Searches for dark matter particles have come up empty so far, driving theorists to get more creative with their ideas.
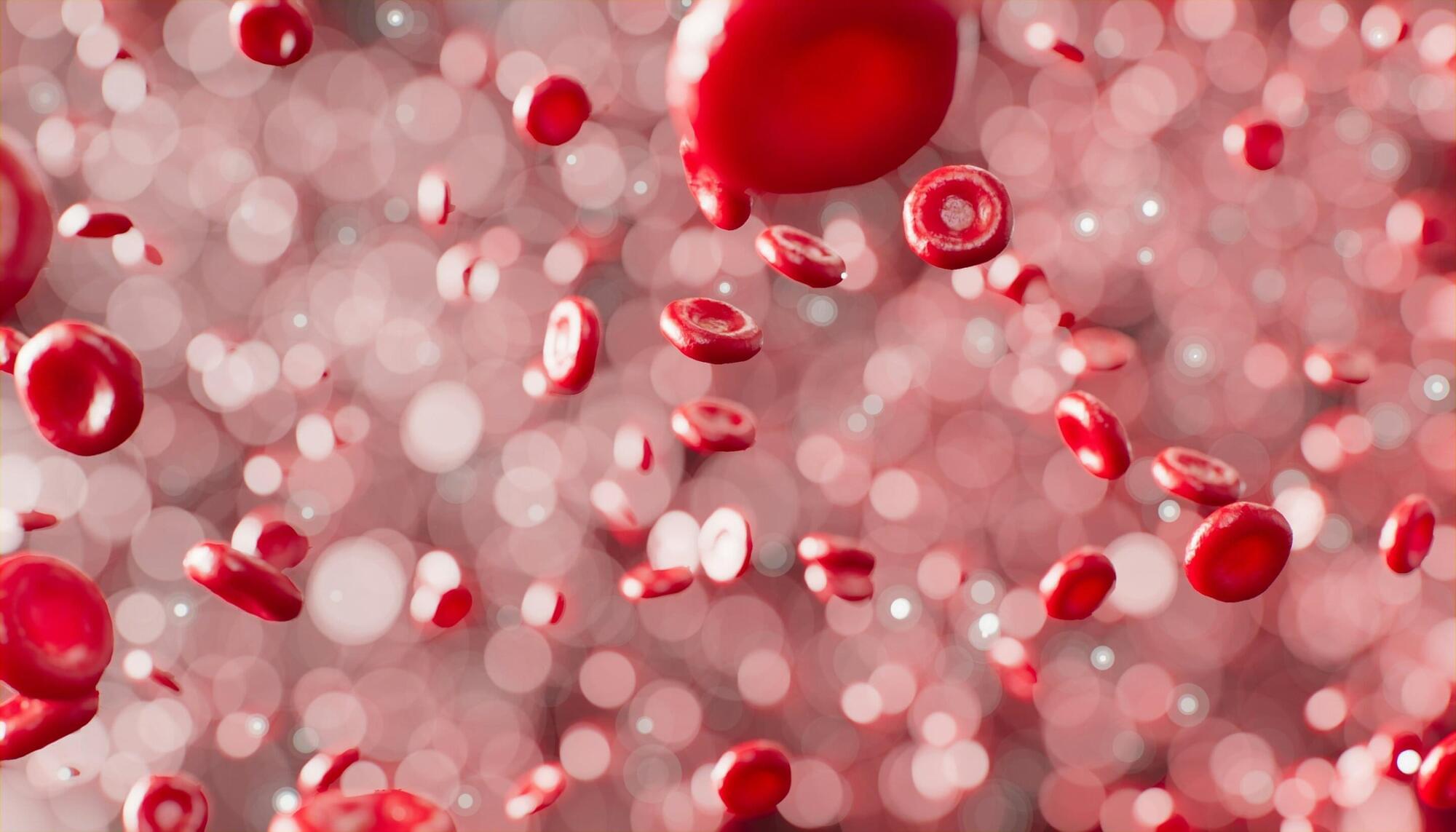




The leading cause of death due to injuries in war is excessive bleeding. A KAIST research team, in which an Army Major participated, has tackled this issue head-on. By developing a next-generation powder-type hemostatic agent that stops bleeding just by spraying it, they have presented an innovative technology that will change the paradigm of combatant survivability.
A joint research team led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Sangyong Jon from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed a powder-type hemostatic agent that forms a powerful hydrogel barrier within approximately one second when sprayed on a wound.
The research was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
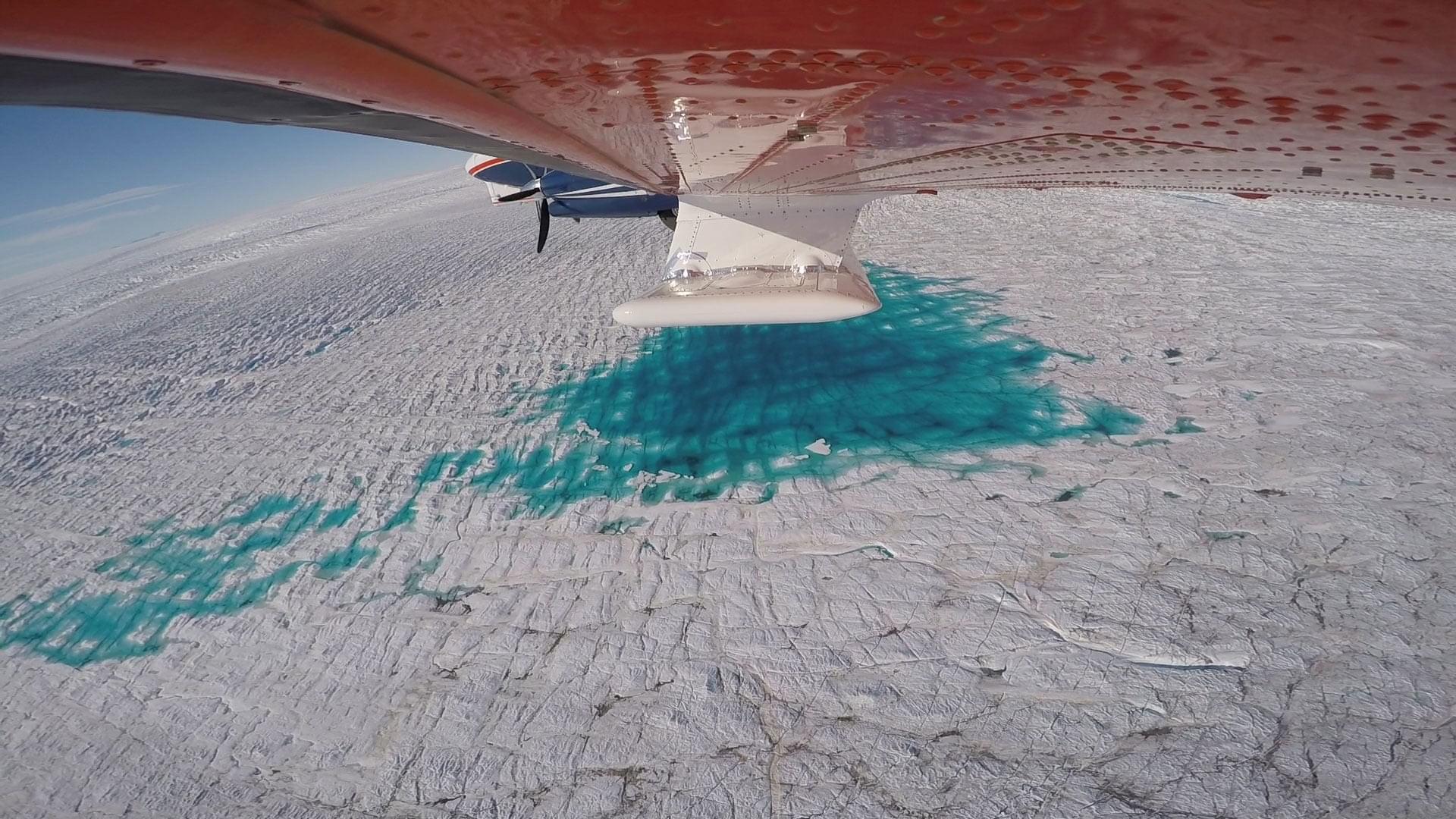


An intertwined history: the earth observer and EOS
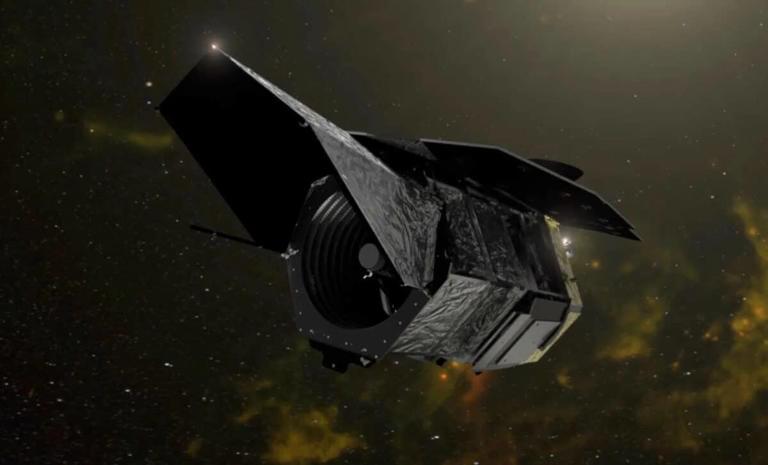

Our universe is filled with galaxies, in all directions as far as our instruments can see. Some researchers estimate that there are as many as 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe. At first glance, these galaxies might appear to be randomly scattered across space, but they’re not. Careful mapping has shown that they are distributed across the surfaces of giant cosmic “bubbles” up to several hundred million light-years across. Inside these bubbles, few galaxies are found, so those regions are called cosmic voids. NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will allow us to measure these voids with new precision, which can tell us about the history of the universe’s expansion.
“Roman’s ability to observe wide areas of the sky to great depths, spotting an abundance of faint and distant galaxies, will revolutionize the study of cosmic voids,” said Giovanni Verza of the Flatiron Institute and New York University, lead author on a paper published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Cosmic recipe The cosmos is made of three key components: normal matter, dark matter, and dark energy. The gravity of normal and dark matter tries to slow the expansion of the universe, while dark energy opposes gravity to speed up the universe’s expansion. The nature of both dark matter and dark energy is currently unknown. Scientists are trying to understand them by studying their effects on things we can observe, such as the distribution of galaxies across space.

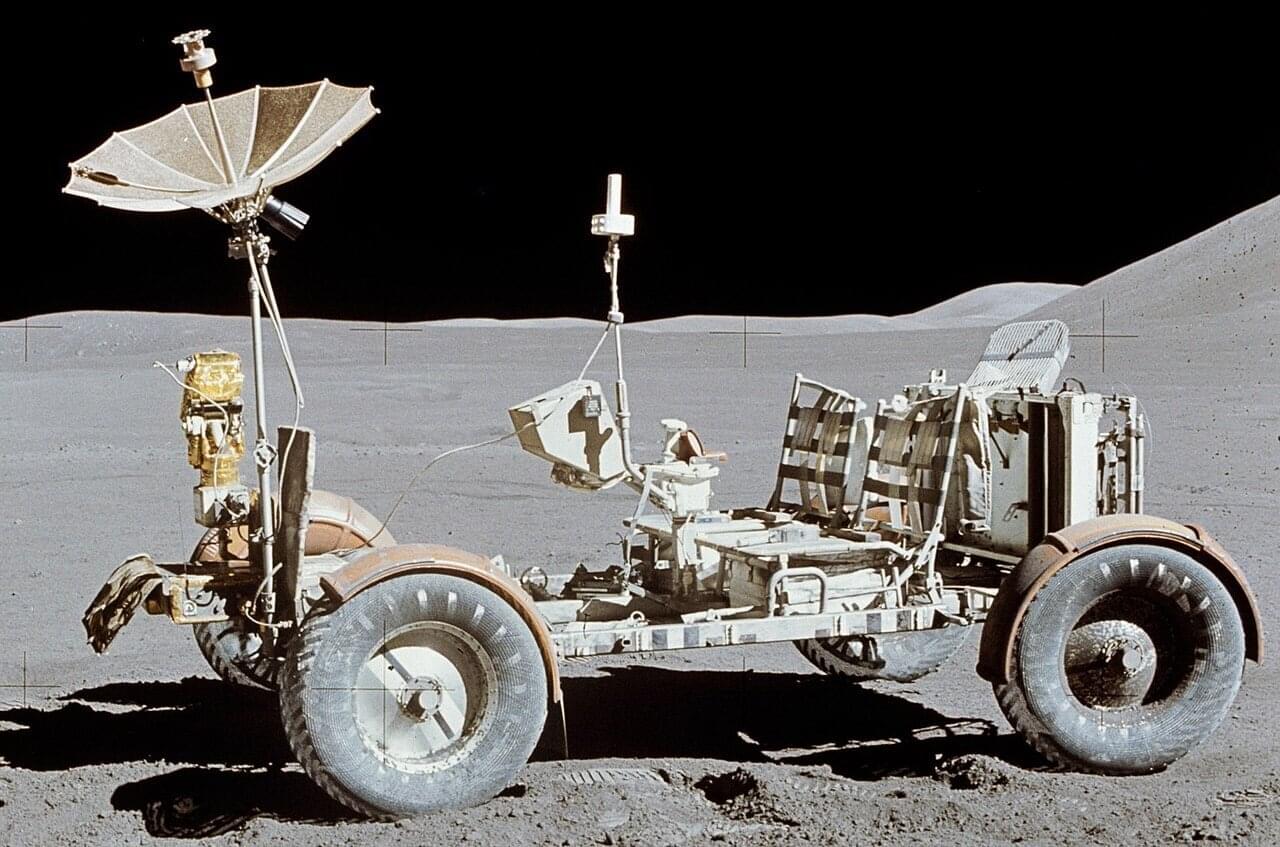
Beneath the moon’s cratered surface lie networks of lava tubes and deep pits, natural caves that could shelter future lunar bases from cosmic radiation and wild temperature swings. These underground structures represent some of the most scientifically valuable areas in the solar system, but they come with the very real challenge of simply getting there.
The entrances to these caves feature steep, rugged terrain with rocks and loose regolith. Small rovers, preferred for lunar exploration because you can deploy many of them to reduce mission risk, face an inherent limitation. Their compact wheels simply can’t climb over obstacles much larger than the wheel diameter itself. Send a swarm of small rovers and even if some fail, others continue the mission. Send one large rover and a single failure ends everything.
Variable diameter wheels are a new thing in lunar exploration and could solve this, expanding when needed to overcome obstacles, then contracting for efficient transport. But building such a wheel for the moon has proven nearly impossible. The lunar environment is uniquely hostile to mechanical systems. Fine, abrasive dust infiltrates everything, and in the airless vacuum, exposed metal surfaces stick together through a process called cold welding. Traditional hinges and joints don’t last long under these conditions.