The tweak addresses the fact that generative AI tools have been stuffed into just about every piece of software professionals use.



Jack Dorsey, the co-founder of Twitter, launched BitChat over the weekend as a beta messaging app that works over Bluetooth networks rather than WiFi or mobile data.
Twitter co-founder and former CEO Jack Dorsey has launched a decentralised messaging app to take on WhatsApp and make communication possible without internet access.
Dorsey, who stepped down as CEO in 2021, wrote on social media that he had launched BitChat, a messaging network that works over Bluetooth networks, for beta testing over the weekend.

Elon Musk’s lawsuit against OpenAI aims to expose the company’s alleged abandonment of its non-profit mission and potential shift to a for-profit model, sparking a heated dispute over the company’s future and integrity ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Understanding the lawsuit timeline and stakes.
🔍 Q: When is Elon Musk’s lawsuit against OpenAI going to trial and what is he claiming?
A: The lawsuit is set to go to trial in April 2026, with Musk arguing he’s owed billions from the value of intellectual property developed from his contributions as the primary funder who wanted OpenAI to remain nonprofit and open source.
📄 Q: What evidence exists in Greg Brockman’s personal files from 2017?



This is the second time in recent months that the AI world has got all excited about math. The rumor mill went into overdrive last November, when there were reports that the boardroom drama at OpenAI, which saw CEO Sam Altman temporarily ousted, was caused by a new powerful AI breakthrough. It was reported that the AI system in question was called Q* and could solve complex math calculations. (The company has not commented on Q*, and we still don’t know if there was any link to the Altman ouster or not.) I unpacked the drama and hype in this story.
You don’t need to be really into math to see why this stuff is potentially very exciting. Math is really, really hard for AI models. Complex math, such as geometry, requires sophisticated reasoning skills, and many AI researchers believe that the ability to crack it could herald more powerful and intelligent systems. Innovations like AlphaGeometry show that we are edging closer to machines with more human-like reasoning skills. This could allow us to build more powerful AI tools that could be used to help mathematicians solve equations and perhaps come up with better tutoring tools.

One intriguing method that could be used to form the qubits needed for quantum computers involves electrons hovering above liquid helium. But it wasn’t clear how data in this form could be read easily.
Now RIKEN researchers may have found a solution. Their work is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
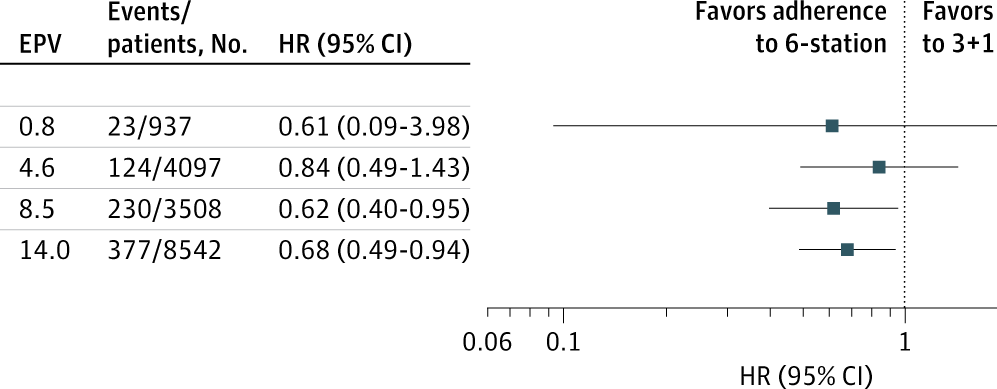
Guideline-adherent lymph node dissection provided a small survival benefit for patients with high-grade or no lepidic pattern LungAdenocarcinoma, but not for those with lepidic pattern alone.
Importance Lymph node dissection for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is controversial. Histologic pattern subtyping reveals heterogeneity of lung adenocarcinoma, yet its association with lymph node involvement and dissection is understudied.
Objective To assess the association between guideline-adherent lymph node dissection, histologic pattern subtyping, and overall survival in patients with clinical T1N0M0 lung adenocarcinoma.
Design, Setting, and Participants This multicenter cohort study used data from the National Cancer Center LungReal database, a multicenter, electronic health records-based database for patients undergoing surgery for lung cancer, from January 2014 to December 2021, with the last follow-up in December 2022. Patients were categorized based on histologic pattern of adenocarcinoma into 2 groups: lepidic without high-grade pattern, and high-grade or no lepidic pattern. The data analysis was performed from April to November 2025.