Are Sun-like stars the only stars where Earth-like worlds exist? This is what a recent study presented this morning at the 2026 meeting of the America | Space



Questions to inspire discussion.
Development & Deployment.
A: Alpameo offers open model weights, open-source inference scripts, simulation tools for edge case testing, and open datasets for training, enabling developers to adapt it into smaller runtime models or build reasoning-based evaluators and autolabeling systems.
Technical Architecture.
🧠 Q: What model architecture powers Alpamayo’s autonomous driving capabilities?
A: Alpameo uses 10B parameter models across five specialized functions: vision, language, action, reasoning, and trajectory generation, forming an integrated reasoning system for autonomous vehicles.
Despite NVIDIA’s advancements in self-driving technology, Tesla’s current lead in autonomous driving, production, and cost advantages are likely to keep it ahead of competitors, including NVIDIA, in the short term Questions to inspire discussion.
Platform Architecture & Business Model 🔧 Q: What type of product is Nvidia’s AI Pameo platform? A: Nvidia’s AI Pameo is a hardware and software toolset for OEMs requiring millions in non-recurring engineering fees and 70% gross margins on chips per vehicle, not a complete consumer solution like Tesla’s FSD. 🏭 Q: What does OEM implementation of Nvidia’s platform require? A: OEMs must have in-house AI talent to integrate, customize, certify, and handle warranty and liability for their specific vehicle models, as Nvidia provides the stack but not per-model engineering. 💰 Q: How does Tesla’s chip economics compare to Nvidia’s approach?
Questions to inspire discussion.
Commercial Availability & Pricing.
A: Unitree is reportedly eyeing a $7 billion IPO, reflecting growing investor confidence in humanoid robotics as a serious commercial category with clear trajectory toward public, industrial, and commercial space operations.
Technical Specifications & Capabilities.
🤸 Q: What physical capabilities does the Unitree H2 demonstrate and how is it engineered?
A: The H2 humanoid performs flying kicks, backflips, and sandbag strikes using 31 degrees of freedom (12 in shoulders, 6 per arm, 3 in torso, 7 per leg), showcasing agility for potential real-world applications.
Tesla’s RoboTaxi plan aims to revolutionize transportation by creating a global, autonomous, and integrated system that could potentially replace traditional car ownership and transform the way people move around.
Questions to inspire discussion.
Cost Optimization Strategy 🚗 Q: How can I minimize transportation costs using Tesla’s pricing tiers? A: Tesla’s AI-controlled pricing offers three tiers: $1 per mile for occasional trips, $60 per day for daily rentals, and $600 per month for leasing, with real-time switching between options based on your usage patterns to optimize costs. 💰 Q: How does AI-generated pricing adapt to my changing transportation needs? A: The system enables seamless switching between $1 per mile and $60 per day options similar to phone plans, with real-time adjustments that automatically select the most cost-effective tier based on current usage.
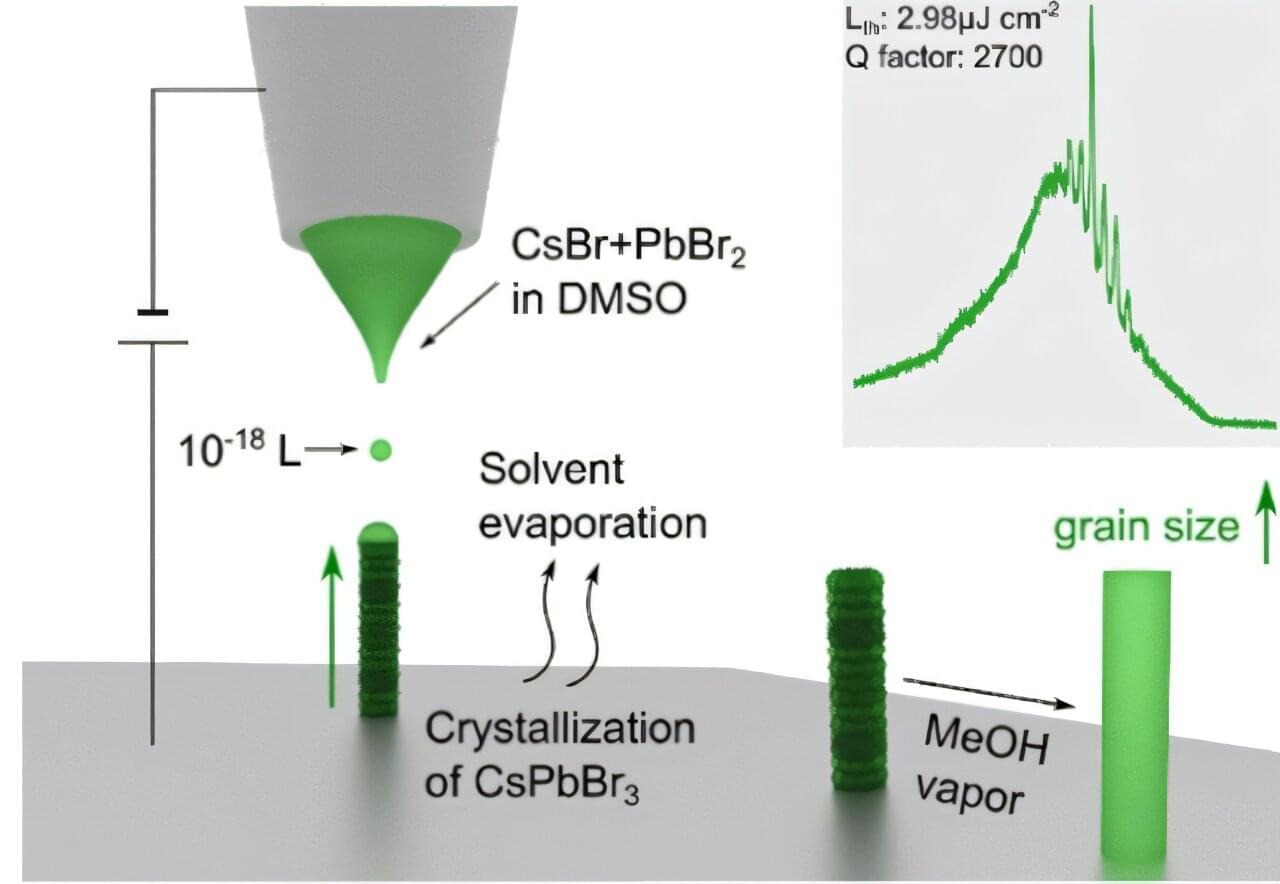
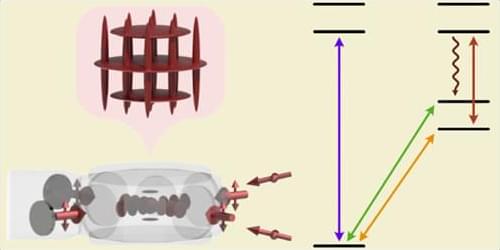
In future high-tech industries, such as high-speed optical computing for massive AI, quantum cryptographic communication, and ultra-high-resolution augmented reality (AR) displays, nanolasers—which process information using light—are gaining significant attention as core components for next-generation semiconductors.
A research team has proposed a new manufacturing technology capable of high-density placement of nanolasers on semiconductor chips, which process information in spaces thinner than a human hair.
A joint research team led by Professor Ji Tae Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Junsuk Rho from POSTECH, has developed an ultra-fine 3D printing technology capable of creating “vertical nanolasers,” a key component for ultra-high-density optical integrated circuits.
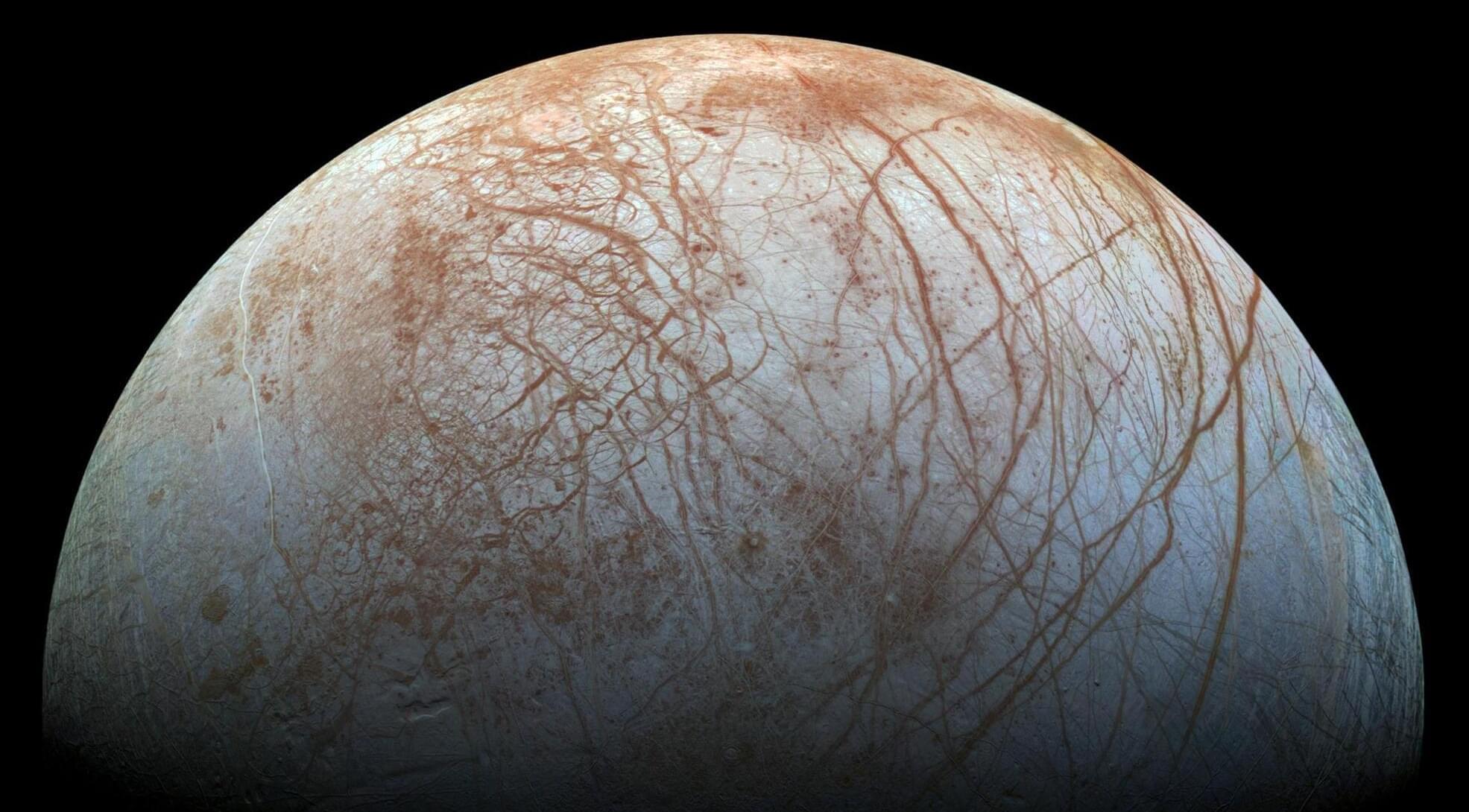

The giant planet Jupiter has nearly 100 known moons, yet none have captured the interest and imagination of astronomers and space scientists quite like Europa, an ice-shrouded world that is thought to possess a vast ocean of liquid salt water. For decades, scientists have wondered whether that ocean could harbor the right conditions for life, placing Europa near the top of the list of solar system bodies to explore.
A new study led by Paul Byrne, an associate professor of Earth, environmental, and planetary sciences, throws cold water on the idea that Europa could support life at the seafloor. The study was published in Nature Communications.
Co-authors from the Department of Earth, Environmental, and Planetary Sciences include Professor Philip Skemer, associate chair of the department; Professor Jeffrey Catalano; Douglas Wiens, the Robert S. Brookings Distinguished Professor; and graduate student Henry Dawson. Byrne, Skemer, Catalano, Wiens, and Dawson are also members of the McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences.