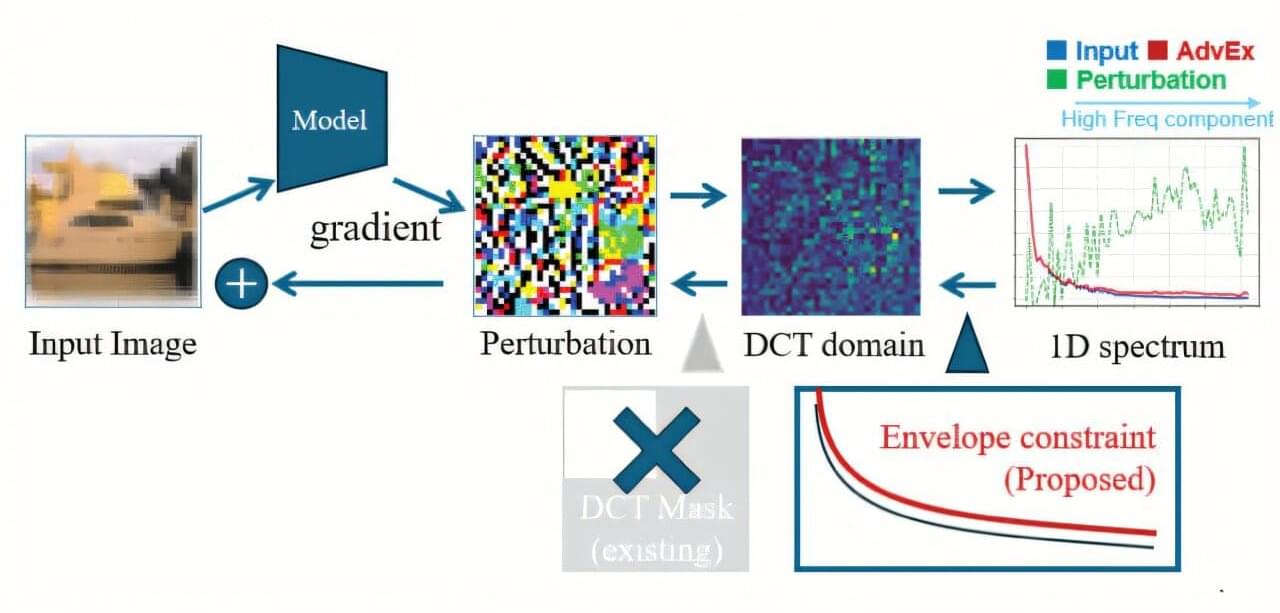
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have become a cornerstone of modern AI technology, driving a thriving field of research in image-related tasks. These systems have found applications in medical diagnosis, automated data processing, computer vision, and various forms of industrial automation, to name a few.
As reliance on AI models grows, so does the need to test them thoroughly using adversarial examples. Simply put, adversarial examples are images that have been strategically modified with noise to trick an AI into making a mistake. Understanding adversarial image generation techniques is essential for identifying vulnerabilities in DNNs and for developing more secure, reliable systems.