The three-dimensional (3D) organization of chromosomes is emerging as an important determinant of multiple cellular processes. We now show that 3D chromatin structures, maintained by the Polycomb complex, record epigenetic perturbation events.



“At that time, I had no professional experience in the videogame industry, and I didn’t even really have an artist portfolio, so I made one in a bit of a rush.” Nonetheless, this was enough to convince Saber, and Hatté joined the team as an environment artist, working primarily on Tomb Raider 4–6 Remastered.
“My role on the team was specifically to work on the environments and remaster the textures,” Hatté says. “It was a life changing experience. I’m incredibly grateful to have been given that opportunity.”
Reamsters aside, Tomb Raider has been dormant since 2018’s Shadow of the Tomb Raider. But late last year, two new Lara Croft adventures were revealed—a second remake of the original game, and a new adventure by Crystal Dynamics pitched as a sequel to Tomb Raider: Underworld.
Extremely cool paper describing optically programmable ~0.3 mm robots with onboard computation and autonomous locomotion! These tiny rectangular machines carry solar cells, optical receivers, electrokinetic actuators, and more. As demonstrations, the authors programmed them (i) to report local temperature by doing a coded dance and (ii) swim towards warmth before stopping and rotating upon reaching a location with a certain level of heat. This is amazing and I hope such devices are further improved so they can be used in biological applications! Love it!
(https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.adu8009)
Autonomous submillimeter robots are built with onboard sensing, computation, memory, communication, and locomotion.

Factors that promote inflammation in C9ORF72 mutation carriers with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or frontotemporal dementia (FTD) have remained elusive. McCourt et al. identified pro-inflammatory forms of glycogen in gut contents of people with ALS/FTD and demonstrate that targeting glycogen in a C9orf72 mouse model extends lifespan and reduces neuroinflammation.
In this talk from the CSCSC 25 Conference on Complex Systems and Contemplative Studies, Dr. Michael Levin asks a question with deep resonance for both science and contemplative practice:
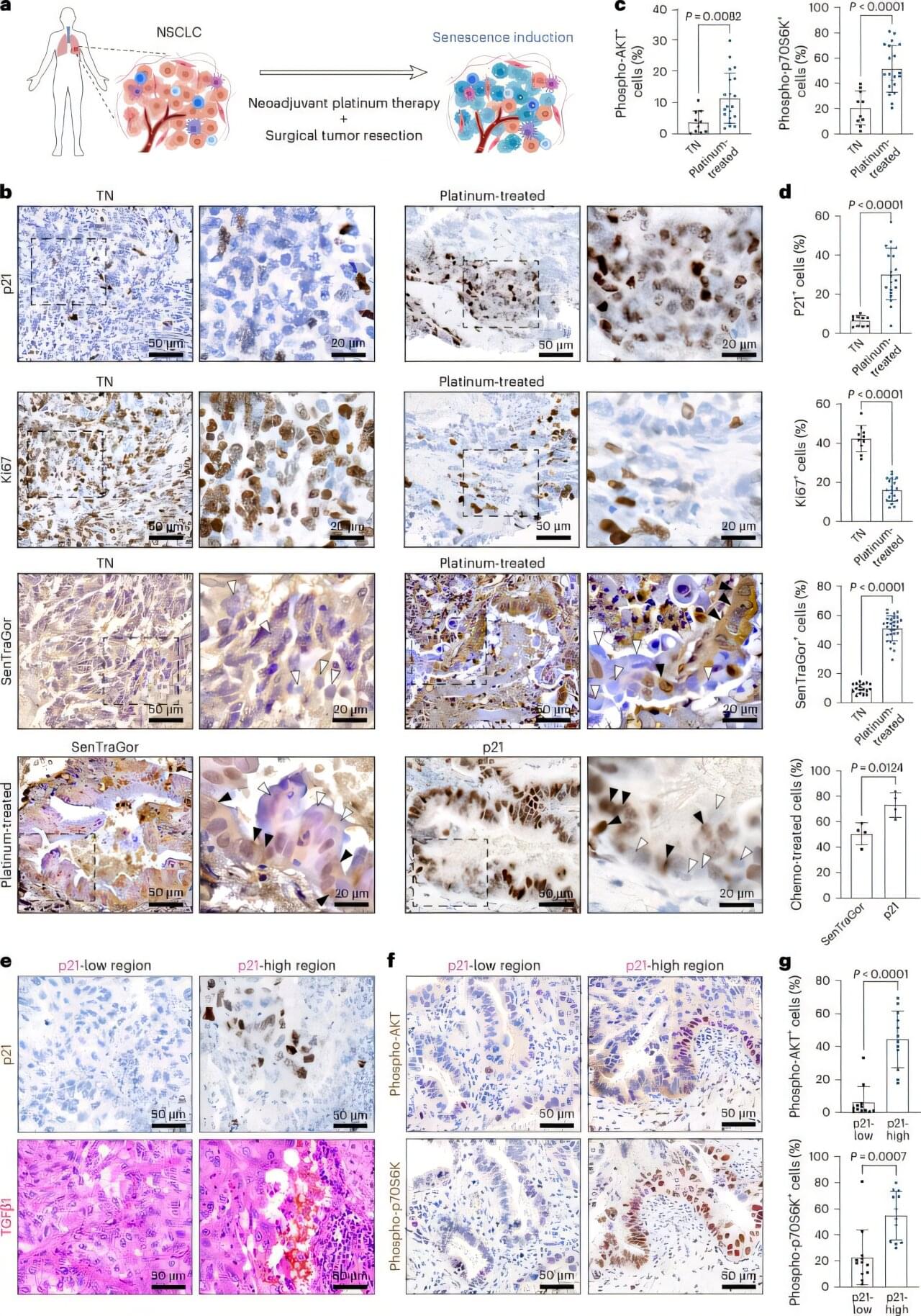
Researchers have identified a biological mechanism that helps explain why some lung and ovarian cancers become resistant to chemotherapy, offering insight into why cancers recur. The study, published in Nature Aging this month, investigated how platinum-based chemotherapies such as cisplatin negatively affect tumor behavior in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC). Although these treatments are widely used, their long-term effectiveness is often limited when tumors return or stop responding.
Professor Ljiljana Fruk and Muhamad Hartono from the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (CEB) contributed to the international collaboration, led by researchers from the Early Cancer Institute and the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute. Their involvement follows her Bionano Engineering group’s recent development of a urine test for early lung cancer detection.

In a study published today, Friday, February 13, 2026, in the journal Nature Aging, researchers show that blood-based biomarkers can support accurate dementia diagnosis across diverse populations when integrated with cognitive and neuroimaging measures. Blood-based biomarkers are emerging as one of the most promising advances for the global diagnosis of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. These tests offer a more accessible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional diagnostic tools such as brain imaging or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
However, most blood-based biomarkers have been developed and validated primarily in relatively homogeneous populations. Genetic background, overall physical health, and environmental and social exposures can substantially influence biomarker levels, raising concerns about how well these tests perform across diverse populations worldwide.

When the Amaterasu particle entered Earth’s atmosphere, the TAP array in Utah recorded an energy level of more than 240 exa-electronvolts (EeV). Such particles are exceedingly rare and are thought to originate in some of the most extreme cosmic environments. At the time of its detection, scientists were not sure if it was a proton, a light atomic nucleus, or a heavy (iron) atomic nucleus. Research into its origin pointed toward the Local Void, a vast region of space adjacent to the Local Group that has few known galaxies or objects.
This posed a mystery for astronomers, as the region is largely devoid of sources capable of producing such energetic particles. Reconstructing the energy of cosmic-ray particles is already difficult, making the search for their sources using statistical models particularly challenging. Capel and Bourriche addressed this by combining advanced simulations with modern statistical methods (Approximate Bayesian Computation) to generate three-dimensional maps of cosmic-ray propagation and their interactions with magnetic fields in the Milky Way.
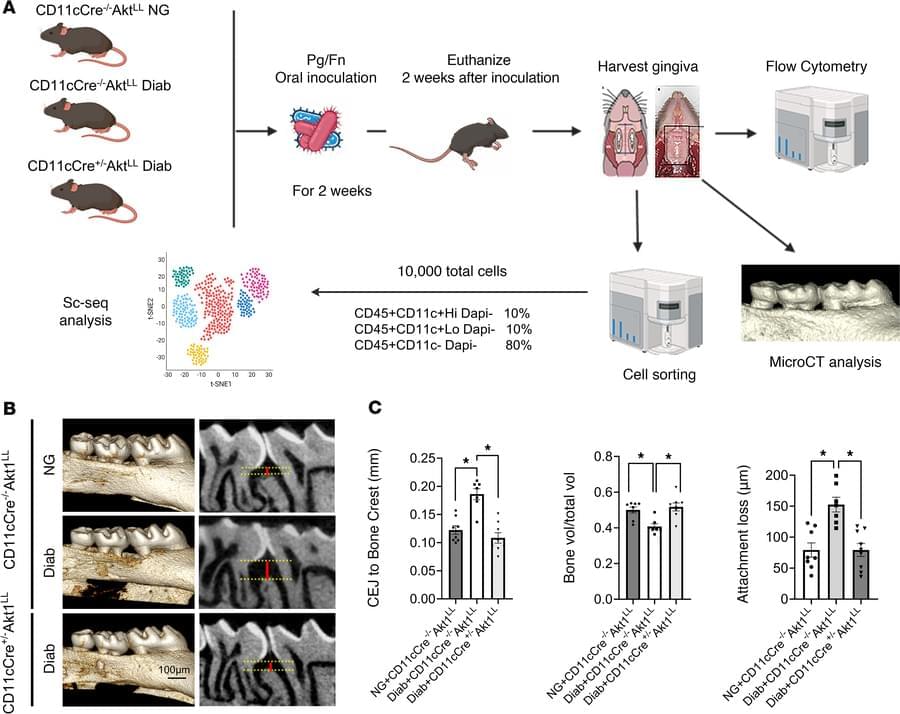
Dana T. Graves & team identify the CD137L/CD137 axis as a pivotal mediator of diabetes-induced inflammatory tissue destruction, in which dendritic cell produced CD137L activates γδ T-cells through CD137, leading to a dysregulated host response and worsening damage from bacterial challenge:
The figure shows microCT images of 3D reconstruction of the molar teeth from mouse models of periodontitis injected with control, CD137L-agonist, CD137L-antagonist antibodies.
1Hospital of Stomatology, Guanghua School of Stomatology and.
2Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
3Department of Periodontics, School of Dental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.