Two major facilities built for AI-era workloads remain unpowered while the city races to expand its electricity supply.



Advancements in AI, robotics, and space exploration are driving us towards a future of sustainable abundance, enabled by innovations such as space-based solar power, humanoid robots, and scalable AI infrastructure. ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Terafabs and AI Chips.
🛠️ Q: What are Elon Musk’s plans for terafabs?
A: Musk plans to build terafabs with 10 lines, each producing 100k wafers/month, costing **$10–20 billion/line.
🔋 Q: What challenges do AI chips face for scaling?
A: Scaling AI faces bottlenecks in AI chips and energy, with Musk’s terafabs and solar power as key solutions.
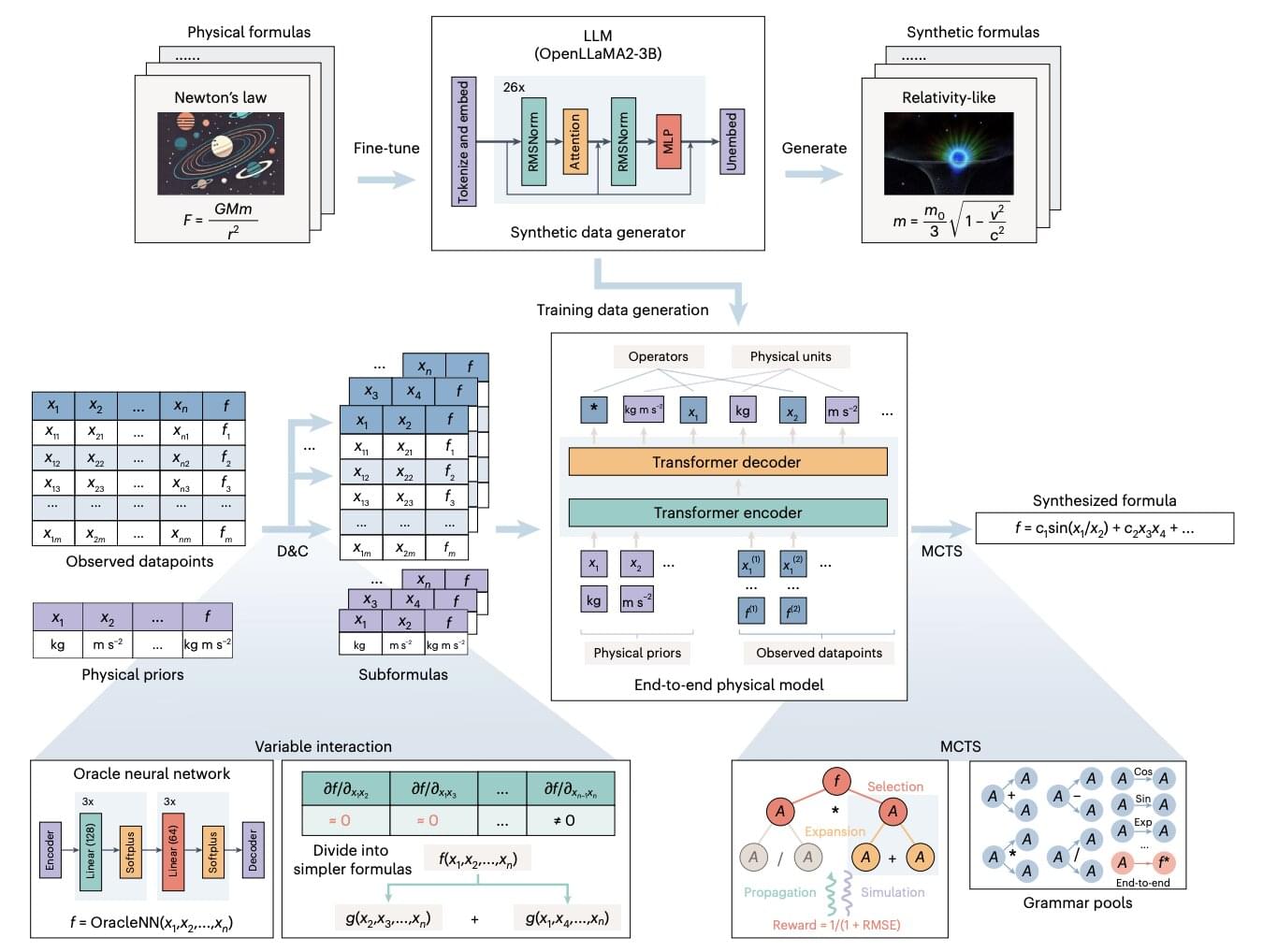
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems, particularly artificial neural networks, have proved to be highly promising tools for uncovering patterns in large amounts of data that would otherwise be difficult to detect. Over the past decade, AI tools have been applied in a wide range of settings and fields.
Among its many possible applications, AI systems could be used to discover physical relationships and symbolic expressions (i.e., mathematical formulas) describing these relationships.
To uncover these formulas, physicists currently need to extensively analyze raw data, thus automating this process could be highly advantageous.

In today’s AI news, Southeast Asia’s largest bank is rolling out an AI chatbot for its corporate clients, giving “round-the-block” access for customer care needs. A pilot version of the generative AI-powered chatbot, named DBS Joy, was rolled out in February. It has since managed over 120,000 unique chats, DBS claimed in a statement. The virtual assistant also cut waiting times, and customer satisfaction scores rose by 23%. The bank’s virtual assistant was first rolled out in 2018, under the same name.
In other advancements, Artificial intelligence giant OpenAI on Monday announced a new initiative that aims to make it easier for service members and veterans to use AI tools when they’re transitioning from military service to the workforce. The ChatGPT-maker announced that service members within 12 months of separation or retirement from, or any veteran within their first year of leaving military service, can access a free year of access to ChatGPT Plus, the company’s subscription-based tool.
Meanwhile, Neurodiverse professionals may see unique benefits from artificial intelligence tools and agents, research suggests. With AI agent creation booming in 2025, people with conditions like ADHD, autism, dyslexia and more report a more level playing field in the workplace thanks to generative AI. A recent study from the UK’s Department for Business and Trade found that neurodiverse workers were 25% more satisfied with AI assistants and were more likely to recommend the tool than neurotypical respondents.
And, San Francisco became a meme — a symbol of American urban decay. Between 2019 and 2024, the city lost 4 per cent of its population, one of the largest declines in America. But thanks to AI — and new “tough on crime” mayor Daniel Lurie — the vibe has, unquestionably, shifted. Since 2020, more than 2,400 AI companies have been founded in San Francisco, a city of just 830,000 people. “Hacker houses”, where bright-eyed coders live communally and build what they hope will be the next Google, have cropped up across the city.
In videos, Six of the most influential minds in artificial intelligence joined FT Live for an exclusive conversation on how their breakthroughs and the current state of AI are shaping our world. Jensen Huang, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, Fei-Fei Li, Yann LeCun, and Bill Dally spoke with the FT’s AI editor, Madhumita Murgia at the FT Future of AI Summit in London. Together, they reflected on decades of pioneering work — from neural networks to generative AI and discuss the ethical, social, and economic implications of the technology they helped to create.
Then, Ellis Hamburger and Alex Heath chat about the Sources launch party, and living in late-stage extractionism. Then, they are then joined by Runway CEO Cristobal Valenzuela to discuss the hardest part about AI, why golf courses are a bigger problem than data centers, and how world models are changing our world forever.
And, David Sacks, White House AI and Crypto Czar, joins Marc, Ben, and Erik on the a16z podcast to explore what’s really happening inside the Trump administration’s AI and crypto strategy. They expose the regulatory capture playbook being pushed by certain AI companies, explain why open source is America’s secret weapon, and detail the infrastructure crisis that could determine who wins the global AI race.

Please see attached a list of predictions for where technology and cybersecurity may transcend in 2026. Thanks for reading and sharing! Chuck Brooks.
Note AI enabled but derived entirely from a wide variety of my own published writings interviews, podcasts, and my book “Inside Cyber”
#2026predictions #tech #artificialintelligence #cybersecurity #quantum | on LinkedIn.
From nuclear nightmares to reality-breaking weapons, we examine how science and fiction imagine the end of everything. What happens when weapons don’t just destroy worlds but unmake reality itself? Explore the science of apocalypse.
Checkout Scav: https://go.nebula.tv/scav?ref=isaacar… Watch my exclusive video Autonomous Space Industry: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Doomsday Devices & Ontological Weaponry Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Editor: Lukas Konecny Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music by Epidemic Sound: http://nebula.tv/epidemic & Stellardrone Chapters 0:00 Intro 1:30 Classical Doomsday Devices 5:57 Cosmic-Scale Doomsday Devices 11:30 Ontological Weaponry – Breaking Reality 12:23 The Erasers of History 16:06 Weapons of Physics Editing 17:55 Mind and Meaning as Targets 20:06 Scavenger Hunt 21:30 Themes and Consequences 22:55 Practical Considerations & Paradoxes 24:07 Doomsday Devices vs. Ontological Weapons 26:48 The Fermi Paradox & Ultimate Destruction.
Watch my exclusive video Autonomous Space Industry: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–…
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Doomsday Devices & Ontological Weaponry.
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Editor: Lukas Konecny.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music by Epidemic Sound: http://nebula.tv/epidemic & Stellardrone.
Chapters.
0:00 Intro.
1:30 Classical Doomsday Devices.
5:57 Cosmic-Scale Doomsday Devices.
11:30 Ontological Weaponry – Breaking Reality.
12:23 The Erasers of History.
16:06 Weapons of Physics Editing.
17:55 Mind and Meaning as Targets.
20:06 Scavenger Hunt.
21:30 Themes and Consequences.
22:55 Practical Considerations & Paradoxes.
24:07 Doomsday Devices vs. Ontological Weapons.
26:48 The Fermi Paradox & Ultimate Destruction.

Understanding the properties of different materials is an important step in material design. X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is an important technique for this, as it reveals detailed insights about a material’s composition, structure, and functional characteristics. The technique works by directing a beam of high-energy X-rays at a sample and recording how X-rays of different energy levels are absorbed.
Similar to how white light splits into a rainbow after passing through a prism, XAS produces a spectrum of X-rays with different energies. This spectrum is called as spectral data, which acts like a unique fingerprint of a material, helping scientists to identify the elements present in the material and see how the atoms are arranged. This information, known as the “electronic state,” determines the functional properties of materials.
Boron compounds have significant applications in semiconductors, Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices, and energy storage. In these materials, atomic modifications, structural defects, impurities, and doped elements, each produce unique, complex variations in spectral data. Detailed analyses of these variations provides key insights into their electronic state and is crucial for rational material design. Traditionally, however, such analyses required extensive expertise and manual labor, especially when large datasets have to be examined visually.

