Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 122 (51) e2518999122, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2518999122 (2025).
Copy.

Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 122 (51) e2518999122, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2518999122 (2025).
Copy.
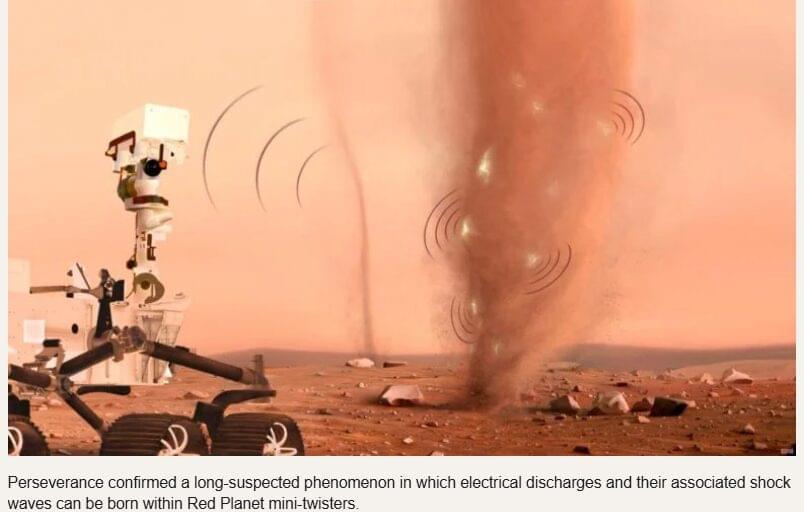


Perseverance confirmed a long-suspected phenomenon in which electrical discharges and their associated shock waves can be born within Red Planet mini-twisters.
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has recorded the sounds of electrical discharges —sparks — and mini-sonic booms in dust devils on Mars. Long theorized, the phenomenon has now been confirmed through audio and electromagnetic recordings captured by the rover’s SuperCam microphone. The discovery, published Nov. 26 in the journal Nature, has implications for Martian atmospheric chemistry, climate, and habitability, and could help inform the design of future robotic and human missions to Mars.
A frequent occurrence on the Red Planet, dust devils form from rising and rotating columns of warm air. Air near the planet’s surface becomes heated by contact with the warmer ground and rises through the denser, cooler air above. As other air moves along the surface to take the place of the rising warmer air, it begins to rotate. When the incoming air rises into the column, it picks up speed like spinning ice skaters bringing their arms closer to their body. The air rushing in also picks up dust, and a dust devil is born.
Further Reading.
This ‘digital brain’ could soon simulate ethically forbidden experiments.
https://ebrains.eu/news-and-events/2025/ten-years-of-pd14-mi…i-research.
A foundation model to predict and capture human cognition.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09215-4
First totally synthetic human brain model has been realized.
https://newatlas.com/medical/synthetic-human-brain-models/
#science #news #explained #research #sciencenews #biotech #robots #ai #artificialintelligence #organoid

Recent advances in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have opened new exciting possibilities for the rapid analysis of data, the sourcing of information and the generation of use-specific content. To run AI models, current hardware needs to continuously move data from internal memory components to processors, which is energy-intensive and can increase the time required to tackle specific tasks.
Over the past few years, engineers have been trying to develop new systems that could overcome this limitation, running AI algorithms more reliably and efficiently. One proposed solution is the development of in-memory computing systems.
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is one of the earliest in-memory computing hardware systems, where memory components search for stored data faster, comparing each stored entry simultaneously based on its content, but faces challenges for AI applications because of the fundamental limitation of silicon transistors.
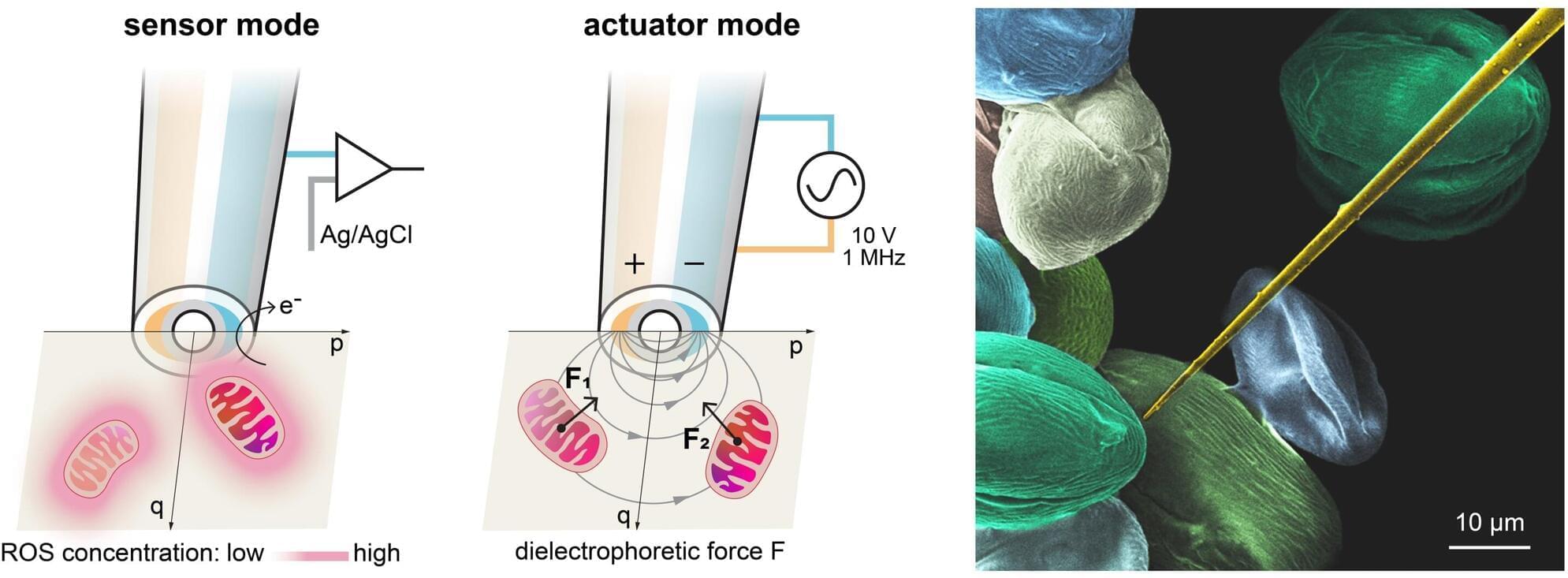
Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with various chronic diseases and cancers, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic syndrome. Gently extracting a single mitochondrion from within a living cell—without causing damage and without the guidance of fluorescent makers—has long been a challenge akin to threading a needle in a storm for scientists.
A team led by Prof. Richard Gu Hongri, Assistant Professor in the Division of Integrative Systems and Design of the Academy of Interdisciplinary Studies at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), in collaboration with experts in mechanical engineering and biomedicine, has developed an automated robotic nanoprobe.
The device can navigate within a living cell, sense metabolic whispers in real time, and pluck an individual mitochondrion for analysis or—all without the need for fluorescent labeling. It is the world’s first cell-manipulation nanoprobe that integrates both sensors and actuators at its tip, enabling a micro-robot to autonomously navigate inside live cells. The breakthrough holds great promise for advancing future treatment strategies for chronic diseases and cancer.
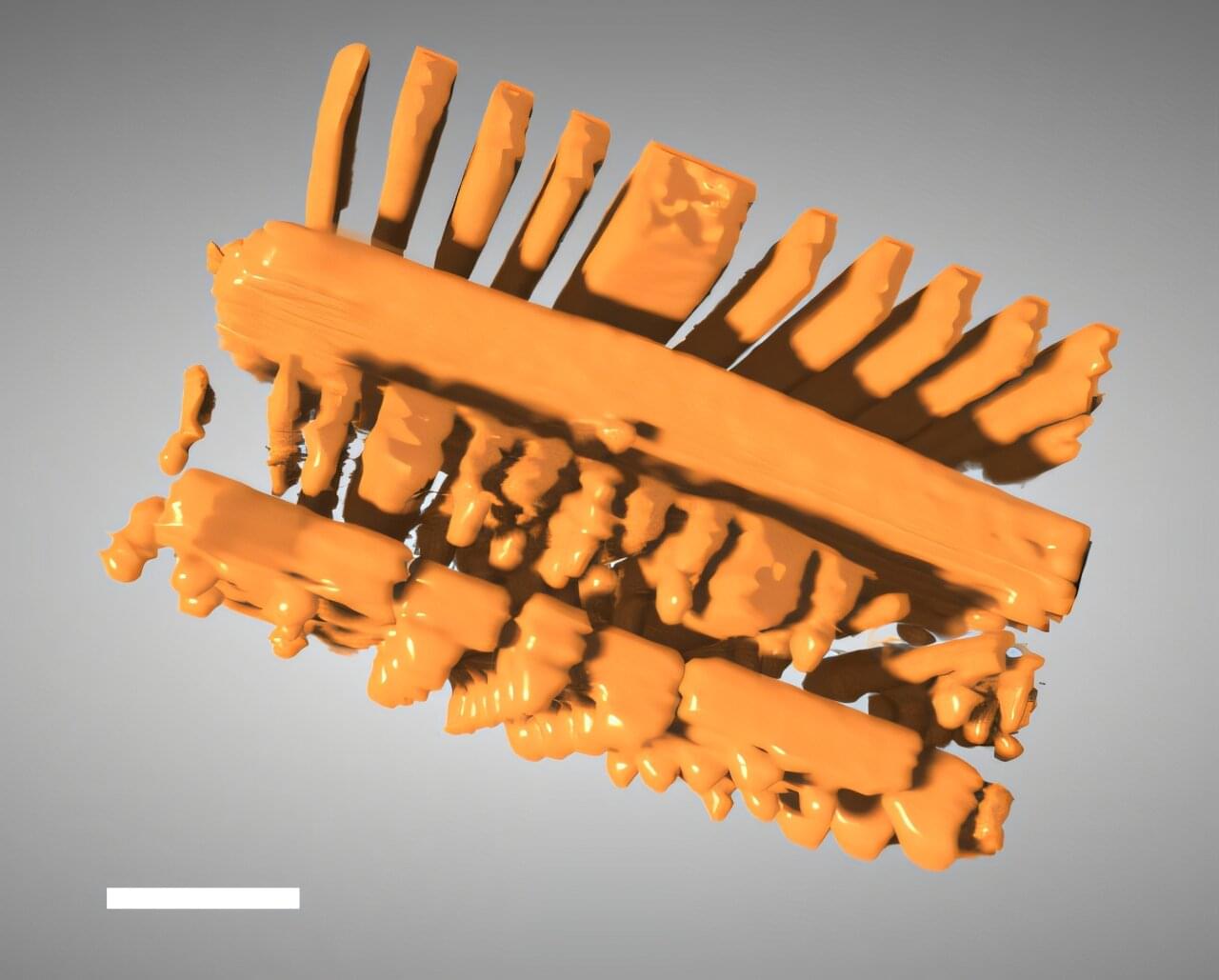
X-ray tomography is a powerful tool that enables scientists and engineers to peer inside of objects in 3D, including computer chips and advanced battery materials, without performing anything invasive. It’s the same basic method behind medical CT scans.
Scientists or technicians capture X-ray images as an object is rotated, and then advanced software mathematically reconstructs the object’s 3D internal structure. But imaging fine details on the nanoscale, like features on a microchip, requires a much higher spatial resolution than a typical medical CT scan—about 10,000 times higher.
The Hard X-ray Nanoprobe (HXN) beamline at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science user facility at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, is able to achieve that kind of resolution with X-rays that are more than a billion times brighter than traditional CT scans.

Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used to analyze medical images, materials data and scientific measurements, but many systems struggle when real-world data do not match ideal conditions. Measurements collected from different instruments, experiments or simulations often vary widely in resolution, noise and reliability. Traditional machine-learning models typically assume those differences are negligible—an assumption that can limit accuracy and trustworthiness.
To address this issue, Penn State researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence framework with potential implications for fields ranging from Alzheimer’s disease research to advanced materials design. The approach, called ZENN and detailed in a study that was featured as a showcase in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, teaches AI models to recognize and adapt to hidden differences in data quality rather than ignoring them.
ZENN, short for Zentropy-Embedded Neural Networks, was developed by Shun Wang, postdoctoral scholar of materials science and engineering; Wenrui Hao, professor of mathematics, Zi-Kui Liu, professor of materials science and engineering, and Shunli Shang, research professor of materials science and engineering.
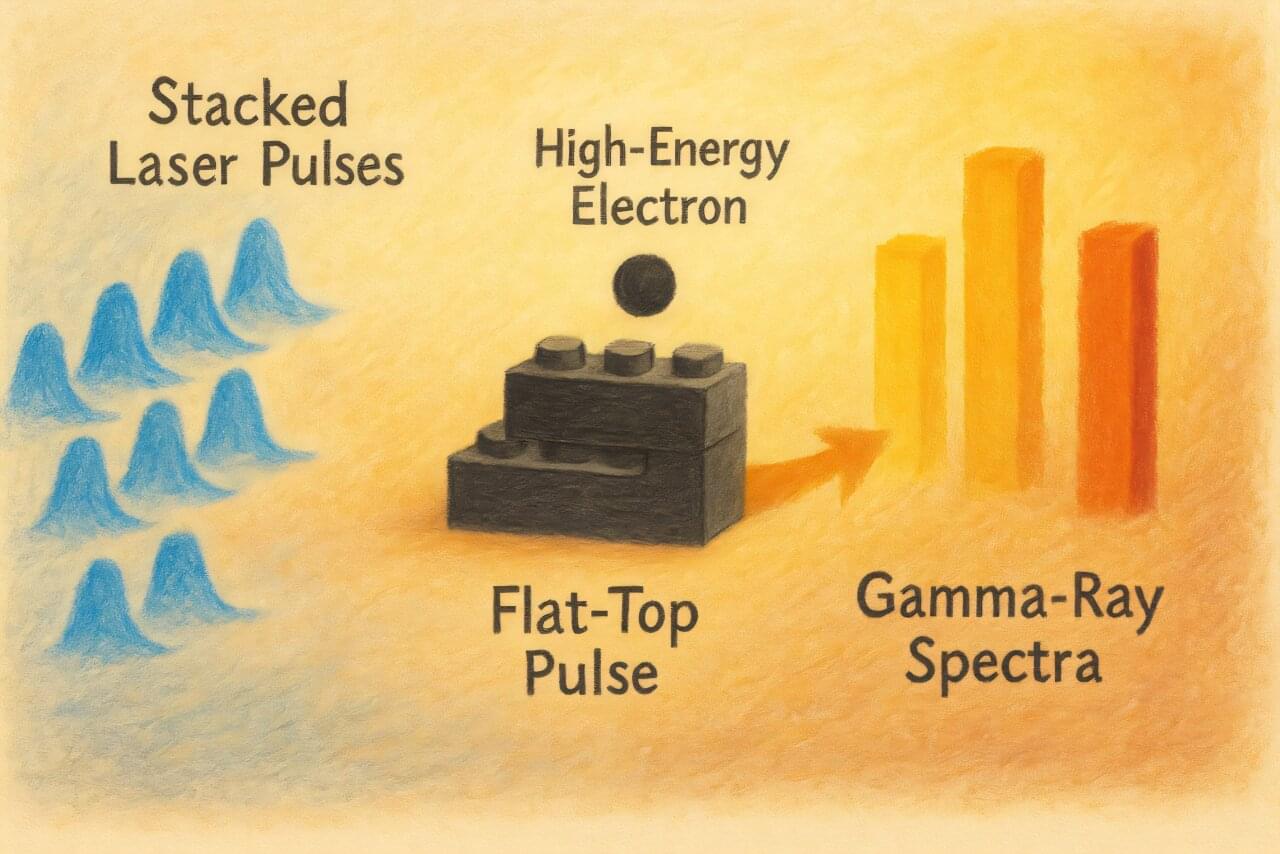
Researchers from Skoltech, MEPhI, and the Dukhov All-Russian Research Institute of Automation have proposed a new method to create compact gamma-ray sources that are simultaneously brighter, sharper, and capable of emitting multiple “colors” of gamma rays at once.
This opens up possibilities for more accurate medical diagnostics, improved material inspection, and even the production of isotopes for medicine directly in the laboratory. The work has been published as a Letter in the journal Physical Review A.
Gamma rays produced using lasers and electron beams represent a promising technology, but until now they have had a significant drawback: the emission spectrum was too “blurred.” This reduced brightness and precision, limiting their applications in areas where clarity is crucial—such as scanning dense materials or medical imaging.

As drones survey forests, robots navigate warehouses and sensors monitor city streets, more of the world’s decision-making is occurring autonomously on the edge—on the small devices that gather information at the ends of much larger networks.
But making that shift to edge computing is harder than it seems. Although artificial intelligence (AI) models continue to grow larger and smarter, the hardware inside these devices remains tiny.
Engineers typically have two options, neither are ideal. Storing an entire AI model on the device requires significant memory, data movement and computing power that drains batteries. Offloading the model to the cloud avoids those hardware constraints, but the back-and-forth introduces lag, burns energy and presents security risks.