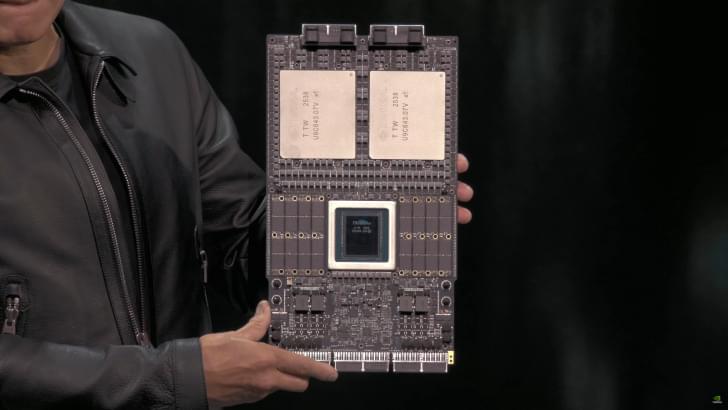
NVIDIA’s next-generation Rubin GPUs have entered production, and the company has also secured samples of HBM4 memory from all major suppliers.
A few weeks ago, NVIDIA’s CEO, Jensen Huang, showcased the next-gen Vera Rubin Superchip for the first time at GTC 2025 in Washington. We got to see two super massive GPUs stacked together with the next-generation Vera CPU, and loads of LPDDR memory on the outskirts. The Vera Rubin Superchip will lay the framework for the next wave of AI computing in data centers, and it looks like there are some good reports regarding the production timeline.