Page 4
Sep 13, 2024
Quantinuum accelerates the path to Universal Fully Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computing
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, quantum physics

More recently, in a period where we upgraded our H2 system from 32 to 56 qubits and demonstrated the scalability of our QCCD architecture, we also hit a quantum volume of over two million, and announced that we had achieved “three 9’s” fidelity, enabling real gains in fault-tolerance – which we proved within months as we demonstrated the most reliable logical qubits in the world with our partner Microsoft.
We don’t just promise what the future might look like; we demonstrate it.
Sep 13, 2024
St. Jude is forging a new frontier in gene editing for cystic fibrosis
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
St. Jude’s Liz Kellogg, Ph.D., uses cryo-EM to study programmable transposons for targeted gene therapies, including potential new treatments for cystic fibrosis.
Sep 13, 2024
Future of CRISPR: Gene Editing Technologies Herald Landmark Clinical Trials
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
The future of CRISPR involves clinical trials focused on treatment for blood diseases and cancers, cardiovascular disease, T1D, and HIV.
Sep 13, 2024
Scientists Puzzled by Hundreds of Little Red Dots in James Webb Images of Distant Universe
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: space

Captured by the James Webb, the Little Red Dots indicate galaxies we’ve never seen before, and what’s inside them is unclear.
Sep 13, 2024
Einstein’s famous equation first demonstrated the creation of matter from light
Posted by Josh Seeherman in categories: energy, information science, physics
Scientists Create Matter from Pure Light, Demonstrating Einstein’s E=mc² Equation in Action.
Physicists at Brookhaven National Laboratory have achieved a groundbreaking experiment, creating matter from light by demonstrating the Breit-Wheeler process. Using the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider, they accelerated heavy ions to generate nearly real photons, leading to the formation of electron-positron pairs. This experiment showcases Einstein’s E=mc² equation in action, aligning with predictions for transforming energy into matter. While these virtual photons act similarly to real ones, the experiment is a crucial step towards proving the process with real photons when technology advances to create gamma-ray lasers. Don’t forget to comment your thought about this!
Sep 13, 2024
Time to Rethink the Big Bang? New Research Suggests Universal Expansion May Not Be What It Seems
Posted by Paul Battista in category: cosmology
A new study challenges the Big Bang theory, in favor of a nearly century old theory to explain the universe’s expansion.
Sep 13, 2024
Cancer breakthrough as new vaccine ‘stops tumours in their tracks and prevents new disease’
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
A GROUNDBREAKING cancer vaccine could stop tumours growing in patients with advanced disease, researchers say.
Designed to prime the body to recognise and fight cancer cells, the jab could stimulate the immune system to help treat the disease more effectively, early trial results show.
Researchers described the results as “an important first step” in developing a new treatment for people with advanced cancers.
Sep 13, 2024
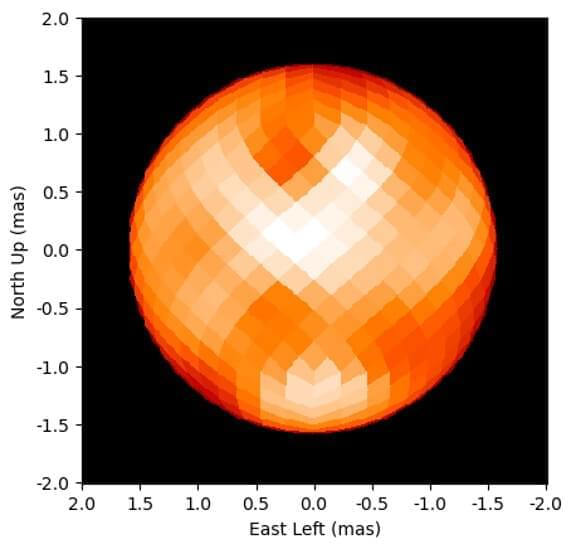
New View of North Star Reveals Spotted Surface
Posted by Natalie Chan in category: space
The team successfully tracked the orbit of the close companion and measured changes in the size of the Cepheid as it pulsated. The orbital motion showed that Polaris has a mass five times larger than that of the Sun. The images of Polaris showed that it has a diameter 46 times the size of the Sun.
The biggest surprise was the appearance of Polaris in close-up images. The CHARA observations provided the first glimpse of what the surface of a Cepheid variable looks like.
CHARA Array false-color image of Polaris from April 2021 that reveals large bright and dark spots on the surface. Polaris appears about 600,000 times smaller than the Full Moon in the sky.
Sep 13, 2024
Gut Microbial Pathway identified as Target for Improved Heart Disease Treatment
Posted by Natalie Chan in category: biotech/medical
Cleveland Clinic researchers have made a significant discovery about how the gut microbiome interacts with cells to cause cardiovascular disease. The study published in Nature Communications found that phenylacetylglutamine (PAG), produced by gut bacteria as a waste product, then absorbed and formed in the liver, interacts with previously undiscovered locations on beta-2 adrenergic receptors on heart cells once it enters the circulation.
PAG was shown to interact with beta-2 adrenergic receptors to influence how forcefully the heart muscle cells contract—a process that investigators believe contributes to heart failure. Researchers showed mutating parts of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor that were previously thought to be unrelated to signaling activity in preclinical models prevented PAG from depressing the function of the receptor.
This is the latest in a series of investigations into PAG, led by Stanley Hazen, MD, Ph.D., chair of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Sciences in Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute and co-section head of Preventive Cardiology. Dr. Hazen’s lab previously demonstrated that elevated circulating levels of PAG in subjects are associated with heightened risk for developing heart failure, and lead to worse outcomes for patients with heart failure.