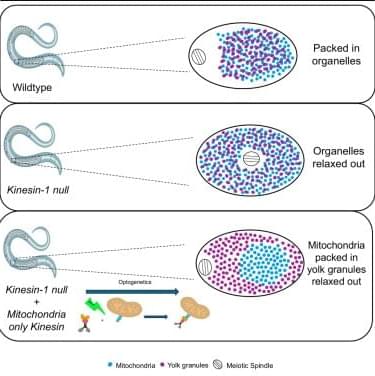
Aquino et al. find that kinesin-driven transport of mitochondria toward the center of a C. elegans oocyte is sufficient to drive movement of the meiotic spindle in the opposite direction to the periphery of the oocyte.
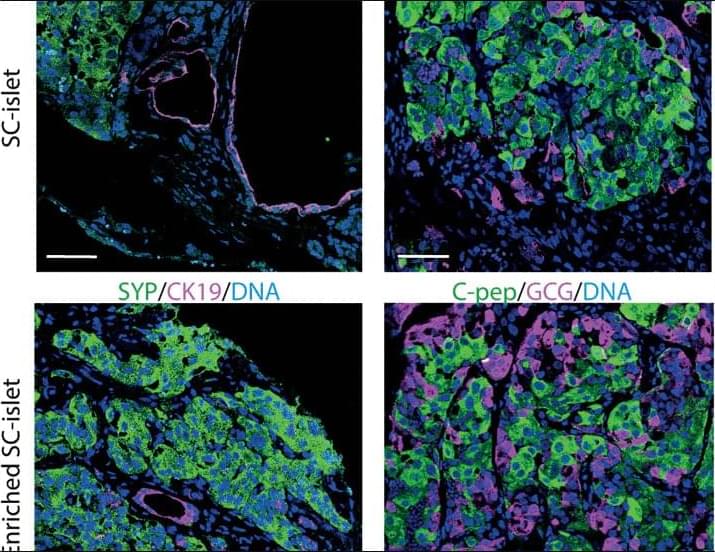
Immune evasion of human stem-cell-derived neural graft in rodent models.
Transplantation rejection is the main challenge in human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived therapies.
The researchers used hPSC line (termed H1-FS-8IM), engineered to overexpress 8 immunomodulatory transgenes, to enable transplant immune evasion.
They show in co-cultures, H1-FS-8IM PSC-derived midbrain neurons evaded rejection by T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
The authors also provide preclinical evidence of pluripotent stem cell line evading immune detection after neural engraftment in a humanized immune system mouse model and reversal of motor symptoms in Parkinsonian rats.
Incorporation of a suicide gene within the universal donor cell ensures safety for cell-based therapies. https://sciencemission.com/A-cloaked-human-stem-cell-derived-neural-graft
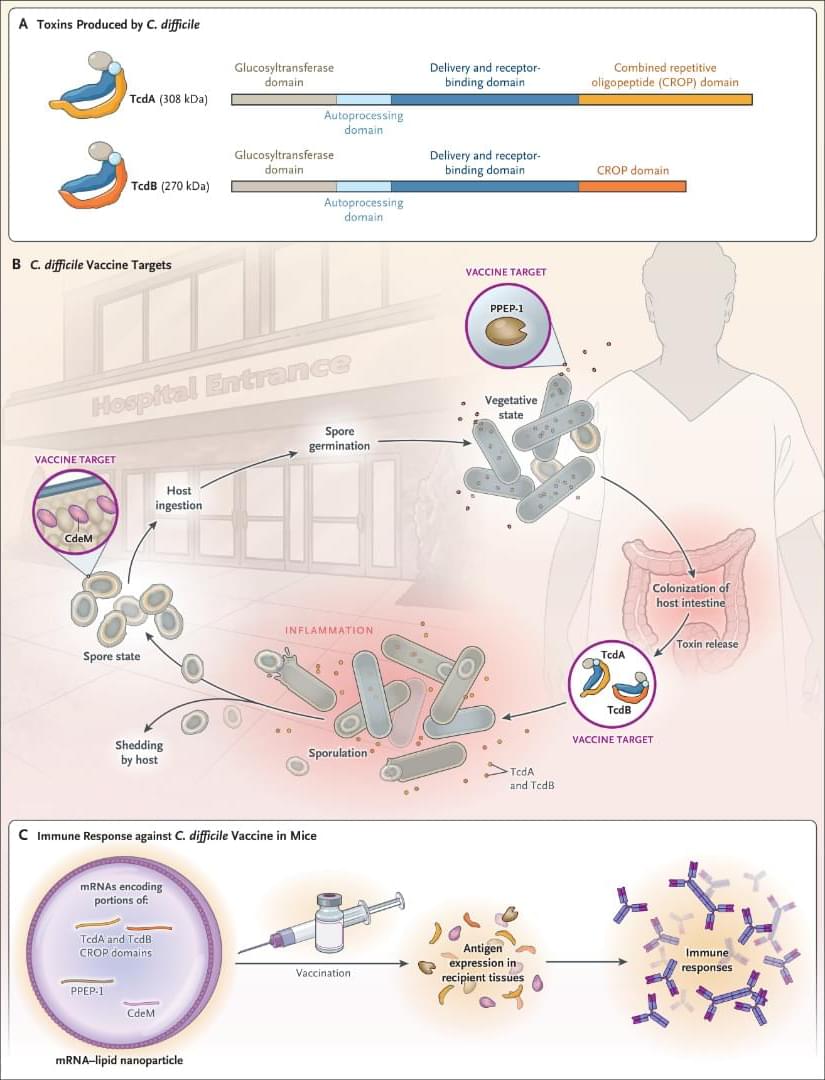
A recent study of an mRNA vaccine in a mouse model of Clostridioides difficile infection provided proof of concept of a protective effect.
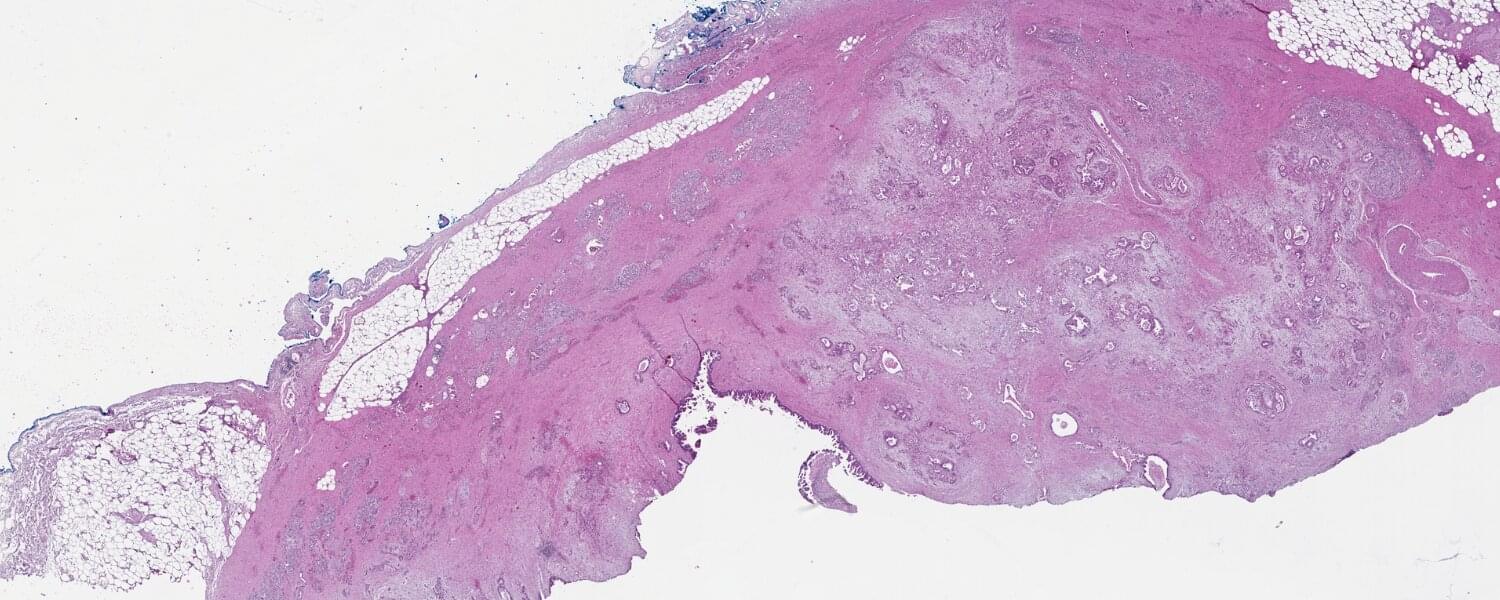
Van Andel Institute scientists and collaborators have developed a new method for identifying and classifying pancreatic cancer cell subtypes based on sugars found on the outside of cancer cells.
These sugars, called glycans, help cells recognize and communicate with each other. They also act as a cellular “signature,” with each subtype of pancreatic cancer cell possessing a different composition of glycans.
The new method, multiplexed glycan immunofluorescence, combines specialized software and imaging techniques to pinpoint the exact mix of pancreatic cancer cells that comprise tumors. In the future, this information may aid in earlier, more precise diagnosis.
The team at Omron Sinic X say that, by 2050, they hope their AI can conduct whole experiments independently of human scientists.
Reports of extraterrestrial beings, particularly the iconic “grey aliens,” have permeated modern folklore and ufology since the mid-20th century. These beings — typically described as small-statured humanoids with large, black almond-shaped eyes, diminutive noses and mouths, and grey skin — have become embedded in our cultural consciousness (Sagan, 1995). But what if these entities are not visitors from distant stars, but rather glimpses of our own evolutionary future? This essay explores a compelling hypothesis: that the grey aliens reported in countless encounters might be evolved or bio-engineered humans from our future, adapted specifically for subterranean existence following a global catastrophe.
Humanity stands at a crossroads of existential risk. Climate change, nuclear proliferation, biological warfare capabilities, and ecological collapse represent just a few of the potential calamities that could force a dramatic reshaping of human civilization (Bostrom, 2013). If surface conditions on Earth became inhospitable — whether through nuclear winter, extreme solar radiation following ozone depletion, or uninhabitable surface temperatures — surviving populations might be driven underground, initiating a profound evolutionary divergence.
“When faced with extinction-level threats, species often undergo rapid adaptation to secure their survival,” notes evolutionary biologist Dr. Elena Rodriguez (2022, p. 87). “Humans, with their capacity for technological intervention in their own biology, could potentially accelerate this process by orders of magnitude.”
Stargate SG1 (TV Program),Stargate Atlantis (TV Program),David Hewlett, Rodney McKay,actor,writer,director,father,son,parenting, Dad,family,stargate atlantis t…