We’re on a journey to advance and democratize artificial intelligence through open source and open science.



A research team at the Jülich Supercomputing Center, together with experts from NVIDIA, has set a new record in quantum simulation: for the first time, a universal quantum computer with 50 qubits has been fully simulated—a feat achieved on Europe’s first exascale supercomputer, JUPITER, inaugurated at Forschungszentrum Jülich in September.
The result surpasses the previous world record of 48 qubits, established by Jülich researchers in 2022 on Japan’s K computer. It showcases the immense computational power of JUPITER and opens new horizons for developing and testing quantum algorithms. The research is published on the arXiv preprint server.
Quantum computer simulations are vital for developing future quantum systems. They allow researchers to verify experimental results and test new algorithms long before powerful quantum machines become reality. Among these are the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE), which can model molecules and materials, and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), used for optimization problems in logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence.

Researchers studying how large AI models such as ChatGPT learn and remember information have discovered that their memory and reasoning skills occupy distinct parts of their internal architecture. Their insights could help make AI safer and more trustworthy.
AI models trained on massive datasets rely on at least two major processing features. The first is memory, which allows the system to retrieve and recite information. The second is reasoning, solving new problems by applying generalized principles and learned patterns. But up until now, it wasn’t known if AI’s memory and general intelligence are stored in the same place.
So researchers at the startup Goodfire.ai decided to investigate the internal structure of large language and vision models to understand how they work.
Concrete 3D printing reduces both time and cost by eliminating traditional formwork, the temporary mold for casting. Yet most of today’s systems rely on extrusion-based methods, which deposit material very close to a nozzle layer by layer. This makes it impossible to print around reinforcement bars (rebars) without risk of collision, limiting both design flexibility and structural integrity of builds.
Kenji Shimada and researchers in his Carnegie Mellon University’s Computational Engineering and Robotics Laboratory (CERLAB), are breaking through that limitation with a new simulation tool for spray-based concrete 3D printing.
“Spray-based concrete 3D printing is a new process with complicated physical phenomena,” said Shimada, a professor of mechanical engineering. “In this method, a modified shotcrete mixture is sprayed from a nozzle to build up on a surface, even around rebar.”
For the first time, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have succeeded in using nanorobots to stimulate stem cells with such precision that they are reliably transformed into bone cells. To achieve this, the robots exert external pressure on specific points in the cell wall. The new method offers opportunities for faster treatments in the future.
Prof. Berna Özkale Edelmann’s nanorobots consist of tiny gold rods and plastic chains. Several million of them are contained in a gel cushion measuring just 60 micrometers, together with a few human stem cells. Powered and controlled by laser light, the robots, which look like tiny balls, mechanically stimulate the cells by exerting pressure.
“We heat the gel locally and use our system to precisely determine the forces with which the nanorobots press on the cell—thereby stimulating it,” explains the professor of nano-and microrobotics at TUM. This mechanical stimulation triggers biochemical processes in the cell. Ion channels change their properties, and proteins are activated, including one that is particularly important for bone formation.

Pioneering breakthroughs in healthcare — for everyone, everywhere, sustainably.
Komeil Nasrollahi is a seasoned innovation and business‐development leader currently serving as Senior Director of Innovation & Venture Partnerships at Siemens Healthineers (https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/), where he is charged with forging strategic collaborations, identifying new venture opportunities and accelerating transformative healthcare technologies.
With an academic foundation in industrial engineering from Tsinghua University (and additional studies in the Chinese language) and undergraduate work in civil engineering from Azad University in Iran, Komeil blends technical fluency with global business acumen.
Prior to his current role, Komeil held senior positions driving business engagement and international investment, including leading market‐entry and growth initiatives across China and the U.S., demonstrating a strong ability to navigate cross‐cultural, high‐stakes innovation ecosystems.
In his current role, Komeil works at the intersection of healthcare, technology and venture creation—identifying high-impact innovations that align with Siemens Healthineers’ mission to “pioneer breakthroughs in healthcare, for everyone, everywhere, sustainably.”

Imagine you’re watching a movie, in which a character puts a chocolate bar in a box, closes the box and leaves the room. Another person, also in the room, moves the bar from a box to a desk drawer. You, as an observer, know that the treat is now in the drawer, and you also know that when the first person returns, they will look for the treat in the box because they don’t know it has been moved.
You know that because as a human, you have the cognitive capacity to infer and reason about the minds of other people—in this case, the person’s lack of awareness regarding where the chocolate is. In scientific terms, this ability is described as Theory of Mind (ToM). This “mind-reading” ability allows us to predict and explain the behavior of others by considering their mental states.
We develop this capacity at about the age of four, and our brains are really good at it.
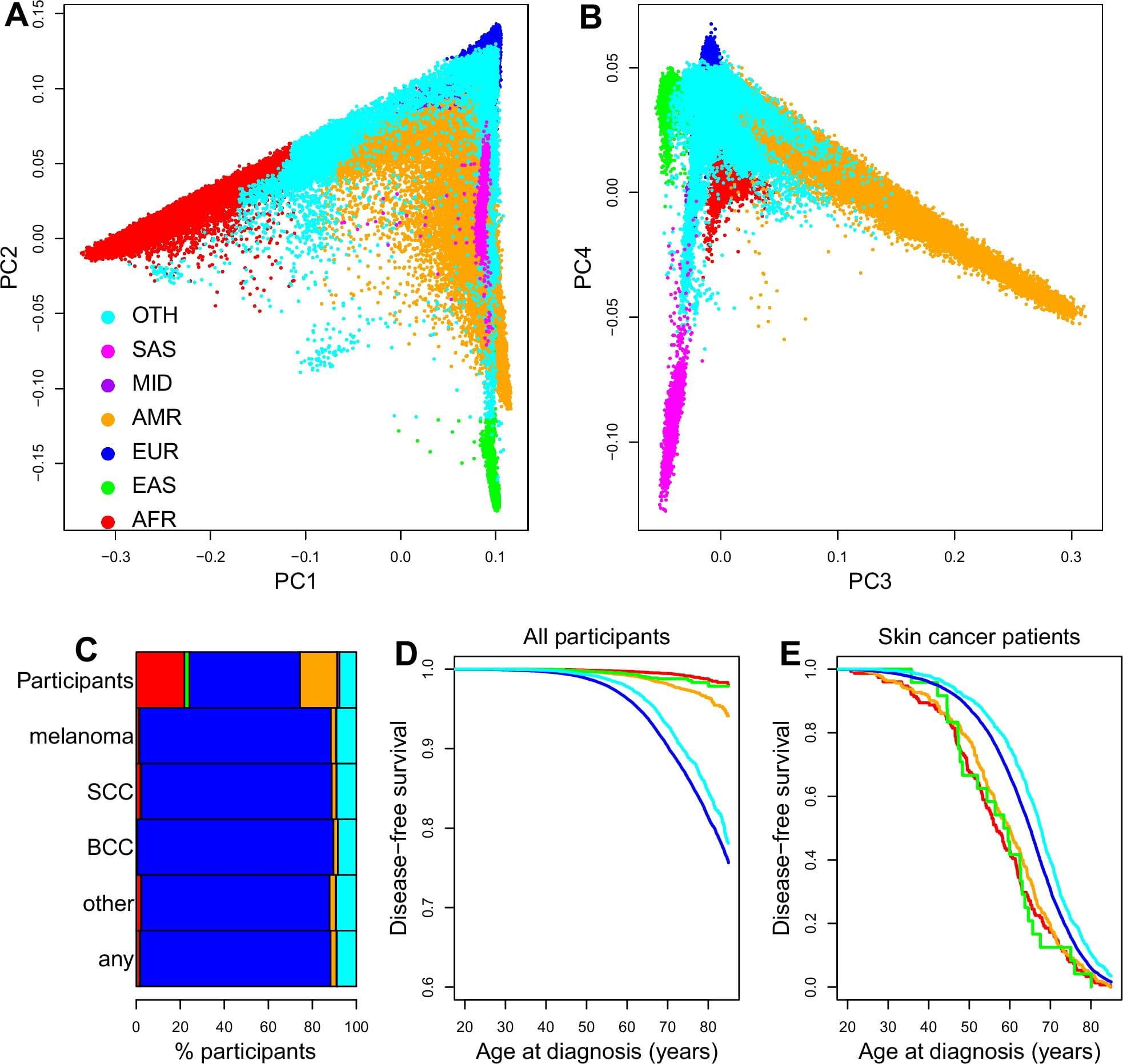
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have developed a new approach for identifying individuals with skin cancer that combines genetic ancestry, lifestyle and social determinants of health using a machine learning model. Their model, more accurate than existing approaches, also helped the researchers better characterize disparities in skin cancer risk and outcomes.
The research is published in the journal Nature Communications.
Skin cancer is among the most common cancers in the United States, with more than 9,500 new cases diagnosed every day and approximately two deaths from skin cancer occurring every hour. One important component of reducing the burden of skin cancer is risk prediction, which utilizes technology and patient information to help doctors decide which individuals should be prioritized for cancer screening.