Nov 8, 2024
Frontiers: They basically controlled butterflies in a virtual environment wirelessly with human organoids
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biological, robotics/AI, virtual reality
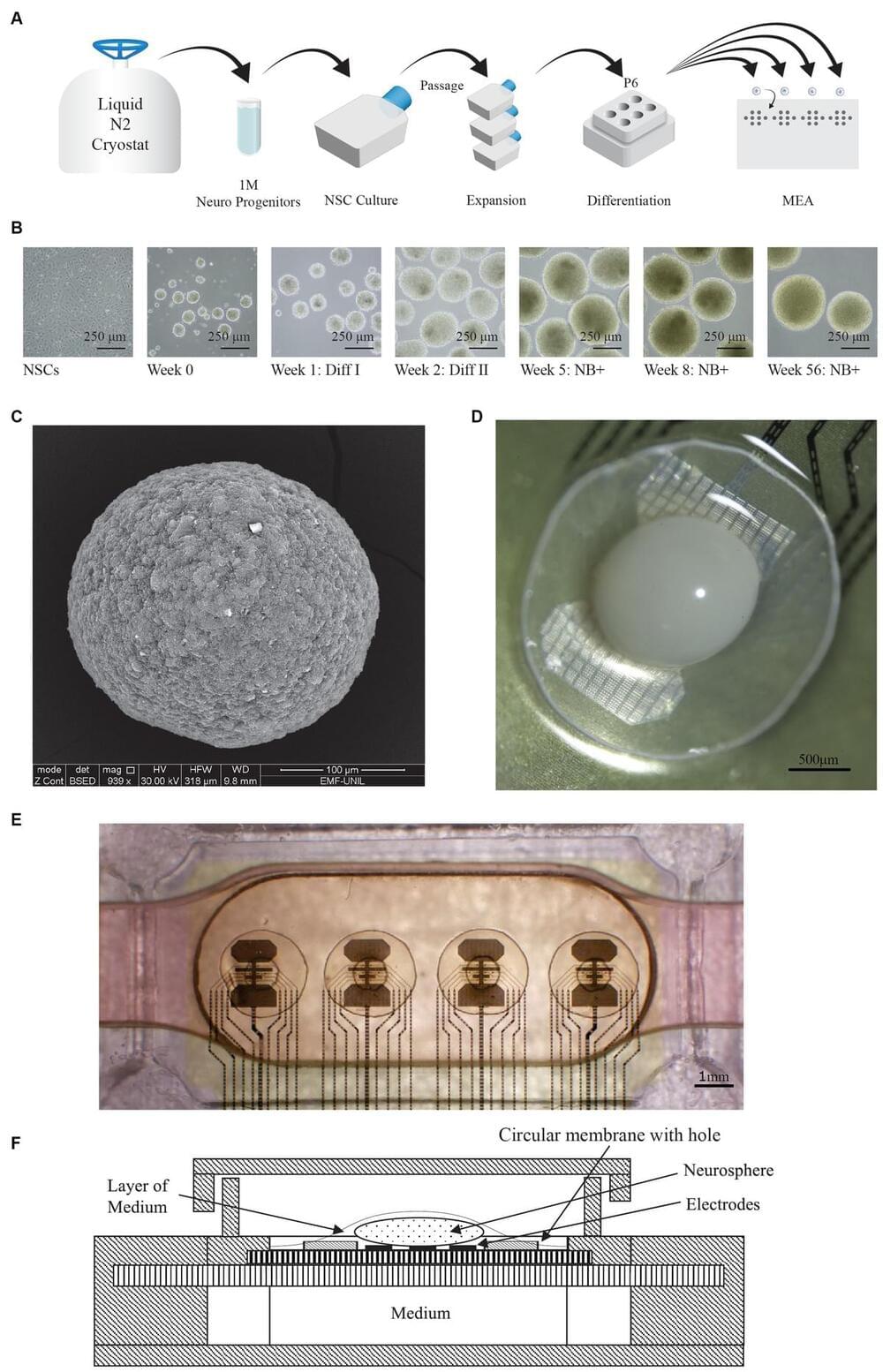
Wetware computing and organoid intelligence is an emerging research field at the intersection of electrophysiology and artificial intelligence. The core concept involves using living neurons to perform computations, similar to how Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are used today. However, unlike ANNs, where updating digital tensors (weights) can instantly modify network responses, entirely new methods must be developed for neural networks using biological neurons. Discovering these methods is challenging and requires a system capable of conducting numerous experiments, ideally accessible to researchers worldwide. For this reason, we developed a hardware and software system that allows for electrophysiological experiments on an unmatched scale. The Neuroplatform enables researchers to run experiments on neural organoids with a lifetime of even more than 100 days. To do so, we streamlined the experimental process to quickly produce new organoids, monitor action potentials 24/7, and provide electrical stimulations. We also designed a microfluidic system that allows for fully automated medium flow and change, thus reducing the disruptions by physical interventions in the incubator and ensuring stable environmental conditions. Over the past three years, the Neuroplatform was utilized with over 1,000 brain organoids, enabling the collection of more than 18 terabytes of data. A dedicated Application Programming Interface (API) has been developed to conduct remote research directly via our Python library or using interactive compute such as Jupyter Notebooks. In addition to electrophysiological operations, our API also controls pumps, digital cameras and UV lights for molecule uncaging. This allows for the execution of complex 24/7 experiments, including closed-loop strategies and processing using the latest deep learning or reinforcement learning libraries. Furthermore, the infrastructure supports entirely remote use. Currently in 2024, the system is freely available for research purposes, and numerous research groups have begun using it for their experiments. This article outlines the system’s architecture and provides specific examples of experiments and results.
The recent rise in wetware computing and consequently, artificial biological neural networks (BNNs), comes at a time when Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are more sophisticated than ever.
The latest generation of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Meta’s Llama 2 or OpenAI’s GPT-4, fundamentally rely on ANNs.